Table of Contents
Mercedes E-Class (7G-Tronic) Case Study: Delayed Shifting When Accelerating & “Park” Not Engaging
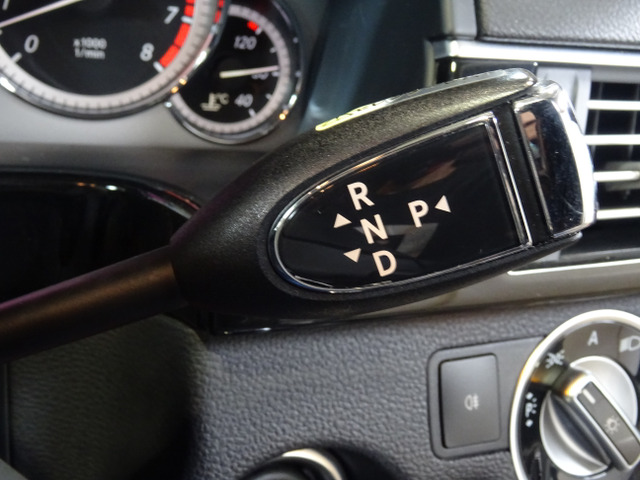

In this case study, we delve into a specific instance of delayed shifting and parking issues in a Mercedes E-Class With 7G TRONIC Transmission, brought to a dealership by an owner experiencing significant transmission problems. We will explore the diagnostic process, fault codes identified, and the subsequent repairs that led to the resolution of the issue.
Vehicle & Complaint
| Item | Detail |
|---|---|
| Model | Mercedes-Benz E-Class W212 |
| Transmission | 7G-Tronic (722.9) with VGS (Y3/8) |
| Owner Complaint | 1) Delayed shifting when accelerating 2) Cannot engage Park (P) |
| Driving Risk | Roll-away risk when Park won’t engage; accelerated clutch wear from delayed shifts |
DTCs Found (XENTRY Short Test)
| Code | Plain-English Meaning | Where It Points |
|---|---|---|
| P07E600 | Park pawl cannot be released | Park mechanism control |
| P07E400 | Park pawl cannot be engaged | Park mechanism control |
| P07B571 | Park pawl Sensor A malfunction | Park position feedback |
| P076977 | Y3/8y11 park-pawl switchover valve, internal electrical test failed | Park solenoid/driver |
| P087000 | Oil pressure sensor “C” electrical fault | Pressure sensing/loom/VGS |
| P060C00 | Internal CPU fault in control unit | VGS electronics |
| P170900 | Specified position of Y3/8 cannot be reached | Hydraulic/solenoid/adaptations |
| P056200 | Low system voltage | Battery/charging/grounds |
| U012600 | Lost comm with steering column module | Network/power stability (can block park logic) |
Interpretation: Multiple “electrical/position” faults across park control and pressure regulation typically implicate the VGS (mechatronics) driver and/or park pawl hardware with low voltage as a contributing factor. The pressure-sensor DTC and P170900 explain the delayed upshifts.
Root-Cause Summary
- 1. VGS (Fully Integrated Transmission Control) internal fault → inconsistent solenoid/valve control, failed self-tests, delayed shifts.
- 2. Park pawl subsystem fault (Y3/8y11 + Sensor A) → P cannot be commanded/confirmed.
- 3. Contributing factors: low voltage event (P0562), thermostat/ATF temp control, contaminated fluid/filter age.
Symptom → Cause → First Fix
| Symptom | Likely Cause | First Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Delayed shifts on throttle | VGS driver fault; PRV modulation off; ATF condition | Verify voltage; ATF/filter; mechatronics evaluation |
| Park won’t engage/release | Park solenoid Y3/8y11 or Sensor A; mechanical pawl hang-up | Replace faulty components; verify cable/actuator; re-adapt |
| DTCs return after clear | VGS internal error | Replace/codify VGS; run adaptations |
| Intermittent warnings | Low voltage / ground quality | Battery/alternator test; ground refresh |
Repair Process (Step-by-Step)
1. Stabilize Power & Baseline
- – Connect battery maintainer (12.5–14.5 V).
- – Clear old codes; re-scan to confirm current faults.
2. Mechanical Safety & Park Control Check
- – Chock wheels. Confirm driver-door/shift interlock logic OK.
- – Read park pawl status in live data; attempt actuation of Y3/8y11.
3. Fluid & Thermostat
- – Verify ATF level/temperature; inspect fluid condition (burnt/contaminated?).
- – Replace transmission thermostat if temperature management is unstable (helps consistent shift learn).
4. Pan Down & Inspection
- – Drain ATF; remove pan & filter. Check magnet debris.
- – Inspect loom/13-pin connector for fluid wicking and pin tension.
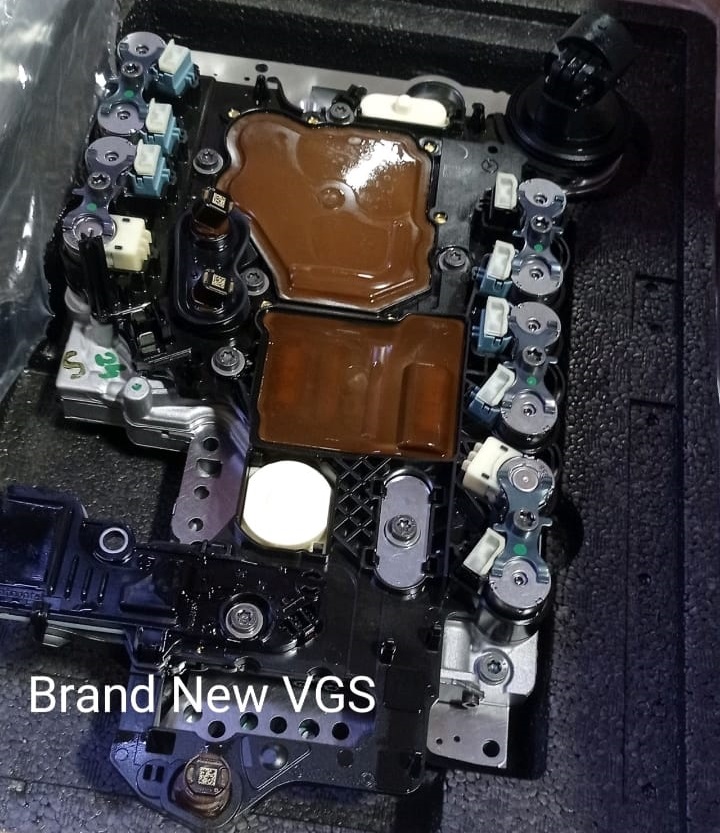
5. VGS / Mechatronics Decision
- – Given CPU/internal test + multi-PRV/park DTCs, replace VGS (Y3/8) assembly.
- – Renew connector sleeve, seals, bolts per WIS.

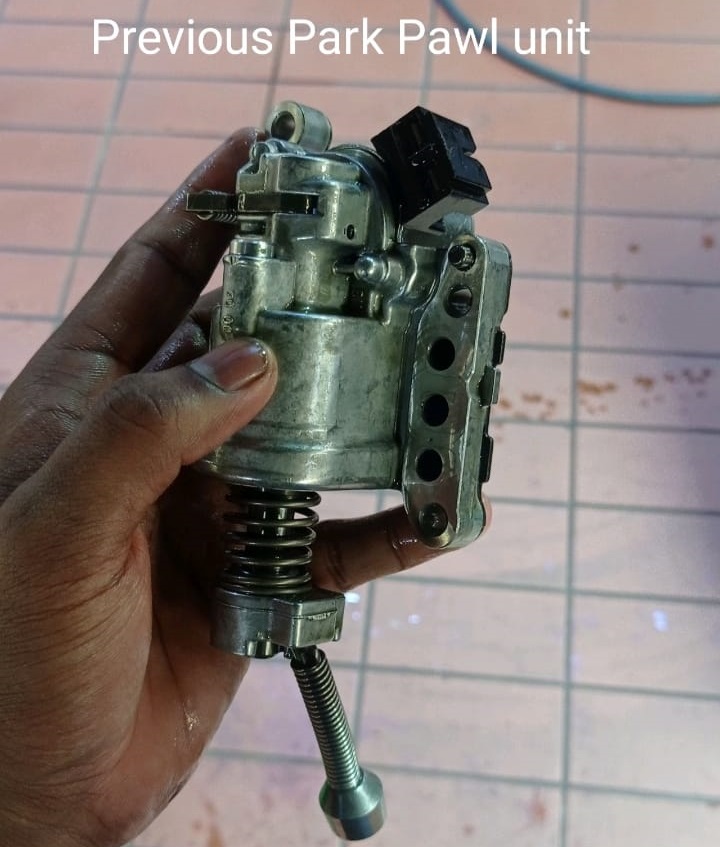
6. Park Pawl Hardware
- – Replace park pawl assembly (and Y3/8y11 if not integrated) and Sensor A as indicated by guided tests.
- – Inspect linkage/actuator for binding; lubricate contact points as specified.


7. Service & Flush
- – Flush lines and cooler if contamination suspected.
- – Fit new filter and pan gasket; refill with MB-approved ATF; set level at temperature.
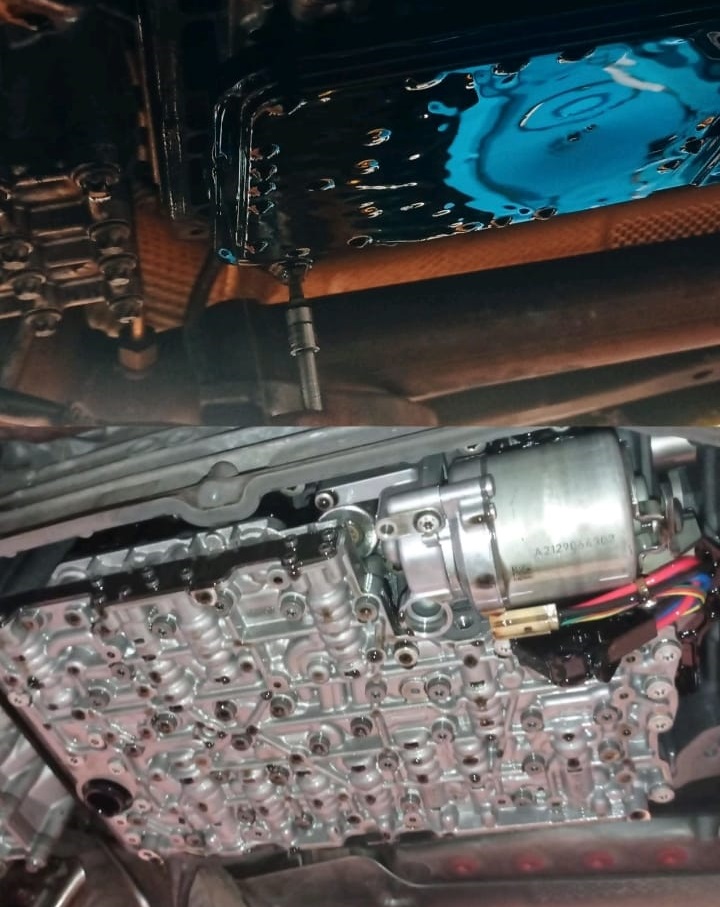

8. Software & Adaptations
- – Perform SCN coding/data restore for new VGS.
- – Run standstill and running adaptations (no pending DTCs, ATF temp in range, tires at spec).
9. Validation Drive & Final QA
- – Urban + highway loop; verify gear target vs. actual, TCC slip, no roll-away prompts.
- – Re-scan: zero current faults; recheck for leaks after heat-soak.
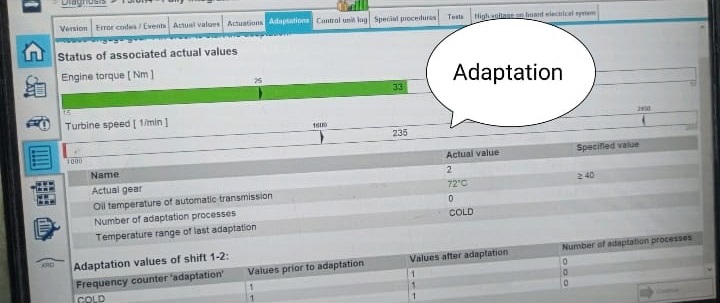
Outcome: Park engagement confirmed, no delay on upshifts, no fault return.
Explore More Mercedes Transmission Issues
For a deeper dive into gearbox problems slipping into Neutral, delayed/harsh shifts, “Not in P” warnings, and hybrid faults visit our hub: Mercedes Transmission Issues – Causes and Fixes. You’ll find grouped case studies, step-by-step diagnostics, symptom–cause–fix tables, and prevention tips to resolve shifting issues quickly and confidently.
Technician’s Tables
Live-Data Checkpoints
| Parameter | Healthy Behavior | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Park status | Immediate, consistent “P” confirmation | Flapping/unknown state |
| PRV currents | Stable, repeatable | Dropouts/spikes under load |
| Turbine vs engine speed | Proportional at stall/launch | Turbine zero/erratic when in gear |
| TCC slip | Low/steady at cruise | High/uncontrolled slip |
| ATF temperature | In spec for learn | Over/under temp → aborted adaptations |
Parts/Operations Performed
| Item | Action | Why |
|---|---|---|
| VGS (Y3/8) | Replace, SCN code, adapt | Internal CPU/driver faults |
| Park pawl + Sensor A + Y3/8y11 | Replace | Park engagement faults |
| Thermostat | Replace | Stable ATF temp for smooth shifts |
| ATF filter & pan gasket | Replace | Flow & filtration restored |
| ATF service/flush | Perform | Remove contamination; correct spec |
Time & Cost (Indicative)
| Operation | Typical Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Full diagnosis + live data | 1.0–1.5 h | Includes voltage & interlock checks |
| VGS replace + SCN coding | 1.0–2.0 h | Tooling & online coding |
| Park pawl/solenoid service | 2.0–3.5 h | Model-specific access |
| Thermostat + ATF/filter | 1.0–1.5 h | Temp-based level set |
| Adaptations + validation drive | 0.5–1.0 h | Preconditions critical |
Parts and labor vary by region; use as planning guidance.
Prevention & Maintenance
- – Battery/charging health: low voltage triggers logic and comm faults test annually.
- – ATF & filter: many specialists recommend service every 60–80k km (4–5 years) even if labeled “lifetime.”
- – Thermal management: ensure thermostat/cooling efficiency to protect clutch fills and learn values.
- – After battery replacement or software work, re-run adaptations if shift feel changes.
- – Address minor delays early; they rarely “self-heal.”
FAQs: Delayed Shifting When Accelerating
1) Why wouldn’t Park engage even though the lever shows P?
Park confirmation depends on the pawl actuator (Y3/8y11) and Sensor A feedback, plus VGS logic. If the solenoid, sensor, or VGS driver fails or voltage is unstable the car won’t confirm P, and the cluster may warn of roll-away risk.
2) Can low voltage really cause shifting and park issues?
Yes. P0562 indicates low system voltage, which can corrupt driver tests, block adaptations, and confuse network modules (e.g., U0126 steering-column comms), indirectly preventing Park logic.
3) Will a simple ATF change fix delayed shifts?
If the cause is mild fluid degradation, it helps. But with P170900 / park-pawl DTCs / internal CPU faults, you’ll likely need VGS and park-pawl repairs plus adaptations.
4) What are adaptations and why are they required?
They are the TCU’s learned values for clutch fill and overlap timing. After component replacement or voltage loss, running standstill & running adaptations restores smooth shift quality.
5) Is it safe to drive while Park is unreliable?
Avoid it. Always use the parking brake and park on level ground until repairs are complete. Unreliable Park is a safety risk.
6) Could this require a full transmission replacement?
Uncommon. Most cases resolve with VGS/mechatronics + park-pawl repairs, fresh ATF/filter, and complete adaptations.
Conclusion
In this E-Class W212, stacked DTCs across park control, pressure sensing, and a VGS internal CPU fault explained both delayed upshifts and no-Park complaints. Replacing the VGS, park-pawl hardware, thermostat, and servicing the ATF/filter followed by proper coding and adaptations returned factory-smooth shifting and reliable Park engagement.
Author
Written by: Mercedes Expert
Automotive Technical Trainer & Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Specialist
With years of hands-on experience repairing and diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specializes in case-study-based troubleshooting guides that blend workshop accuracy with educational clarity.
Last Updated: September 2025






Leave a Reply