Table of Contents
Car Turns Over But Wont Start: A Real Case Study in the Mercedes-Benz E-Class W213
When your car turns over but won’t start, it’s one of the most frustrating automotive issues the starter motor spins, yet the engine refuses to run. This problem can arise from electrical, fuel, or control system faults.
In this detailed case study, we’ll examine how a Mercedes-Benz E-Class W213 equipped with the M274 engine was diagnosed and repaired after exhibiting this exact symptom. The structured diagnostic process below illustrates how professional technicians systematically pinpoint the real cause instead of relying on guesswork.
Vehicle Overview
| Model | Mercedes-Benz E-Class W213 |
|---|---|
| Engine | M274 2.0L Turbocharged Inline-4 |
| Complaint | Car turns over but won’t start |
| System Affected | Fuel delivery system |
| Diagnostic Tool | Mercedes STAR (XENTRY) System |

Step 1 : Customer Complaint & Initial Symptoms
The customer reported that the vehicle cranked normally, but did not start.
Observations:
- – The starter motor functioned properly (engine turned over).
- – The dashboard displayed no fault messages.
- – Fuel level was adequate.
These clues indicated that the starter circuit and battery were fine. The issue had to lie in the engine management likely fuel or ignition delivery.
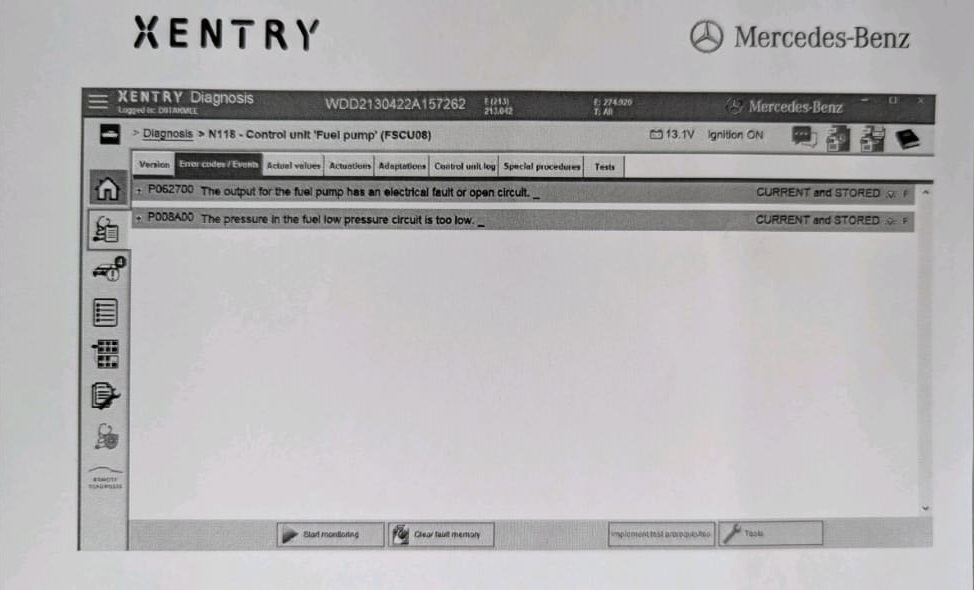
Step 2 : Running a Quick Test & Retrieving Fault Codes
A Quick Test using the Mercedes-Benz STAR diagnostic tool (XENTRY) was performed.
Findings:
- Two fault codes were stored in the Fuel Pump Control Unit:
- – One current fault (active)
- – One stored fault (historic)
Both codes indicated potential irregularities in fuel pump actuation or voltage control.
At this stage, the fault was narrowed down to fuel delivery either the pump itself or the control module that powers it.
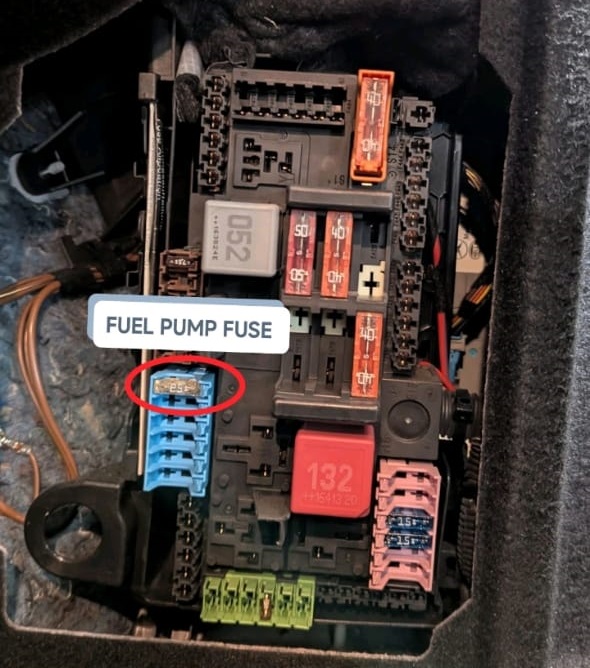
Step 3 : Checking the Fuel Pump Fuse
The next logical step was to inspect the fuse protecting the fuel pump circuit.
Findings:
- – The fuse was intact and functioning correctly.
- – Voltage was present at both sides of the fuse.
This ruled out a simple electrical failure and confirmed that power supply was reaching the fuel pump circuit.
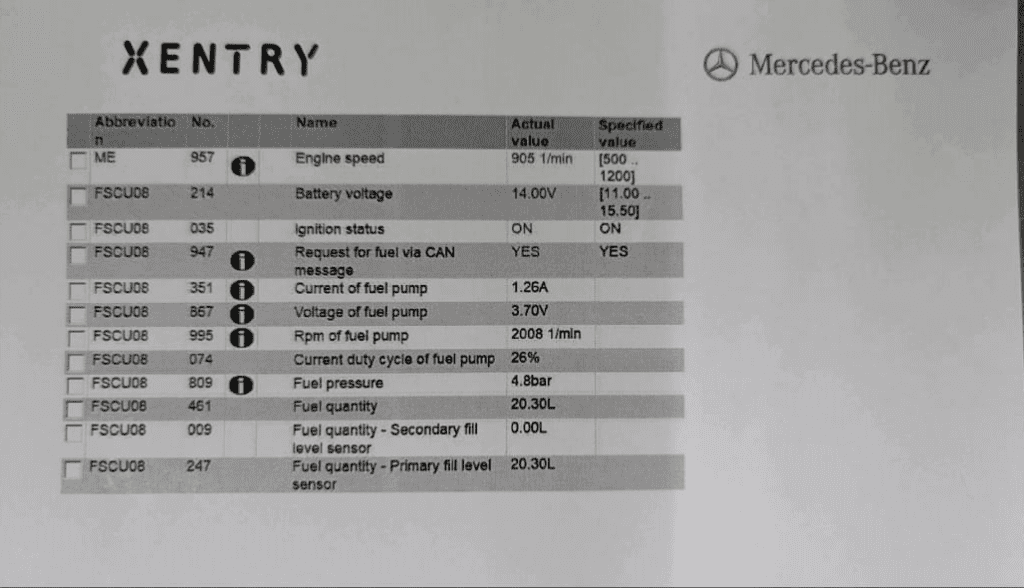
Step 4 : Verifying Actual Fuel Pump Values
Using live data through XENTRY, the technician monitored actual values from the fuel pump module.
Findings:
- – The readings were incorrect and unstable, confirming that fuel pressure was not building up in the rail.
- – The ECU was commanding pump operation, but the pump wasn’t delivering fuel.
At this point, the fault could either lie in the control unit or the fuel pump itself.
Step 5 : Performing the Guided Test for the Fuel Pump Control Unit
Mercedes’ STAR system provides guided test sequences that check control units systematically.
Results:
- – The test revealed an internal fault within the Fuel Pump Control Unit.
- – Power delivery and signal outputs were inconsistent.
Conclusion:
The Fuel Pump Control Unit was diagnosed as faulty and needed replacement.


Step 6 : Replacing the Fuel Pump Control Unit
A new genuine Mercedes control unit was installed, followed by:
- – Re-coding and adaptation to the vehicle using XENTRY.
- – Clearing all stored fault codes.
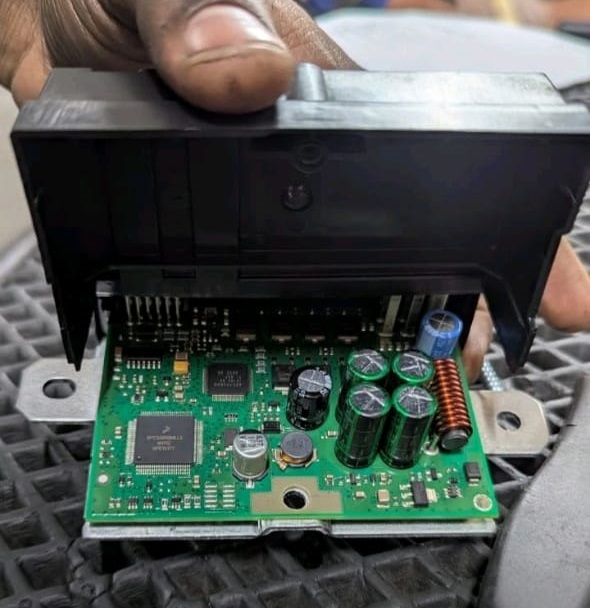

Post-Replacement Check:
After installation, the vehicle still cranked but wouldn’t start.
This indicated that the control unit failure wasn’t the root cause it had likely been a secondary symptom. The next logical step was to inspect the fuel pump itself.
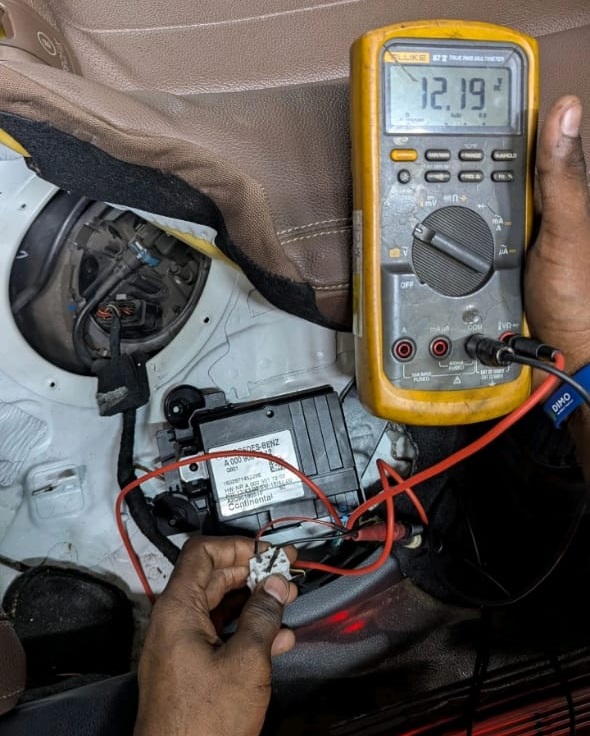
Step 7 : Diagnosing the Fuel Pump
To confirm whether the fuel pump was operational:
- 1. Power and ground signals to the pump were checked both OK.
- 2. Voltage output from the control unit was verified stable.
- 3. A manual fuel pressure test was performed using a gauge.
Findings:
- – Zero pressure detected in the fuel rail.
- – The fuel pump was not pumping fuel, despite receiving power.
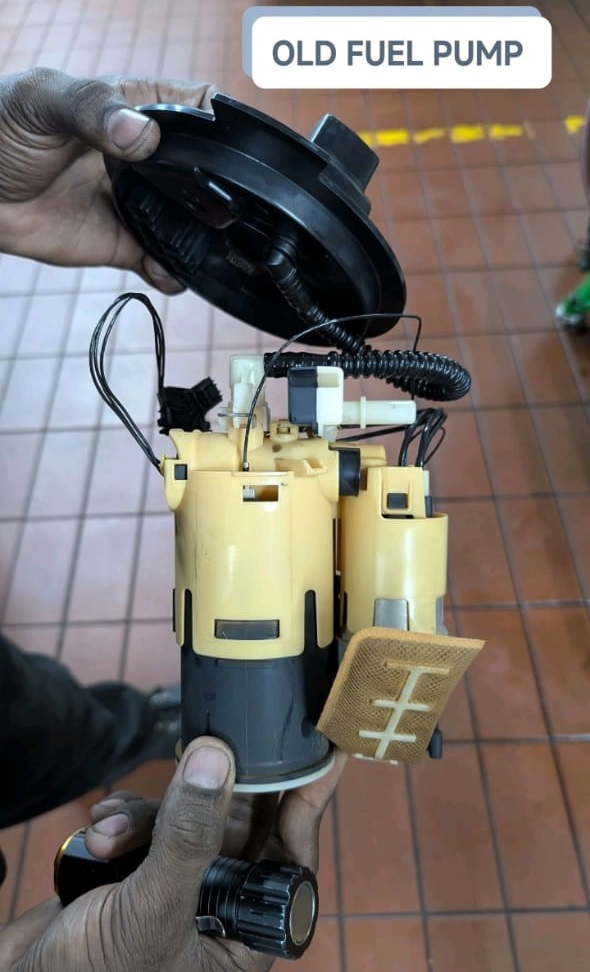

Root Cause:
A mechanical failure inside the in-tank fuel pump prevented fuel from reaching the engine.
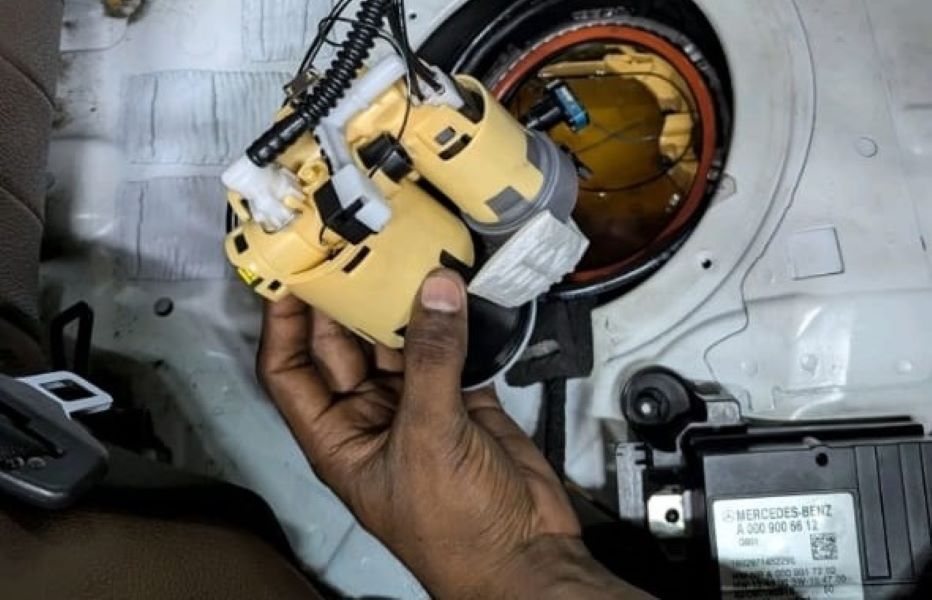
Step 8 : Replacing the Fuel Pump
A new OEM in-tank fuel pump was fitted.
Steps:
- 1. Disconnected the battery.
- 2. Removed the rear seat cushion to access the pump hatch.
- 3. Opened the fuel pump access panel and disconnected electrical connectors and fuel lines.
- 4. Replaced the defective pump with a new, factory-approved unit.
- 5. Reassembled and reconnected all lines securely.
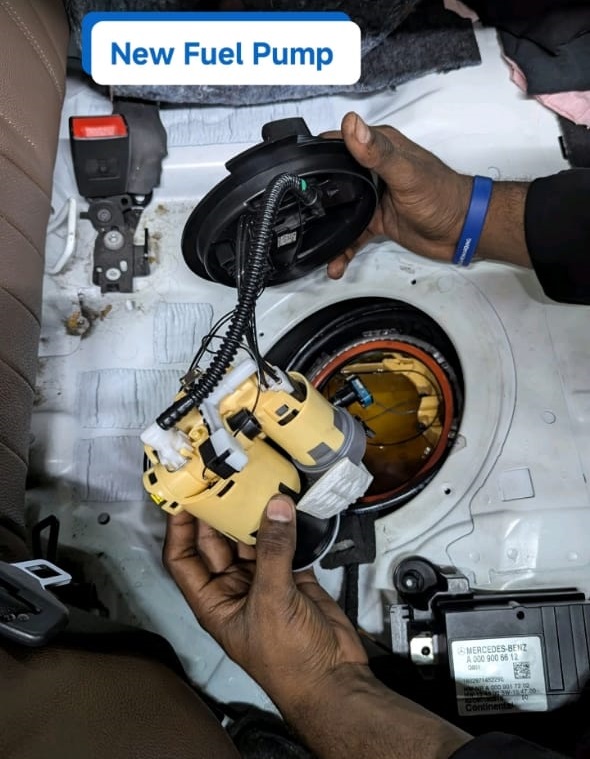

After reinstallation:
- – The technician re-checked live data.
- – Fuel pressure values now matched manufacturer specifications.
Result: The car started immediately and ran smoothly.
Root Cause Summary
| Component Tested | Status | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Healthy | Power supply normal |
| Fuse | Intact | Not the issue |
| Control Unit | Replaced | Not the root cause |
| Fuel Pump | Defective | Main cause of no-start |
| Power Supply | Stable | Confirmed OK |
Related Diagnostic Resource
If you’re facing similar starting problems, explore our full troubleshooting hub:
Mercedes No Start Issues: Causes, Fixes & Case Studies : a complete guide covering electrical, fuel, and ECU-related no-start scenarios across multiple Mercedes models.
Where Is the Fuel Pump Located on the Mercedes E-Class W213?
The fuel pump in the Mercedes-Benz E-Class W213 (M274 engine) is located inside the fuel tank, beneath the rear seat bottom cushion.
Access Steps:
- 1. Remove the rear seat bottom.
- 2. Locate and unscrew the fuel pump access cover.
- 3. Disconnect wiring harnesses and fuel lines.
- 4. Remove the locking ring or screws holding the pump.
- 5. Lift out the pump carefully to avoid damaging the seal.
This in-tank configuration keeps the pump cool and efficient by using surrounding fuel for temperature regulation.
Where Is the Fuel Pump Control Module Located?
The Fuel Pump Control Module (also known as the Fuel Pump Driver Module) is typically located near the fuel tank or beneath the rear seat area.
It regulates voltage to the pump, ensuring precise fuel delivery.
Common Failure Symptoms:
- – Car cranks but won’t start
- – Intermittent stalling or low fuel pressure
- – Fault codes stored in the Fuel Pump Control Unit (N118/3)
- – No power signal to the pump
If replacing the module, it’s critical to:
- – Verify power and ground integrity
- – Check CAN communication lines
- – Code the new unit properly using STAR/XENTRY

Diagnostic Lessons & Takeaways
- 1. Start Simple: Always begin with a quick test and fuse inspection.
- 2. Don’t Assume the First Fault Code Is Final:
In this case, the control unit appeared faulty, but the actual issue was the mechanical pump. - 3. Check Actual Values:
Live data is often more revealing than static fault codes. - 4. System Interdependence:
The fuel pump and its control unit are tightly linked one failing can mimic the symptoms of the other. - 5. Confirm Repair:
After replacement, always verify fuel pressure and perform a post-repair test drive.
Conclusion
When a Mercedes E-Class W213 turns over but won’t start, it can be due to issues in the fuel delivery system not necessarily electronics.
In this case, a failed fuel pump caused a complete loss of pressure despite power and control signals being normal. Replacing the defective pump restored normal operation, confirming the value of a structured diagnostic approach.
Whether you’re a technician or enthusiast, this case shows that proper testing not parts swapping is the key to resolving modern Mercedes no-start issues effectively.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: October 2025






Leave a Reply