Table of Contents
Loss of Power in Car While Driving – A Case Study
Experiencing a sudden loss of power in car while driving can be both alarming and dangerous. One such case involved a Mercedes-Benz C Class W205 with an OM626 engine. The vehicle exhibited a lack of acceleration beyond 3000 rpm and an illuminated check-engine indicator. This article delves into the diagnostic process, the identified fault, and the resolution of the issue.
Case Study: Mercedes-Benz W205 OM626 CDI Engine

Customer Complaint
The owner of a Mercedes-Benz W205 reported that the check-engine light had come on and the vehicle would not accelerate beyond 3000 rpm. Concerned about the potential causes and risks, the owner sought professional assistance.
Diagnostic Process
Upon receiving the vehicle, the technician used the STAR DIAGNOSIS system to identify any fault codes. The diagnostic tool revealed the following fault code:
- P040100 – The flow rate of the exhaust gas recirculation positioner (low pressure) is too low.
This fault code indicated a potential issue with the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, specifically suggesting a low flow rate.
Investigation and Findings
To confirm the diagnosis and pinpoint the exact cause, the technician performed a series of checks:
Actual Values and Functions Check:
- The exhaust system’s actual values and functions were evaluated to ensure all components were operating within their specified ranges.
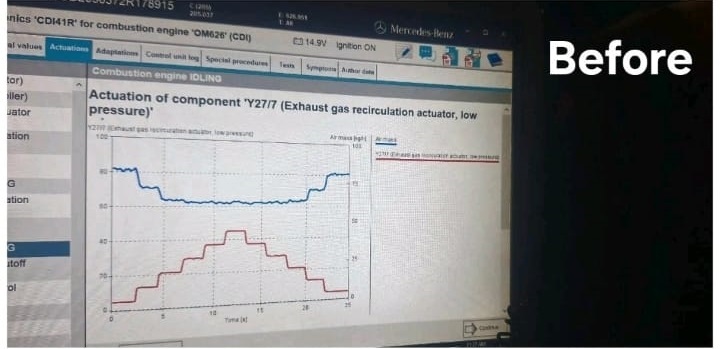
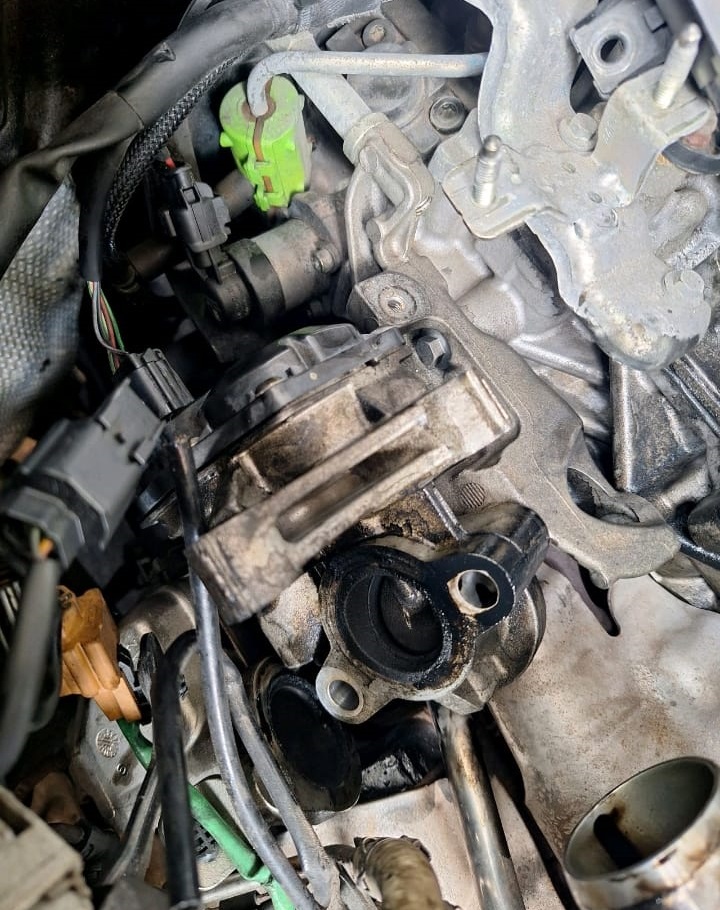
EGR Unit Inspection:
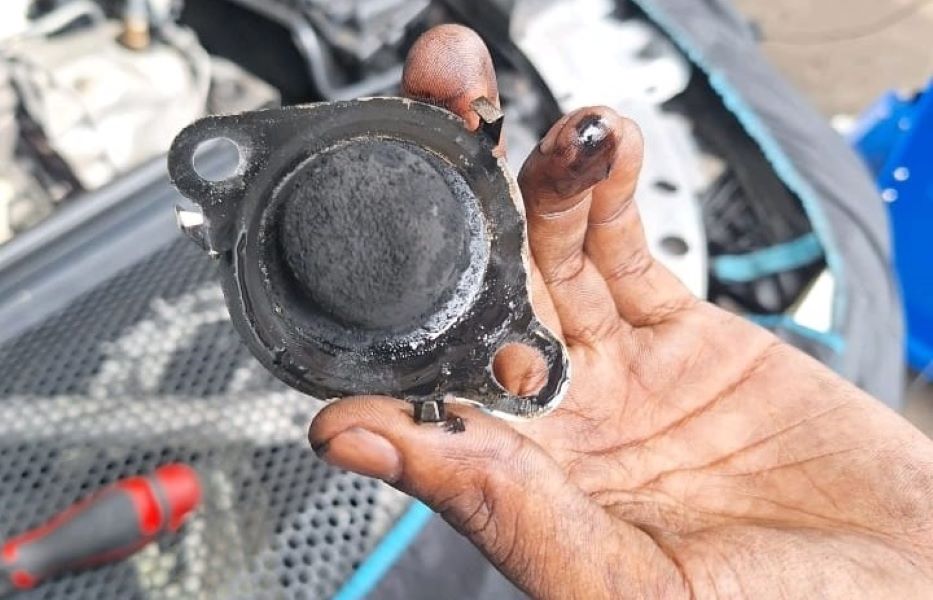
- The EGR unit was inspected to identify any blockages or malfunctions. During this inspection, the technician found a clogged EGR filter.

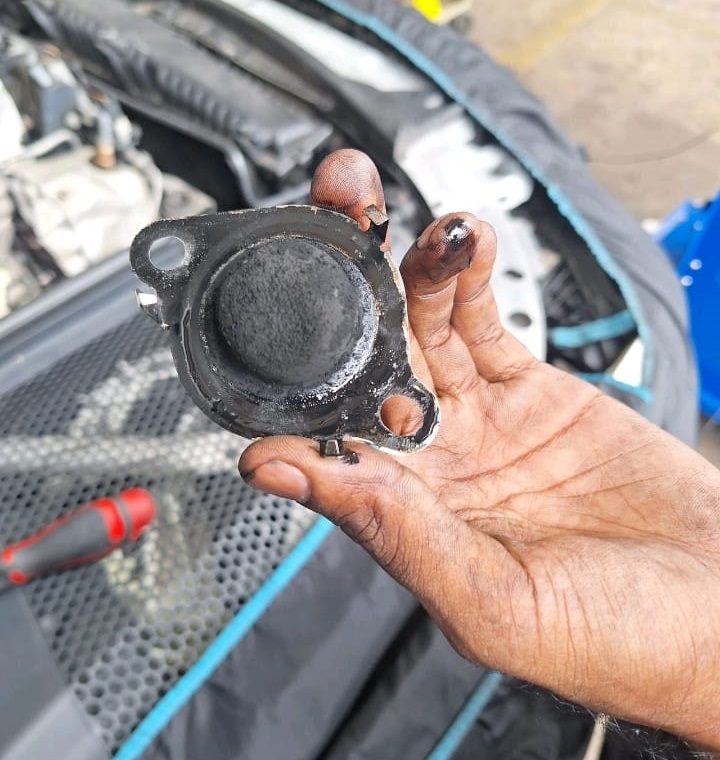
Resolution
The clogged EGR filter was determined to be the root cause of the low flow rate in the EGR system. The technician proceeded with the following steps to resolve the issue:
Cleaning the EGR Filter:
- The EGR filter was carefully cleaned to remove the accumulated soot and debris that had caused the blockage.

System Recheck:
- After cleaning the filter, the EGR system was rechecked to ensure proper flow rates and functionality. The STAR DIAGNOSIS system confirmed that the fault code was no longer present.
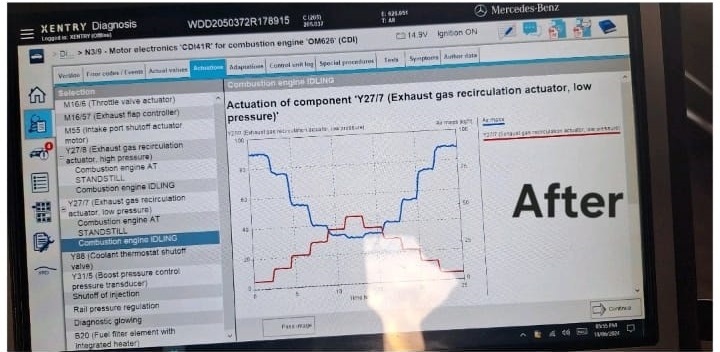
Road Test:
- A thorough road test was conducted to ensure the vehicle’s performance had returned to normal. The vehicle now accelerated smoothly beyond 3000 rpm without any issues.
This case study highlights the importance of thorough diagnostics and the role of the EGR system in maintaining engine performance. A clogged EGR filter can significantly impact a vehicle’s power and drivability. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning indicators like the check-engine light can prevent such issues and ensure a smooth driving experience.
What Is An EGR Valve And What Does It Do ?
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is a crucial component in modern vehicles designed to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at what the EGR valve does and why it’s essential for your car’s performance and environmental impact.
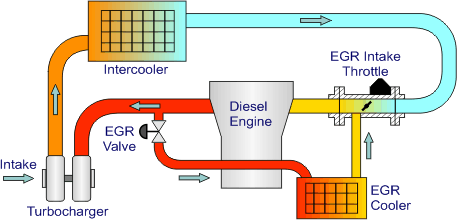
Function of the EGR Valve
The primary function of the EGR valve is to recirculate a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold. This process serves several key purposes:
- Reduces Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Emissions: By recirculating exhaust gases, the EGR valve helps lower the combustion temperature within the engine. High combustion temperatures lead to the formation of nitrogen oxides, harmful pollutants that contribute to smog and air pollution. By reducing these temperatures, the EGR valve helps decrease NOx emissions.
- Improves Fuel Efficiency: Lowering the combustion temperature can also enhance fuel efficiency. When the engine runs cooler, it can operate more efficiently, leading to better fuel economy.
- Prevents Engine Knocking: High combustion temperatures can cause premature ignition of the fuel-air mixture, leading to engine knocking. The EGR valve helps prevent this by keeping the combustion process within optimal temperature ranges.
How does EGR valve work ?
The EGR valve operates by opening and closing at specific times during the engine’s operation. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its functioning:
- Opening the Valve: When the engine is running under load or at higher speeds, the EGR valve opens to allow a controlled amount of exhaust gases to enter the intake manifold.
- Mixing with Intake Air: These exhaust gases mix with the incoming air-fuel mixture, diluting it and lowering the combustion temperature.
- Closing the Valve: When the engine is idling or under light load, the EGR valve remains closed to ensure optimal performance and prevent rough idling.
How to Clean the EGR System ?
Cleaning the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and reducing harmful emissions. Over time, the EGR valve and associated components can become clogged with carbon deposits, which can lead to reduced efficiency and increased emissions. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to clean the EGR system.
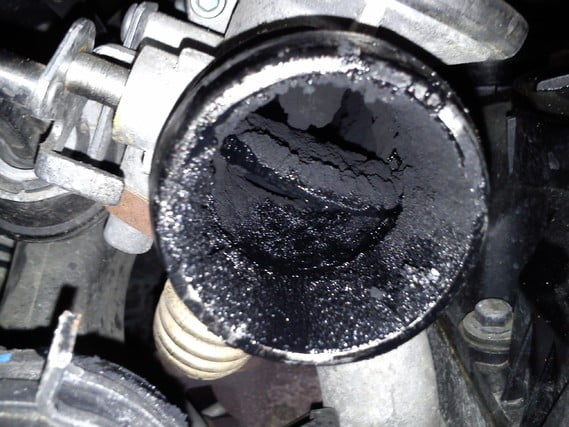

1. Locate the EGR Valve and Components
The EGR valve is typically located on or near the intake manifold. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location and layout of the EGR system components.
2. Remove the EGR Valve
- Disconnect the Battery: To avoid any electrical issues, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Disconnect Electrical Connections and Vacuum Lines: Carefully remove any electrical connectors and vacuum lines attached to the EGR valve.
- Unbolt the EGR Valve: Using the appropriate tools, unbolt the EGR valve from its mounting position. Be mindful of any gaskets that may need to be replaced upon reinstallation.
3. Clean the EGR Valve
- Spray Cleaner: Spray the EGR valve with the EGR valve cleaner or carburetor cleaner. Make sure to cover all surfaces, especially areas with visible carbon deposits.
- Scrub Carbon Deposits: Use a small brush to scrub away stubborn carbon deposits. Be gentle to avoid damaging the valve.
- Wipe Clean: Wipe the valve clean with a rag or paper towel. Repeat the cleaning process if necessary until the valve is free of carbon buildup.






Leave a Reply