Table of Contents
Active Brake Assist Functions Limited Mercedes: A Diagnostic Case Study
Active Brake Assist (ABA) is one of the most critical safety systems in modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It automatically applies the brakes in emergency situations, helping prevent or reduce the severity of collisions.
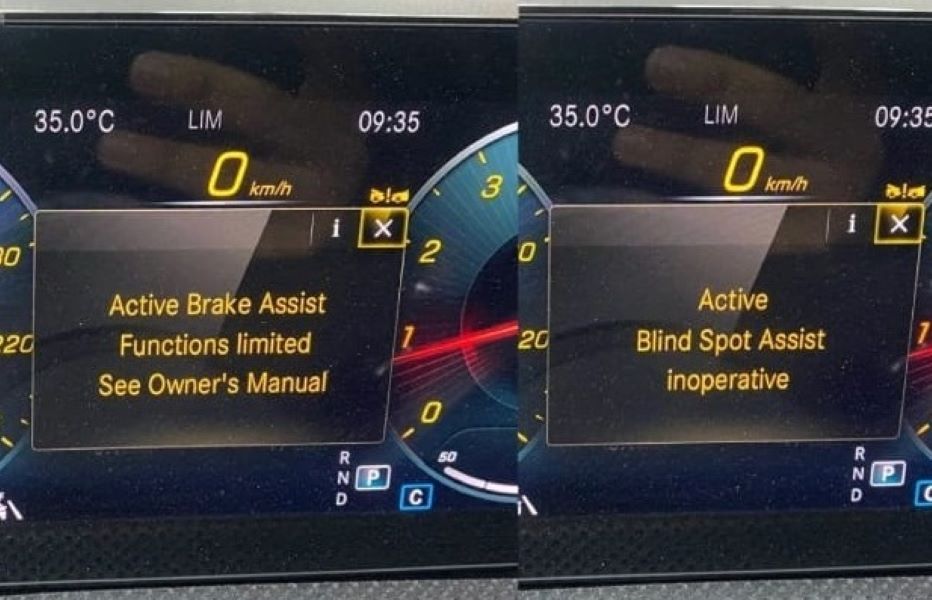
When the message “Active Brake Assist Functions Limited” appears on the dashboard, it means the system is partially disabled and the car’s automatic braking response may not work as intended.
In this real-world case study, we examine a Mercedes-Benz CLA250 that displayed multiple assist system warnings. The issue turned out to be more complex than a simple sensor failure, underscoring the importance of methodical diagnostics instead of random part replacement.
For a broader understanding of how ABS, ESP, and Brake Assist systems work together, visit our hub: Mercedes Brake System Problems: ABS, ESP & Brake Assist Guide
Customer Complaint
The customer reported several dashboard warnings active at once:
- – Active Brake Assist Functions Limited
- – Active Blind Spot Assist Inoperative
- – Active Distance Assist Inoperative
- – Active Lane Keeping Assist Inoperative
The car had previously visited another garage, where the front radar sensor was replaced due to “no communication with DISTRONIC.”
However, despite that repair, all warnings persisted meaning the problem lay deeper within the system.


System Background: Mercedes Intelligent Drive
The Mercedes Intelligent Drive system integrates multiple ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), including:
- – Active Brake Assist
- – DISTRONIC PLUS (adaptive cruise)
- – Active Lane Keeping Assist
- – Active Blind Spot Assist
- – Adaptive Highbeam Assist Plus
- – Attention Assist
- – Night View Assist
These systems share data through the FlexRay network and rely on communication with the Intelligent Drive Control Module (N62).
A fault in one module can disrupt several assistive functions at once.
Initial Diagnosis
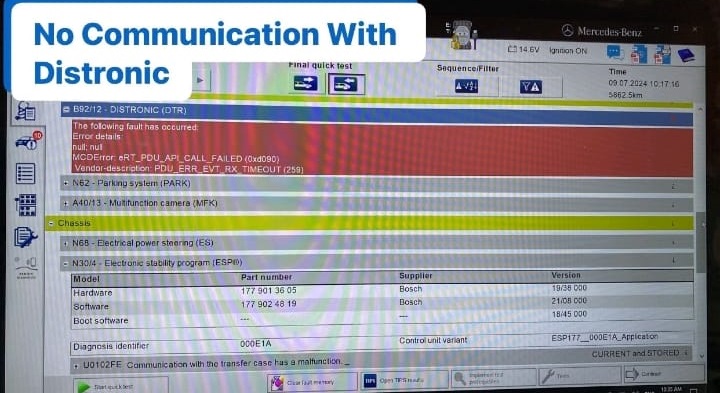
Using the XENTRY diagnostic tool, technicians performed a full system scan.
The main fault recorded in the ESP (Electronic Stability Program) module was:
U0102FE – No communication / missing message with DISTRONIC or Intelligent Drive Control Module.
This confirmed a communication failure on the FlexRay bus, affecting multiple assistance systems simultaneously.
Detailed Diagnostic Process
Step 1: Wiring and Connector Inspection
The first step was to inspect the radar and Intelligent Drive harness connections.
All connectors were clean, sealed, and properly seated. Continuity and ground checks showed no open circuits or short circuits.
This ruled out a simple wiring issue.
Step 2: Component-Level Inspection
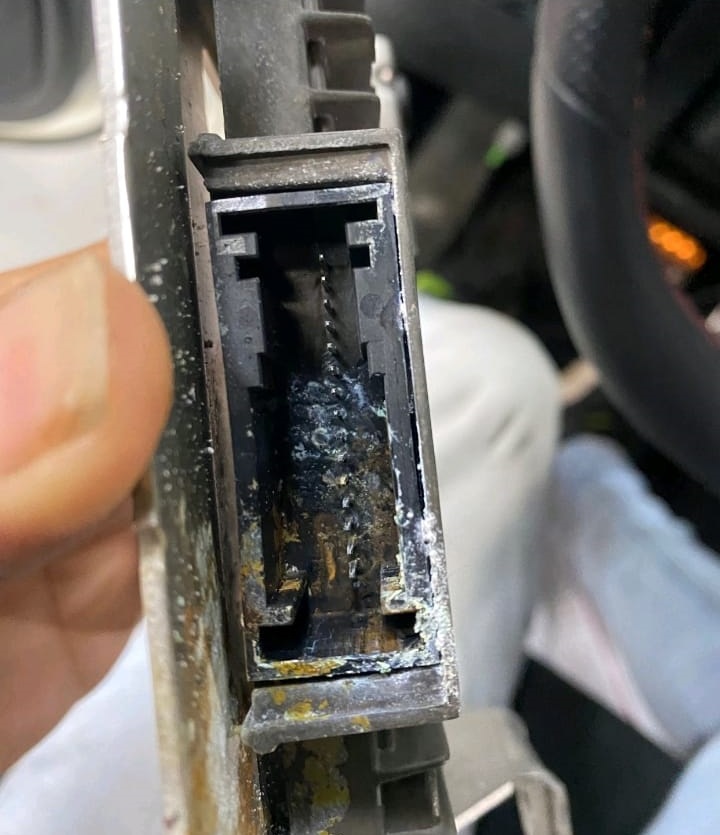
Next, the Intelligent Drive Control Module (N62) was physically inspected.
It was located behind the front bumper area a region vulnerable to water ingress and road moisture.
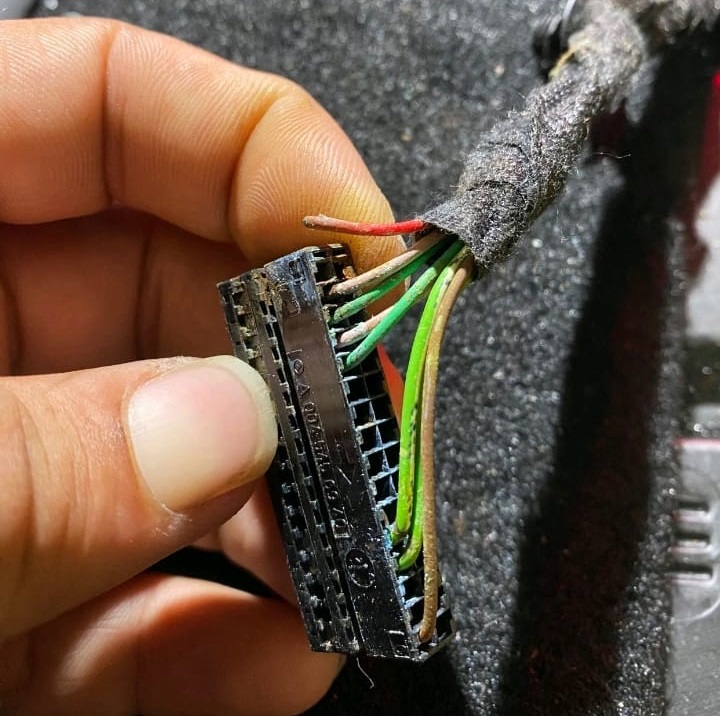
Upon removal, technicians discovered visible corrosion and water damage inside the control unit confirming that the module had failed internally.


Step 3: Identifying the Root Cause
The corrosion had destroyed critical circuit traces inside the module, explaining the total communication loss with other systems.
Because this control module handles radar, brake assist, and distance monitoring, its failure caused multiple assist features to go offline simultaneously.
Repair & Programming
To resolve the issue, the following steps were taken:
- 1. Replace the corroded Intelligent Drive Control Module with a new genuine Mercedes unit.
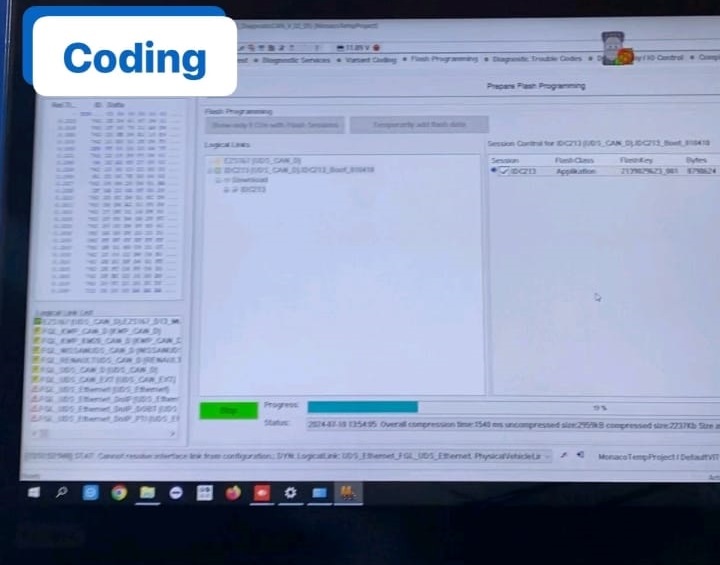
- 2. Reprogram the module using XENTRY Diagnosis, performing online coding and calibration to synchronize with the vehicle’s CAN and FlexRay networks.
- 3. Clear all stored fault codes and reinitialize system self-tests.
- 4. Verify communication between ESP, DISTRONIC, and the new module.
Post-repair results:
- – All dashboard warnings cleared.
- – Active Brake Assist, Blind Spot Assist, and Distance Assist fully restored.
- – No stored or current fault codes detected.
Final Status: Vehicle systems fully operational, safety functions restored.
Technical Insight: Understanding Active Brake Assist
Active Brake Assist (ABA) works by combining radar sensors, cameras, and control algorithms to detect obstacles ahead.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Obstacle Detection | Radar and camera sensors constantly scan for vehicles or pedestrians. |
| Risk Assessment | Calculates distance and relative speed to identify potential collisions. |
| Driver Warning | Issues visual and acoustic alerts if the driver doesn’t react. |
| Automatic Braking | Applies partial or full braking pressure if necessary. |
When “Functions Limited” appears:
It means one or more of the system’s data sources (e.g., radar, camera, or control unit) is not communicating correctly.
Related Diagnostic Resource
If your Mercedes is displaying electrical or braking system warnings, explore our complete diagnostic hubs:
Mercedes Electrical Problems: Fix SAM, ECU & CAN Bus Faults; learn how to diagnose power supply interruptions, short circuits, and communication faults affecting your vehicle’s electronic control modules.
Mercedes Brake System Problems: ABS, ESP & Brake Assist Guide; a complete guide to diagnosing and repairing brake system faults, from ABS and ESP errors to BAS hydraulic and sensor malfunctions.
Together, these hubs provide a comprehensive troubleshooting roadmap from electrical and communication faults in control modules to advanced braking and stability system diagnostics.
Benefits of Active Brake Assist
- – Prevents rear-end collisions by automatically applying brakes.
- – Reduces impact speed if a collision cannot be avoided.
- – Supports distracted or fatigued drivers by intervening quickly.
- – Integrates with ESP and DISTRONIC for seamless vehicle safety control.
Limitations of Active Brake Assist
| Condition | Effect on System |
|---|---|
| Heavy rain, fog, or snow | Sensors may lose accuracy. |
| Dirt or ice on radar lens | False or limited readings. |
| Misaligned radar sensor | Incorrect object detection. |
| Low voltage or battery issues | May disable assist systems temporarily. |
Even after repair, keeping sensors clean, dry, and correctly calibrated is critical for long-term reliability.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
- – Inspect radar and camera areas regularly for moisture or corrosion.
- – Avoid using non-OEM front bumpers or grilles, which can interfere with radar signals.
- – Keep firmware updated through authorized Mercedes service.
- – Check drainage channels near front sensors for blockages to prevent water intrusion.
- – If multiple driver assist systems fail at once, suspect a communication module rather than isolated sensors.
FAQs: Active Brake Assist Functions Limited Mercedes
Q1: What causes “Active Brake Assist Functions Limited” to appear?
Usually, a fault in the radar sensor, Intelligent Drive module, or communication wiring. Water damage and corrosion are common triggers.
Q2: Can I drive with the warning on?
Yes, but collision prevention features won’t function properly. Manual braking still works, but automatic interventions are disabled.
Q3: Does the system reset itself after repair?
After replacing or reprogramming the faulty module, the system typically resets automatically once all communication faults are cleared.
Q4: Can dirty radar sensors cause the same warning?
Yes, dirt, ice, or damaged front bumper covers can obstruct radar signals and temporarily disable Active Brake Assist.
Conclusion
This Mercedes-Benz CLA250 case study demonstrates that complex assist system faults often stem from a single communication failure.
In this instance, replacing the corroded Intelligent Drive Control Module restored full operation of Active Brake Assist, DISTRONIC, Blind Spot Assist, and Lane Keeping Assist.
The takeaway? Always perform complete system diagnostics not just part replacements.
For a deeper understanding of Mercedes braking and safety systems, read our hub:
– Mercedes Brake System Problems: ABS, ESP & Brake Assist Guide
Author Bio
Mercedes Expert is an automotive technical trainer and Mercedes-Benz diagnostics expert with extensive hands-on experience in XENTRY, DTS Monaco, and advanced system troubleshooting. He specializes in transforming real workshop case studies into structured learning content to help technicians, car owners, and enthusiasts understand complex vehicle systems.
Last update: November 2025





Leave a Reply