Table of Contents
Engine Crank But no Start : Mercedes-Benz S400 Hybrid W221 Case Study
When your Mercedes engine cranks but doesn’t start, it can be confusing the starter turns, but the engine never fires up. This issue can stem from faults in the fuel system, ignition, or engine control circuits.
In this real-world case, we’ll walk through a detailed diagnosis and repair of a Mercedes-Benz S400 Hybrid (W221) equipped with the M276 3.5L V6 engine, which suffered from a no-start condition caused by a faulty fuel pump.
By following this diagnostic path, technicians and owners alike can understand how to test, confirm, and fix this problem efficiently.
Vehicle Overview
| Model | Mercedes-Benz S400 Hybrid (W221) |
|---|---|
| Engine | M276 – 3.5L V6 Hybrid Powertrain |
| Complaint | Engine cranks but won’t start |
| Root Cause | Fuel pump malfunction |
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedure
1. Customer Complaint
The owner reported that the engine cranked normally, but never started no ignition response, no combustion, only prolonged cranking.
This meant the starter circuit was functional, but the fuel or ignition system was failing to engage.
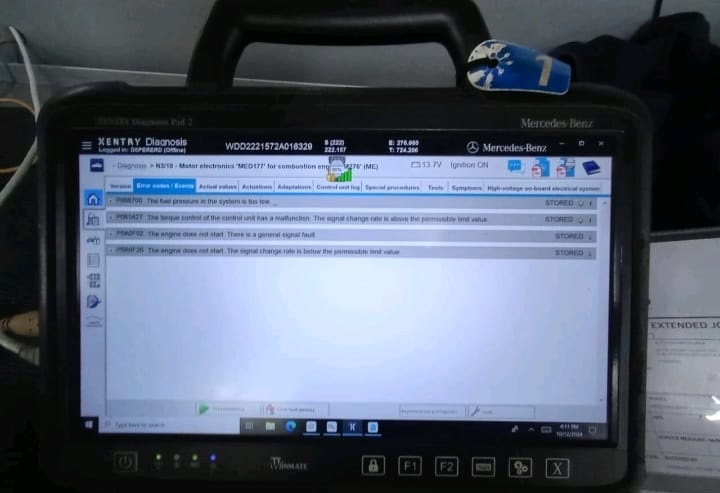
2. Initial Diagnostics : XENTRY Quick Test
The technician connected the Mercedes STAR/XENTRY diagnostic system to perform a short test on the ME (Motor Electronics) control unit.
| Diagnostic Finding | Observation |
|---|---|
| Fault code stored | Fuel pressure malfunction |
| Affected control unit | ME-SFI (Engine control module) |
No other faults were stored, suggesting the engine control logic was active, but fuel delivery was compromised.
3. Visual Inspection
Before replacing parts, the workshop carried out a comprehensive visual check:
- – No fuel leaks found along the fuel rail or injectors.
- – Fuel pump control unit showed no physical damage or corrosion.
- – Connectors were clean, dry, and secure.
Conclusion: Fuel leak ruled out; electronic fault suspected in the fuel supply system.
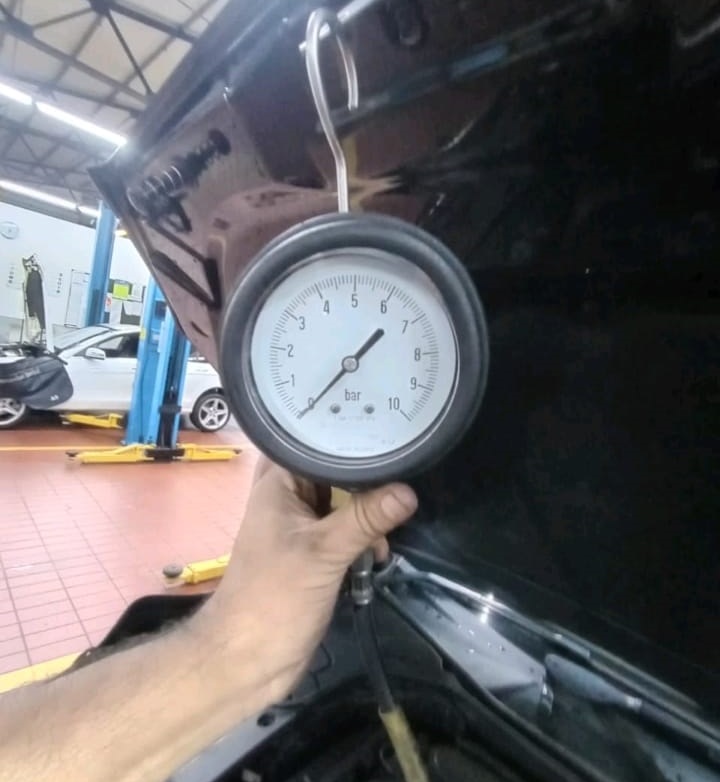
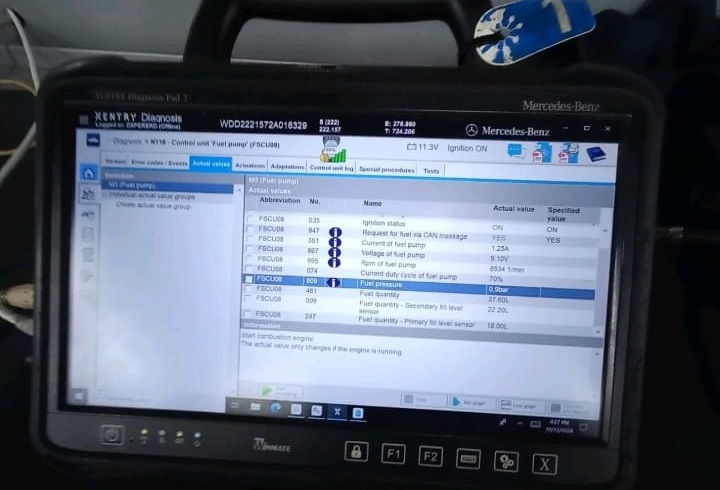
4. Fuel Pressure Testing
Using both XENTRY live data and a manual gauge, the team confirmed pressure loss in the fuel system.
| Test | Expected Value | Measured Value | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| XENTRY reading | 4.0 – 6.0 bar (at ignition ON) | 0.9 bar | Low pressure |
| Manual gauge (fuel rail) | 4.0 – 6.0 bar | 0.0 bar | No delivery |
These results confirmed zero fuel flow to the engine the fuel pump was not operating despite proper ECU command signals.

Root Cause: Fuel Pump Failure
After verifying power supply and ground continuity, the fuel pump itself was identified as the failure point.
This was consistent with the fuel pressure fault code and no combustion symptoms during cranking.
Repair Procedure : Fuel Pump Replacement
Replacing a fuel pump on a Mercedes hybrid requires special care to avoid electrical hazards.
Step 1 : Preparation
- – Disconnect the 12V auxiliary battery.
- – Disable hybrid high-voltage system (safety lockout).
- – Move rear seats forward to access the fuel tank module.
Step 2 : Removal
– Remove the rear seat cushion.
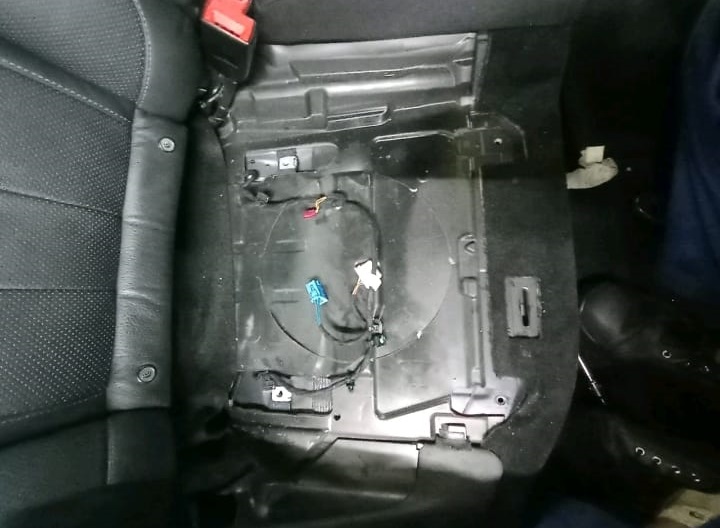

– Lift the service cover over the fuel tank access port.
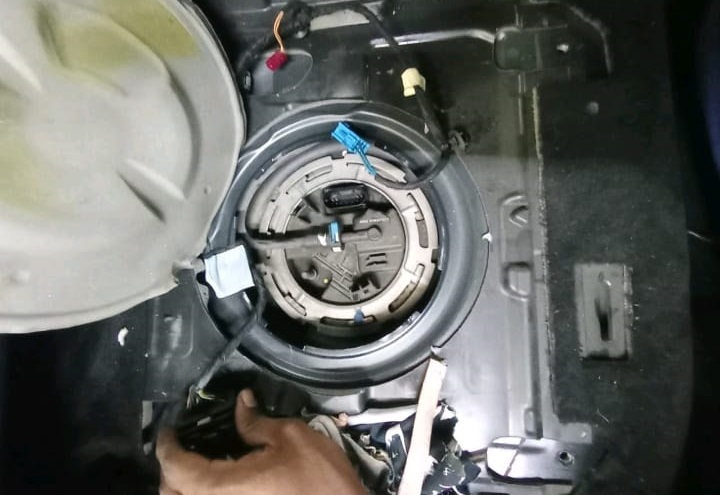

– Disconnect fuel lines and electrical connectors.
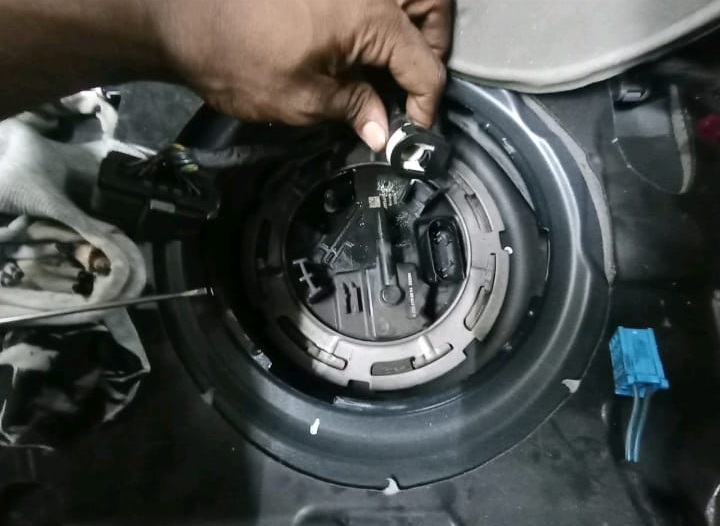

– Extract the old pump using a Mercedes claw wrench for the locking ring.
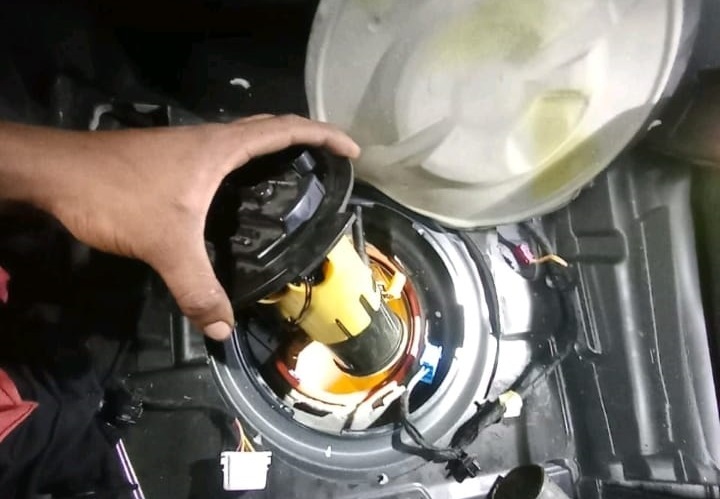

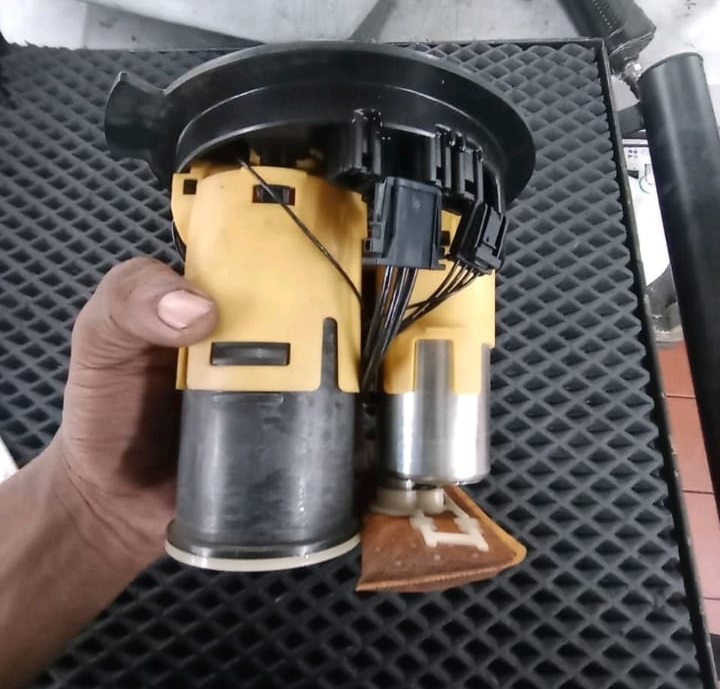
Step 3 : Installation
- – Fit a new OEM fuel pump with a fresh sealing ring.
- – Reconnect all hoses and connectors securely.
- – Clear all stored fault codes using XENTRY.
- – Cycle ignition ON/OFF to prime the fuel system.

Post-Repair Testing
| Test Type | Expected Result | Actual Result |
|---|---|---|
| Engine start | Should start instantly | Started successfully |
| Fuel pressure reading | 4.5–5.5 bar at idle | Within range |
| Fault codes | None present | Cleared successfully |
| Idle stability | Smooth | Normal |
The engine started on the first attempt, confirming that fuel delivery was fully restored and the hybrid system was operating normally.
Diagnostic Summary
| Step | Tool / Method | Result | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick test | XENTRY Diagnostic | Fuel pressure fault | Fuel system issue |
| Visual inspection | Physical check | No leaks, no corrosion | Pump suspected |
| Pressure test | Manual gauge | 0.0 bar | Pump failure confirmed |
| Component replacement | Fuel pump | New OEM installed | Normal operation restored |
Key Lessons & Takeaways
| Lesson | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Cranking ≠ Starting | If the starter engages but the engine won’t fire, focus on fuel, spark, and compression. |
| 2. XENTRY Saves Time | Quick fault code retrieval narrows the diagnostic scope immediately. |
| 3. Fuel Pressure Tests Are Essential | Always verify with both live data and a manual gauge. |
| 4. Hybrid Safety First | Always disconnect both 12V and HV circuits before opening the fuel system. |
| 5. Always Perform Post-Repair Verification | Confirms that fuel pressure and ECU readings align with specs. |
Preventive Maintenance Tips
| Action | Frequency / Advice |
|---|---|
| Replace fuel filter | Every 60,000–80,000 km |
| Keep tank above ¼ full | Prevents fuel pump overheating |
| Check fuel pressure at each major service | Detects early degradation |
| Use OEM-approved fuel pump components | Maintains pressure stability |
| Avoid extended storage without fuel stabilizer | Reduces varnish and clogging |
Related Diagnostic Resource
If you’re facing similar starting problems, explore our full troubleshooting hub:
Mercedes No Start Issues: Causes, Fixes & Case Studies : a complete guide covering electrical, fuel, and ECU-related no-start scenarios across multiple Mercedes models.
FAQ: Engine Crank But no Start
1. Why does my Mercedes crank but not start?
This usually indicates a fuel delivery problem, ECU fault, or ignition timing issue. Check for fuel pressure before replacing components.
2. Can a bad fuel pump cause no-start with no warning lights?
Yes, the fuel pump can fail silently, and the ECU only detects it when pressure drops below threshold during cranking.
3. How do I test the fuel pump without removing it?
Measure fuel rail pressure using XENTRY or a mechanical gauge. If pressure reads below 1 bar during cranking, the pump may have failed.
4. Do hybrid Mercedes models have different fuel systems?
They use a 12V electric pump, but hybrid modules require proper isolation and safety disconnection before repairs.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: October 2025






Leave a Reply