Table of Contents
Engine Doesn’t Start and Gear Shift Light Not Working : Mercedes-Benz C300 W204 Case Study
A Mercedes-Benz C300 W204 equipped with the 7G-TRONIC transmission was brought into the workshop with a major complaint:
“The engine doesn’t start, and the gear shift light isn’t working.”
At first glance, this might seem like an ignition or battery issue, but the real cause was far more complex. This case study highlights how a single component failure in this case, the auxiliary oil pump can cause cascading faults across multiple systems in a modern Mercedes.
Vehicle Overview
| Model | Mercedes-Benz C300 W204 |
|---|---|
| Transmission | 7G-TRONIC (722.9) |
| Complaint | Engine doesn’t start and gear shift light not working |
| System Affected | Drivetrain CAN Bus Network |
Customer Complaint: Engine Doesn’t Start & Gear Shift Light Inoperative
The customer reported that the vehicle would not start at all no cranking sound, no gear indicator illumination on the instrument cluster, and the gear selector remained unresponsive.
These combined symptoms immediately hinted at a communication breakdown within the CAN Bus (Controller Area Network), which links the engine, transmission, and other key modules.
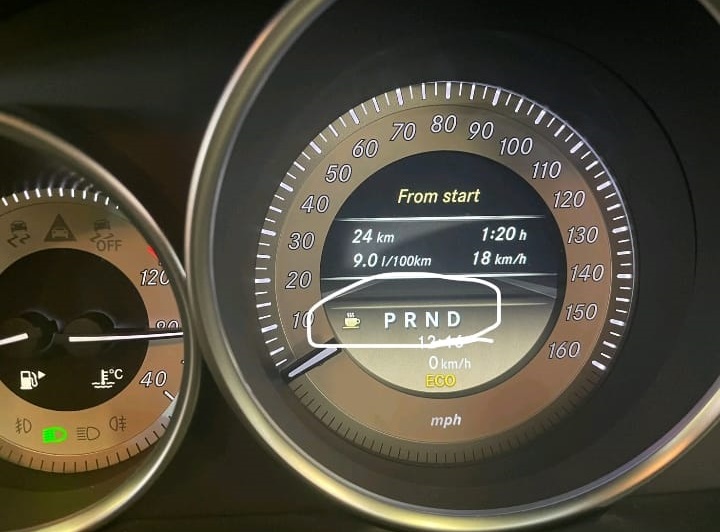


Step 1: Diagnostic Verification
The first step was to confirm the customer’s complaint.
Upon testing, technicians verified that:
- – The engine did not crank or start.
- – The gear shift light remained off, even with ignition ON.
- – No mechanical sounds or relay clicks were heard, suggesting electronic system failure.
The next logical step was to perform a full system scan using the Mercedes-Benz XENTRY Star Diagnosis tool.
Step 2: Fault Code Analysis
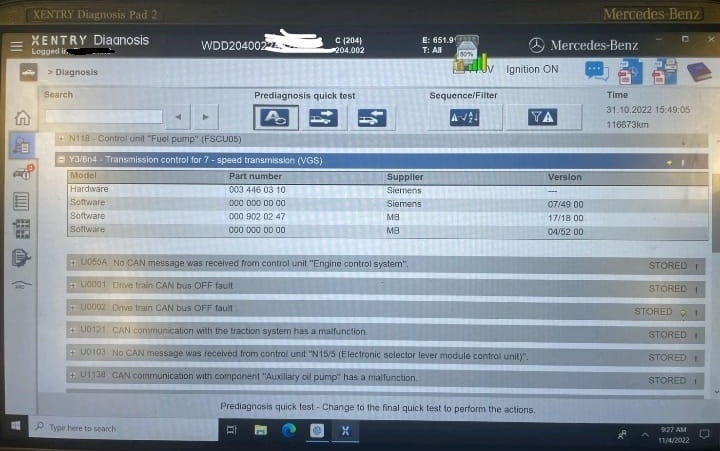
The diagnostic scan retrieved multiple CAN communication faults across different control units:
| Fault Code | Description |
|---|---|
| U055A | No CAN message from Engine Control Unit |
| U0001 | Drive Train CAN Bus OFF |
| U0002 | Drive Train CAN Bus OFF (Recurrent Fault) |
| U0121 | CAN Communication with Traction System Malfunction |
| U0103 | No CAN message from Control Unit “N15/5” (EIS/Transmission) |
| U1138 | CAN Communication with Auxiliary Oil Pump Malfunction |
Interpretation:
All codes pointed to a CAN Bus interruption a loss of communication among drivetrain modules such as the ECU, transmission control unit (TCU), and auxiliary oil pump.
Among these, U1138 was the most revealing, suggesting the auxiliary oil pump had stopped communicating altogether.
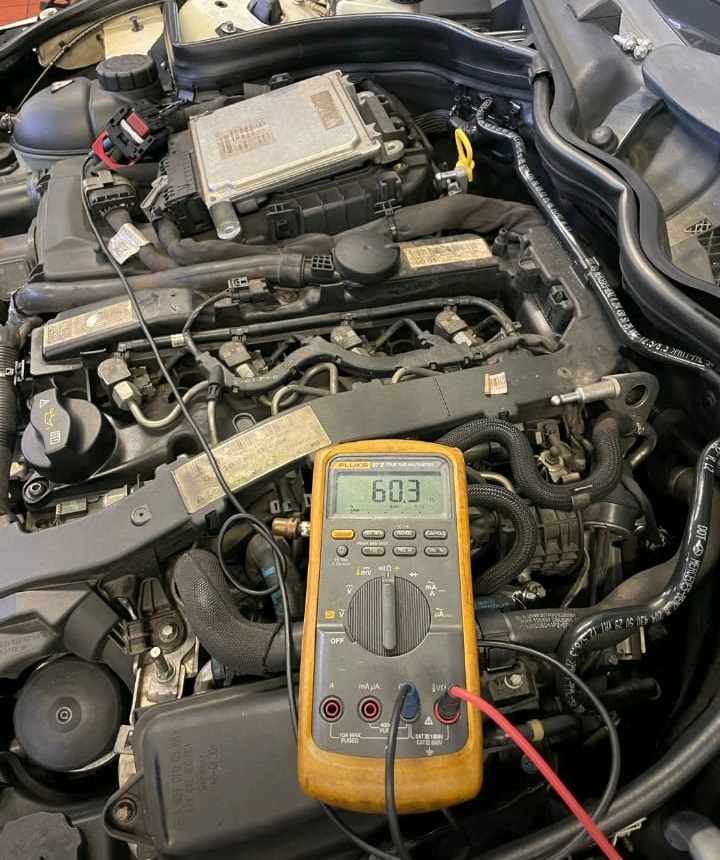
Step 3: CAN Bus Network Testing
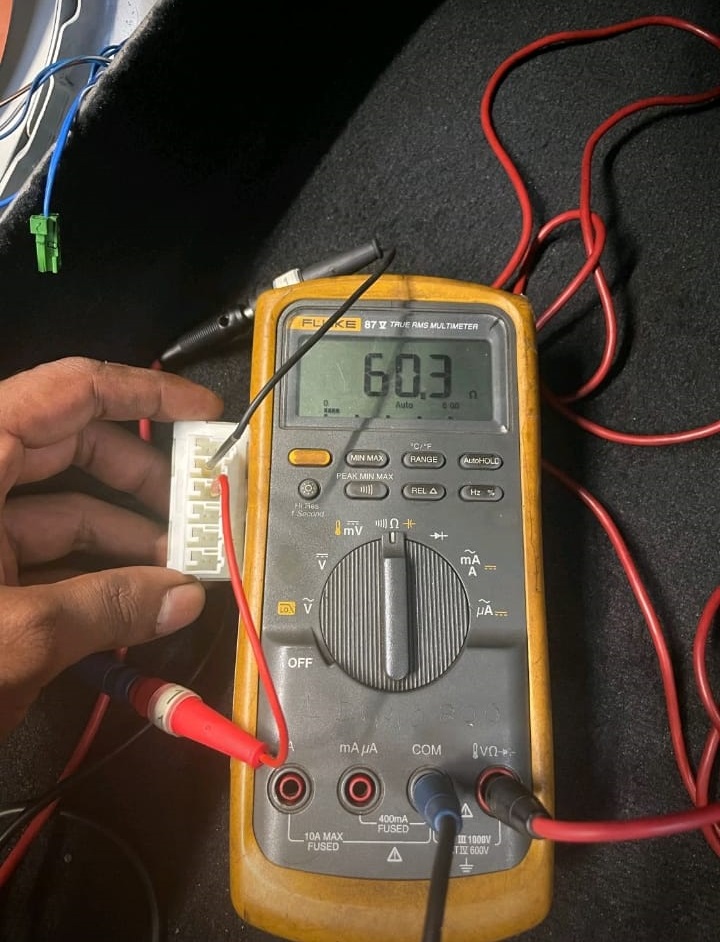
The next step was to confirm the integrity of the physical CAN network. Using Mercedes-Benz wiring diagrams and a digital multimeter, the technician checked resistance and continuity.
CAN Bus Resistance Test:
- – Measured resistance at the CAN potential distributor: 60 ohms
- – Normal range: 60 ± 2 ohms
This confirmed that the CAN wiring itself was healthy there were no open circuits or shorts between CAN High and CAN Low.
However, communication to the auxiliary oil pump was dead, confirming that the fault lay inside the component or its control electronics.



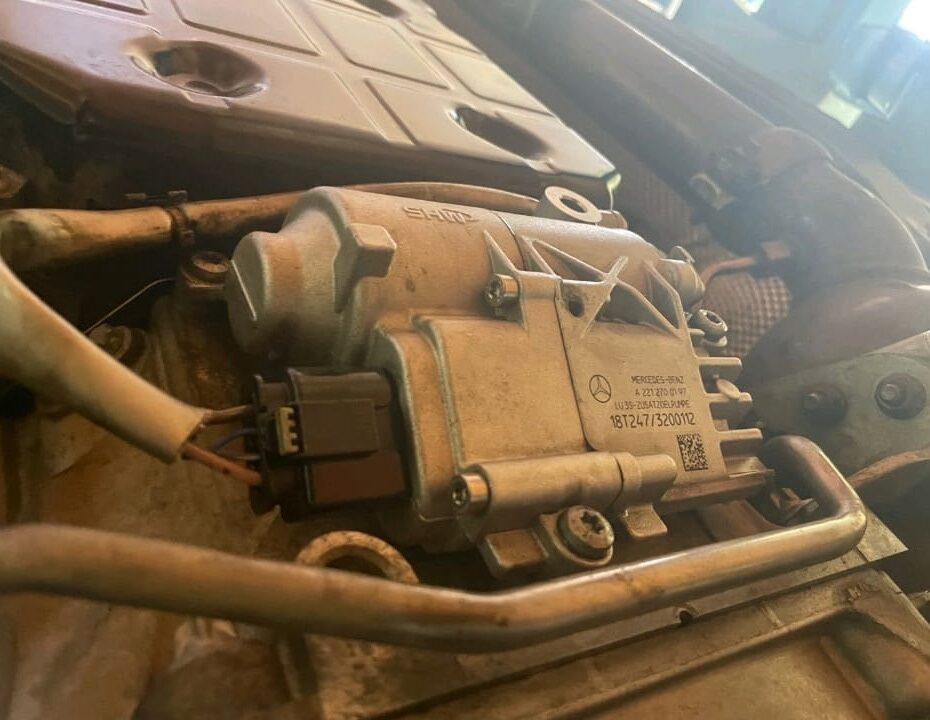
Step 4: Root Cause Identified ; Faulty Auxiliary Oil Pump
The auxiliary oil pump on this Mercedes C300 plays a critical role in transmission operation.
It is responsible for:
- – Maintaining fluid pressure for the 7G-TRONIC transmission.
- – Supporting start-stop functionality when the engine shuts off.
- – Ensuring smooth gear engagement during startup or idling.
When the auxiliary oil pump fails electronically, it can disrupt CAN Bus communication, effectively shutting down the entire drivetrain system.
This explains both symptoms:
- 1. Engine wouldn’t start → Because the ECU and TCU lost CAN synchronization.
- 2. Gear shift light didn’t illuminate → Because the transmission module couldn’t communicate via the CAN Bus.

Step 5: Repair Process – Replacing the Auxiliary Oil Pump
Once confirmed, the decision was made to replace the faulty auxiliary oil pump.
Step-by-Step Repair:
1. Safety First:
- – The battery was disconnected to isolate all voltage sources.
- – The transmission fluid temperature was allowed to cool before work began.
2. Access the Auxiliary Oil Pump:
- – The pump is mounted externally on the transmission housing.
- – The vehicle was lifted on a hoist for safe underbody access.
3. Remove the Faulty Pump:
- – Electrical connector unplugged and wiring inspected.
- – Hydraulic lines detached and sealed to prevent fluid leakage.
- – Mounting bolts removed, and the pump extracted.
4. Install the New OEM Auxiliary Oil Pump:
- – New seals and O-rings were fitted.
- – Electrical connector checked for corrosion and secured.
- – Transmission fluid level was refilled and corrected.
5. System Initialization:
- – Using XENTRY, the technician cleared all fault codes.
- – The drivetrain CAN Bus was reinitialized.
- – Communication across ECU, TCU, and auxiliary oil pump modules was verified.
Step 6: Verification and Results
After installation and system reset:
- – The engine started immediately.
- – The gear shift light illuminated normally.
- – No fault codes reappeared.
- – A test drive confirmed proper shifting and transmission performance.
| System | Before Repair | After Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Start | Not possible | Starts normally |
| Gear Shift Light | Off | Functional |
| CAN Communication | Offline | Restored |
| Fault Codes | 6 active | 0 active |
The root cause of the issue was conclusively identified as a failed auxiliary oil pump, which had caused a total loss of drivetrain communication.
Related Diagnostic Resource
If you’re facing similar starting problems, explore our full troubleshooting hub:
Mercedes No Start Issues: Causes, Fixes & Case Studies : a complete guide covering electrical, fuel, and ECU-related no-start scenarios across multiple Mercedes models.
Understanding the Auxiliary Oil Pump in Mercedes-Benz
The auxiliary oil pump is a vital support system in 7G-TRONIC and newer Mercedes transmissions.
Main Functions
- – Cooling: Circulates transmission fluid to maintain temperature.
- – Lubrication: Ensures smooth gear changes and protects components.
- – Support for Start-Stop Systems: Maintains fluid pressure during engine stop phases.
Common Symptoms of Failure
| Symptom | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Transmission overheating | Pump not circulating fluid |
| Harsh or delayed shifting | Insufficient hydraulic pressure |
| Engine won’t start | CAN Bus communication fault |
| Warning lights | ECU detects lost communication with pump |
Prevention
- – Regular transmission fluid service (every 60,000–80,000 km).
- – Inspect connectors and wiring during routine maintenance.
- – Avoid aftermarket pump replacements that may not meet CAN signal specifications.
Key Takeaways
- – Modern Mercedes vehicles rely on inter-module communication; one failed unit can halt the entire system.
- – CAN Bus diagnostics and resistance checks are essential before replacing components.
- – The auxiliary oil pump not only controls transmission fluid flow but also directly affects the engine start authorization process.
- – Always perform OEM module coding and CAN verification after replacement.
Conclusion
This case study of a Mercedes-Benz C300 W204 illustrates how an engine not starting and gear shift light not working can originate from a single component failure within the drivetrain network.
By using a structured diagnostic process scanning, analyzing CAN Bus data, and isolating the fault technicians identified the auxiliary oil pump as the cause.
Replacing and initializing the new pump fully restored communication, allowing the vehicle to start and shift normally.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: October 2025
— Salim, Mercedes Expert
Independent specialist in Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, CAN Bus analysis, troubleshooting case studies, and EV systems.







Leave a Reply