Table of Contents
Mercedes Auto Gearbox Jerking: Case Study, Diagnosis, Repair Process
A Mercedes-Benz E-Class W212 equipped with the 7G-Tronic (722.9) came in with two clear complaints:
- 1. a jerk when selecting R or D, and
- 2. intermittent jerks while driving at low and moderate speeds.
A qualified technician traced the fault to a failed input/turbine speed sensor integrated in the transmission control unit (VGS/mechatronics) of the 7G-Tronic. Replacing the unit and servicing the fluid restored smooth operation.
Vehicle & Complaint
| Item | Detail |
|---|---|
| Model | Mercedes-Benz E-Class W212 |
| Transmission | 7G-Tronic (722.9) with VGS (mechatronics) |
| Primary symptoms | Jerk selecting R/D (range engagement thump) and jerks during light acceleration |
| Initial suspicion | Hydraulic modulation issue or speed sensor signal fault |
| Root cause (this case) | Failed turbine/input speed sensor integrated in VGS/mechatronics |
| Fix | Replace VGS/mechatronics assembly, renew ATF/filter, run adaptations, validate by road test |
Why a Sensor Can Cause “Jerking”
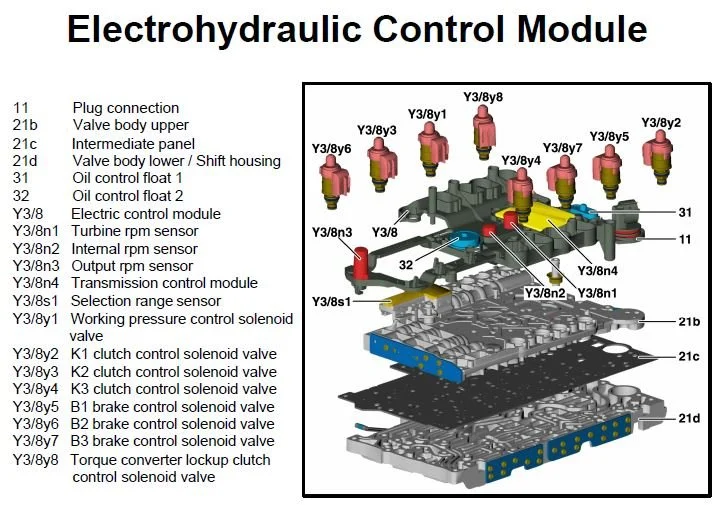
The 7G-Tronic times clutch fills and overlaps using live speed signals (engine, turbine/input, internal, output). If the turbine/input speed signal is missing or noisy, the VGS can’t calculate correct pressure ramps.
The result is delayed engagement followed by a bump, or inconsistent pressure control that feels like on-off jerks while driving. Because the sensor is built into the mechatronics, you typically replace the entire VGS unit rather than one sensor.
Symptoms → Likely Cause → First Checks
| Symptom | Likely Cause(s) | First Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Jerk when selecting R or D | Input speed sensor fault; sticky solenoid; low/incorrect ATF | Scan TCU; verify ATF spec/level; check connector sleeve |
| Jerks at light throttle 15–50 km/h | Noisy/absent turbine speed; adaptation drift | Live data (turbine vs engine/output); adaptation status |
| Stuck in limp with harsh engagement | Sensor implausibility; VGS internal fault | DTCs in TCU (speed/implausible); voltage stability |
| New harshness after battery work | Lost adaptations | Perform standstill/running adaptations |
Diagnostic Workflow (What the Tech Did)
- 1. Global scan (OE-level)
Short test confirmed speed sensor signal errors within the transmission control module and irregular range engagement timing. - 2. Power, grounds, and connector sanity
Battery/charging were healthy. The 13-pin connector sleeve showed no fluid wicking or corrosion. - 3. Live data correlation
During P→R and P→D selections, turbine speed didn’t respond as expected; during gentle tip-in, turbine/internal/output speed traces were inconsistent with commanded pressure. - 4. Decision
Because the speed sensor is integrated in the 722.9 mechatronics and wiring checked out, the plan was to replace the VGS and service the fluid/filter.
Repair Process : Step by Step
Note: Always follow WIS/ASRA procedures, torque values, and safety practices. Keep voltage stable (12.5–14.5 V) during programming and adaptations.
1. Stabilize power & baseline
- – Connect a battery maintainer.
- – Save freeze frames; clear historic codes; confirm which are current.
2. Drain ATF & remove pan
- – Capture a sample to check color/odor.
- – Remove the filter and inspect the magnet for debris (normal fuzz OK; chunks = deeper concern).
3. Remove mechatronics (VGS)
- – Disconnect the 13-pin connector carefully to avoid pin damage.
- – Unbolt and lower the mechatronics/valve body assembly per the specified sequence.
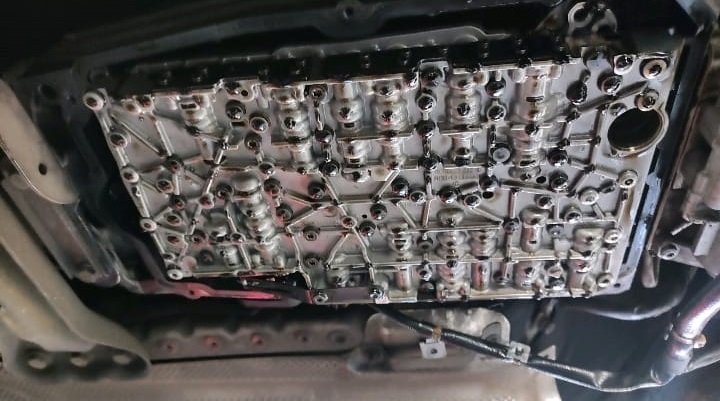

4. Install new VGS
- – Fit the updated assembly (new seals, sleeves, bolts as specified).
- – Verify the manual valve engagement and correct seating.
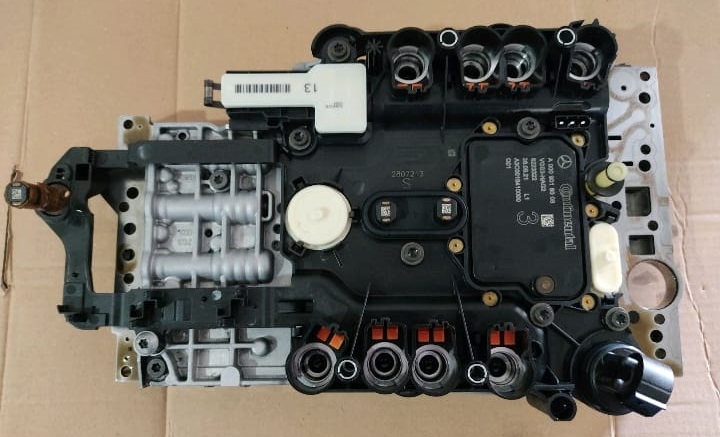
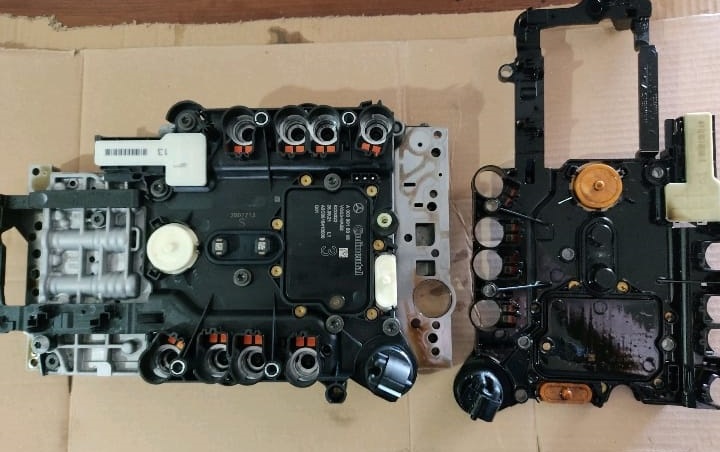

5. Reassembly & ATF service
- – Install new filter and pan with new gasket.
- – Refill with MB-approved ATF for 722.9; set level at temperature per procedure.

6. Programming & adaptations
- – Perform SCN coding/data configuration of the new VGS.
- – Run standstill and running adaptations (no blocking DTCs; ATF temp within range; tires at spec).
7. Validation
- – Repeat P–R–N–D cycles warm and cold; confirm prompt, smooth engagement.
- – Road test (urban + steady cruise); verify turbine/internal/output speed alignment and no code return.
Result: Range engagement bump eliminated; no jerks in traffic; final scan clean.
Technician’s Quick Tables
Symptom–Cause–Fix
| Symptom | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Jerk entering R/D | Turbine speed sensor failure in VGS | Replace VGS, program, adapt |
| Jerks at light throttle | Noisy/absent input speed data; adaptation drift | VGS replacement; run adaptations |
| Harshness after fix | ATF level off; skipped adaptations | Correct ATF level; re-run adaptations |
| Intermittent limp | Electrical dropouts/grounds | Verify voltage, grounds, connector sleeve |
Tools & Preconditions
| Category | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | OE-level tool (XENTRY or equivalent) for coding + adaptations |
| Fluids | MB-approved ATF for 722.9, new filter & pan gasket |
| Power | Stable voltage during programming (maintainer) |
| Info | WIS/ASRA for sequences, torque, ATF temps |
| Safety | PPE; hot ATF handling; clean work area (contamination control) |
Time & Cost (Indicative)
| Operation | Typical Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis + live data | 1.0–1.5 h | Includes voltage, connector checks |
| Mechatronics R&R | 3.0–4.5 h | Model packaging varies |
| ATF/filter service & level set | 0.8–1.2 h | Temp-based procedure |
| Coding & adaptations | 0.5–1.0 h | Requires OE-level tool |
Total cost varies by region; VGS is the big ticket item.
Explore More Mercedes Transmission Issues
For a deeper dive into gearbox problems slipping into Neutral, delayed/harsh shifts, “Not in P” warnings, and hybrid faults visit our hub: Mercedes Transmission Issues – Causes and Fixes. You’ll find grouped case studies, step-by-step diagnostics, symptom–cause–fix tables, and prevention tips to resolve shifting issues quickly and confidently.
What the Transmission Control Unit (VGS/TCU) Does
The VGS is the 7G-Tronic’s electro-hydraulic brain. It reads speeds, temperatures, pressures, and commands solenoids/pressure-regulating valves to coordinate clutch fill and overlap. It stores adaptations so shifts remain smooth as components age. When its integrated speed sensor fails, timing becomes guesswork felt as delays, bumps, and jerks.
Maintenance & Prevention
- – ATF & filter at sensible intervals (many specialists: 60–80k km / 4–5 years) even if “lifetime.”
- – Keep battery/charging healthy; low voltage corrupts adaptations and can trigger false sensor faults.
- – Inspect the 13-pin connector sleeve for leaks at each service.
- – If shift feel worsens after battery work, perform adaptations promptly.
- – Don’t ignore a small range-engagement bump fix early to avoid driveline stress.
More information in the following article : Automatic Transmission Oil Change : Save your Money
FAQs: While Driving Car Jerks
1) Can a simple fluid change fix jerking?
If the cause is marginal ATF or minor adaptation drift, sometimes. But if the turbine speed sensor inside the VGS has failed, fluid alone won’t fix it you’ll need a VGS replacement + coding + adaptations.
2) Is it safe to keep driving with a jerk when selecting R/D?
Not recommended. Each harsh engagement hammers clutches and mounts and can escalate into limp mode. Diagnose and repair promptly.
3) Do I have to program the new VGS?
Yes. The module must be SCN-coded to the VIN/transmission variant. After coding, run standstill and running adaptations so the box relearns clutch fill/overlap timing.
4) How do I know it’s the sensor and not a solenoid?
Live data and guided tests help: with a sensor fault, turbine speed is missing/implausible despite normal solenoid current profiles. With a sticky solenoid, currents/pressures misbehave while speeds are valid. In this case, speeds were the problem.
5) Could engine or transmission mounts cause the jerk?
Worn mounts can amplify what you feel, but they don’t cause a hydraulic timing bump. Fix the control/sensor issue first; then evaluate mounts if any residual feel remains.
6) How often should ATF be changed?
Follow your owner’s manual. Many workshops recommend 60–80k km under normal use and shorter under severe conditions (hot climate, towing, heavy city driving).
Conclusion
On this E-Class W212, jerks at R/D selection and at low speeds traced to a failed turbine/input speed sensor integrated in the VGS. The durable fix was VGS replacement, ATF/filter service, and proper adaptations. Use a disciplined workflow—scan → verify power/connector → live-data correlation → replace/program VGS → adapt → road-verify—to solve gearbox jerking once, correctly.
Author
Written by: Mercedes Expert
Automotive Technical Trainer & Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Specialist
With years of hands-on experience repairing and diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specializes in case-study-based troubleshooting guides that blend workshop accuracy with educational clarity.
Last Updated: September 2025






Leave a Reply