Table of Contents
Noise Timing Chain in Mercedes-Benz S 400 Hybrid : A Detailed Case Study
The Noise Timing Chain issue is a critical concern for many vehicle owners, particularly in modern engines where precision timing is essential for smooth performance. In this article, we examine a real-world case involving a Mercedes-Benz S 400 W222 Hybrid equipped with the M276 engine. The customer reported an engine noise during a cold start and a check engine light on the dashboard.
Our objective was to identify the root cause of the Noise Timing Chain and resolve the issue with a clear diagnostic approach. Follow along as we explain the step-by-step troubleshooting process, the root cause analysis, and the repairs performed to fix the problem.
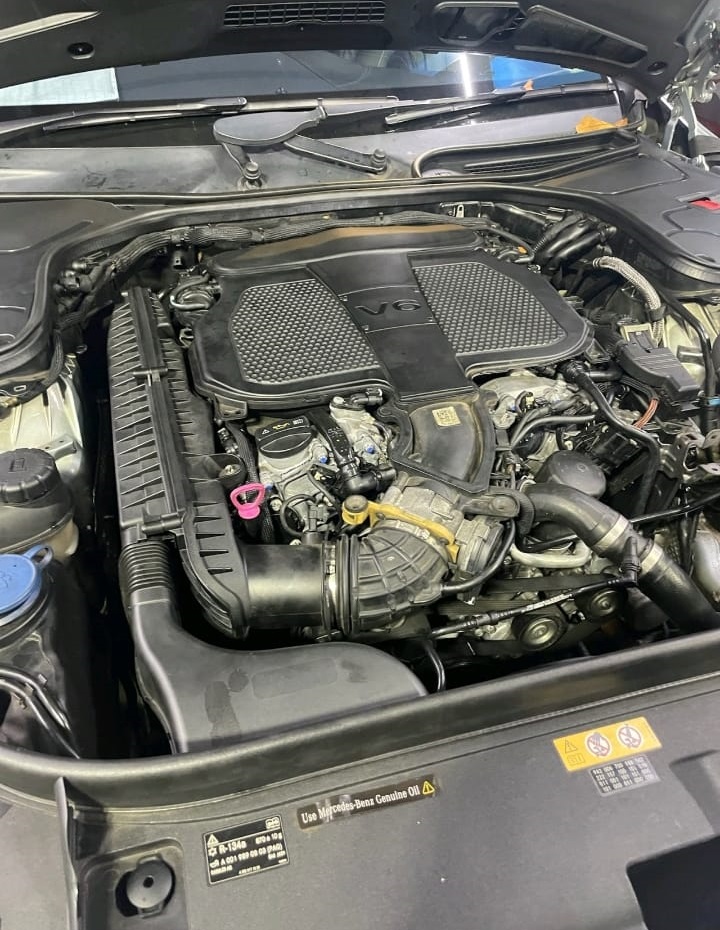

Customer Complaint
The customer brought their Mercedes-Benz S 400 W222 Hybrid to the workshop with the following complaints:
- Noticeable engine noise during cold starts.
- The check engine light illuminated on the dashboard.
Given the symptoms, it was clear that the vehicle required immediate diagnostics to avoid further engine damage.
Initial Diagnosis
1. Performing a Quick Test
To begin the diagnosis, we connected the Xentry diagnosis tool to perform a quick test on the engine control module (ME).
- A fault code was identified:
P002117 – The position of the intake camshaft (cylinder bank 2) deviates from the specified value. The commanded position cannot be reached.
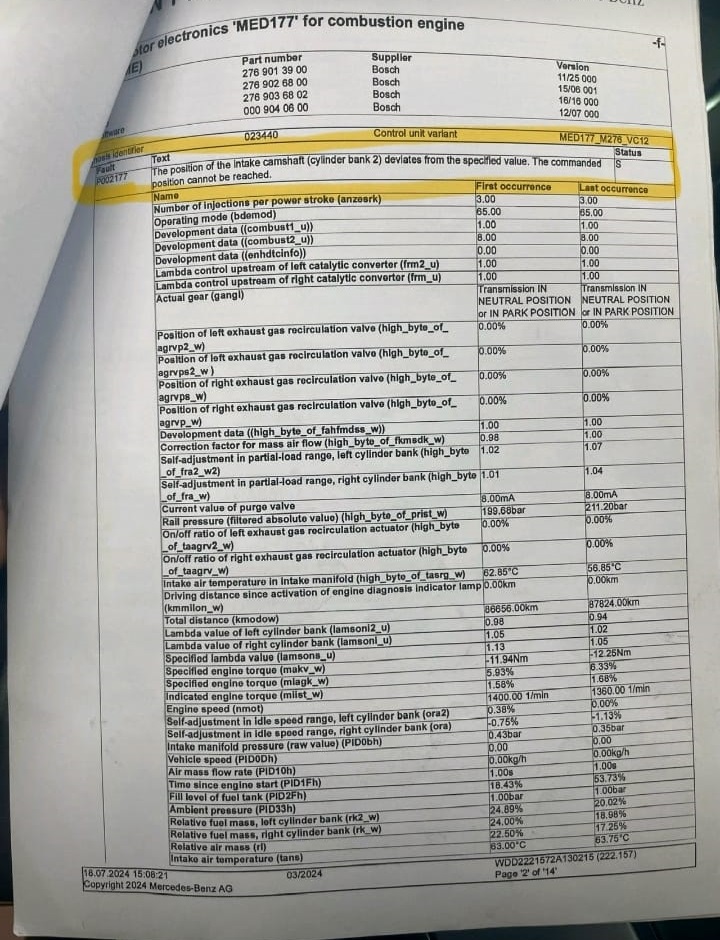
This code indicated a potential issue with the timing system affecting the intake camshaft of cylinder bank 2.
Step-by-Step Inspection
2. Checking Engine Timing
Given the fault code, I proceeded to inspect the engine timing to verify whether the camshaft timing was off. Proper engine timing is critical to avoid Noise Timing Chain issues and misalignment.
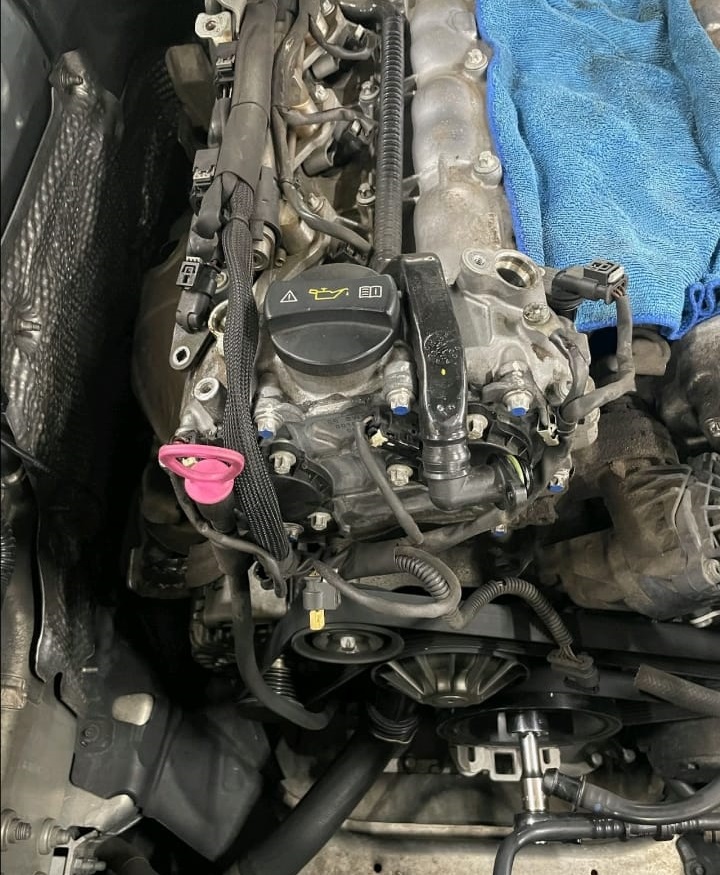

3. Removing the Camshaft Sensor
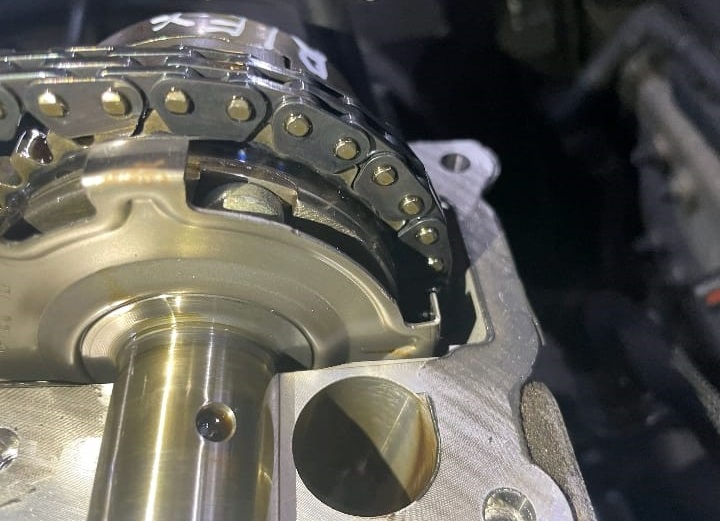
To further investigate, I removed the camshaft position sensor to check the pulse timing wheel mark on the intake camshaft of cylinder bank 2.
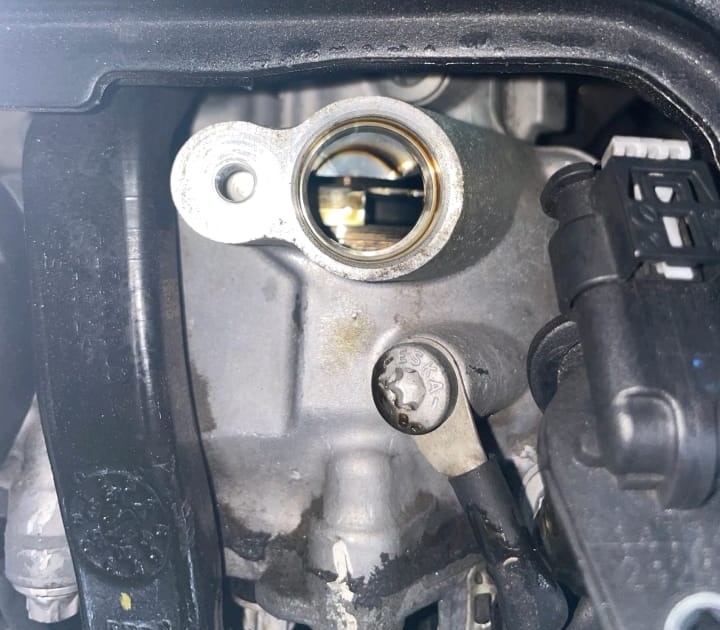

4. Identifying the Root Cause
Upon inspection, I discovered that the cylinder bank 2 intake camshaft pulse wheel was not in its correct position. This misalignment was causing:
- Improper intake valve timing.
- Noise Timing Chain during cold starts.
- Engine performance issues triggering the check engine light.

Repairs Performed
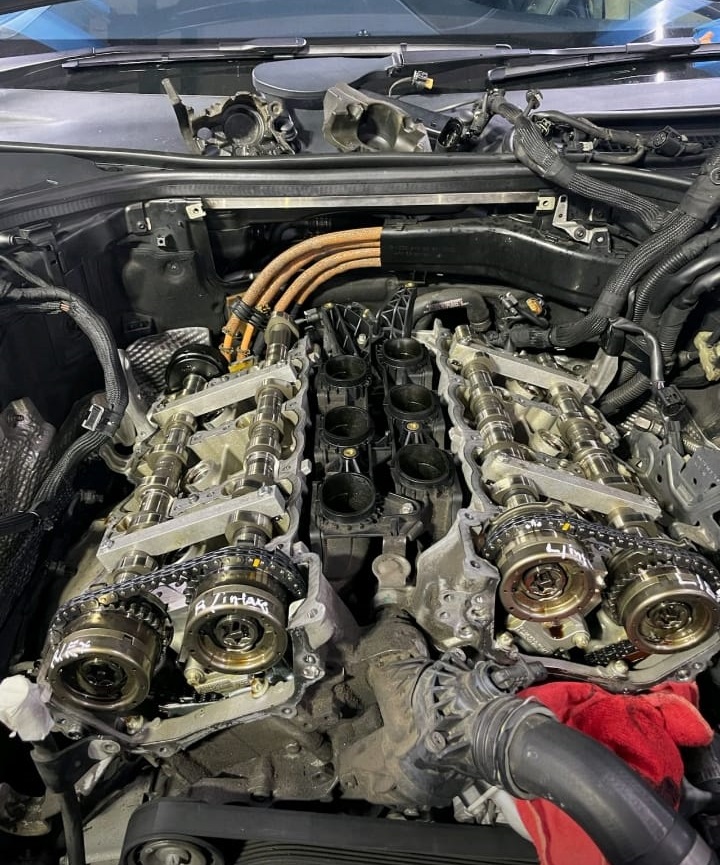
To resolve the Noise Timing Chain issue, the following components were replaced:
- Cylinder Bank 2 Intake Camshaft
- The misaligned pulse wheel indicated that the camshaft was faulty and required replacement.
- All Cam Sprockets
- Replacing all cam sprockets ensured that the engine timing would be restored to factory specifications. Worn or damaged sprockets can exacerbate chain noise and timing deviations.
- Timing Chain Tensioners
- Faulty or worn timing chain tensioners are a common cause of chain slack, leading to noise and poor timing. Replacing the tensioners ensured the timing chain maintained proper tension.
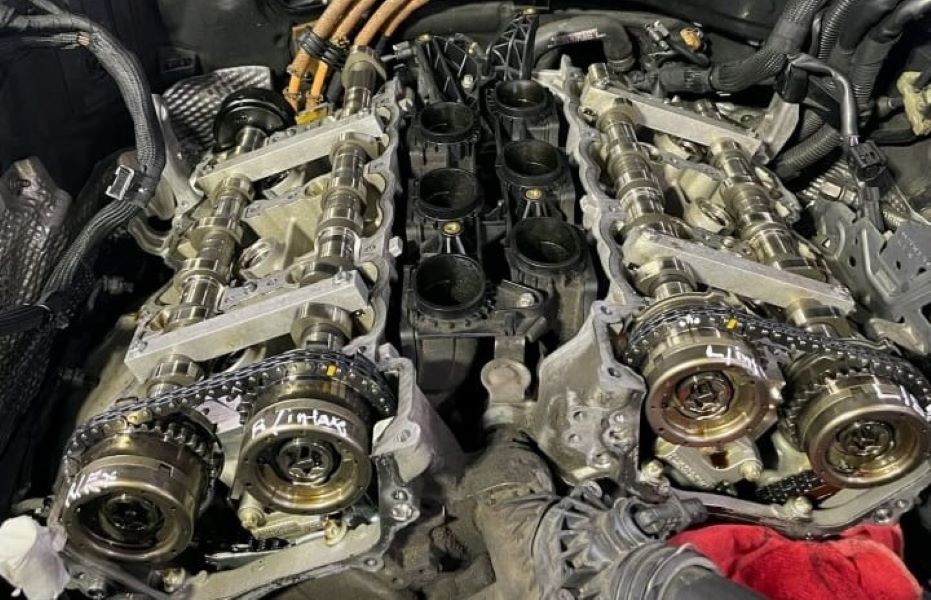
Post-Repair Verification
After replacing the faulty components, I conducted the following checks:
- Rechecking Engine Timing
- Verified that the camshaft, sprockets, and timing chain were properly aligned.
- Clearing Fault Codes
- Cleared the fault code P002117 using the diagnostic tool.
- Test Running the Engine
- Performed multiple cold starts to ensure the Noise Timing Chain issue was resolved.
- Verified that no abnormal engine noise persisted.
- Monitoring for Check Engine Light
- Confirmed that the check engine light no longer appeared on the dashboard.

Root Cause Analysis
The primary cause of the Noise Timing Chain issue in this case was a misaligned cylinder bank 2 intake camshaft pulse wheel. Contributing factors included:
- A worn camshaft component.
- Slack in the timing chain due to aged or faulty timing chain tensioners.
Key Takeaways for Readers
If you’re experiencing a Noise Timing Chain issue, particularly in vehicles equipped with the M276 engine:
- Look for Fault Codes – Use a diagnostic tool to identify camshaft timing faults.
- Inspect the Engine Timing – Misalignment in camshafts or worn sprockets can lead to chain noise.
- Check the Timing Chain Tensioners – Faulty tensioners are a common cause of chain slack and noise.
- Replace Faulty Components – Addressing worn camshafts, sprockets, and tensioners is critical for long-term engine health.
By following this structured approach, you can effectively diagnose and resolve Noise Timing Chain problems, ensuring optimal engine performance and reliability.
Why does my engine make a noise at startup when its cold?
Hearing unusual engine noises during a cold startup can be concerning for any vehicle owner. Whether it’s a ticking, rattling, or squealing sound, these noises often point to specific issues within the engine or related components. Understanding the causes behind these sounds is crucial for identifying problems early and preventing costly repairs. Below, we’ll explore common reasons why your engine makes noise at startup when it’s cold, along with solutions to address them effectively.
1. Cold Engine Oil Viscosity
- Issue: During cold starts, engine oil becomes thicker due to low temperatures, causing delayed lubrication to critical components like the timing chain, camshafts, and lifters. This can produce a brief rattling or ticking noise.
- Solution: Use the recommended oil viscosity for colder climates (e.g., 0W-40 or 5W-30). Synthetic oils perform better at low temperatures as they flow quickly. Learn more in the next article M276 engine
2. Worn Timing Chain Tensioners
- Issue: Timing chain tensioners rely on oil pressure to maintain proper chain tension. When the engine is cold, oil pressure builds up slower, causing temporary slack in the timing chain and resulting in rattling noises.
- Solution: Replace worn timing chain tensioners and ensure the oil system functions properly.
3. Hydraulic Lifters Noise
- Issue: Hydraulic lifters adjust valve clearance automatically. When the oil is thick during cold starts, lifters may not fill with oil immediately, leading to a tapping or ticking noise.
- Solution: Regular oil changes with high-quality, low-viscosity oils can prevent this issue.
4. Loose or Worn Belts
- Issue: Cold weather can cause drive belts (serpentine or accessory belts) to harden or become brittle, producing squealing or whining noises at startup.
- Solution: Inspect and replace worn belts. Check the tensioners and pulleys for proper operation.
5. Worn Engine Components
- Issue: Over time, components like the timing chain, camshaft, or crankshaft develop wear due to age or poor maintenance. When cold, these components expand slightly slower, causing temporary noises until the engine warms up.
- Solution: Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn parts like cam sprockets, timing chains, or tensioners can prevent excessive noise.
6. Frozen or Stiff Engine Mounts
- Issue: Cold weather can stiffen engine mounts, causing vibrations and clunking noises during startup as the engine shifts position.
- Solution: Inspect engine mounts for wear or cracks and replace if needed.
7. Fuel Combustion Issues
- Issue: In colder weather, fuel combustion may be less efficient due to a richer air-fuel mixture during startup, causing a brief knocking or pinging noise.
- Solution: Ensure spark plugs, fuel injectors, and the ignition system are in good condition for optimal cold-start performance.
8. Exhaust System Expansion
- Issue: Cold metals in the exhaust system (manifold, downpipe) contract when the engine is off. Upon startup, thermal expansion can produce ticking or popping sounds.
- Solution: This is typically normal. If the noise persists, inspect the exhaust components for leaks.
9. Insufficient Oil Levels
- Issue: Low oil levels exacerbate cold start noises as critical engine parts lack proper lubrication.
- Solution: Regularly check and maintain engine oil levels to avoid metal-on-metal contact at startup.
10. Addressing the Issue Early
Ignoring noises during cold starts can lead to more severe problems, such as:
- Premature wear of the timing chain.
- Damaged camshaft lobes.
- Increased engine component wear due to poor lubrication.
Conclusion
This case study highlights the importance of timely diagnostics and systematic troubleshooting when dealing with Noise Timing Chain issues. In the Mercedes-Benz S 400 W222 Hybrid with the M276 engine, a misaligned intake camshaft and worn timing components were the root cause of engine noise and timing faults.
By replacing the faulty camshaft, all cam sprockets, and timing chain tensioners, the engine timing was restored, eliminating the noise and resolving the check engine light issue.






Leave a Reply