Table of Contents
Why Wont My Mercedes Start? A Case Study on the Mercedes C300 W204 (M271 Engine)
There’s nothing more frustrating for a Mercedes owner than turning the key and hearing only silence or endless cranking with no ignition. This issue is more common than many think, especially on models like the Mercedes-Benz C300 W204, which combines sophisticated electronics with precise engine management systems.
In this real-world diagnostic case, we uncover why a Mercedes won’t start, showing how professional diagnostics, wiring inspection, and attention to detail led to a simple yet effective repair.
Case Study Overview
| Vehicle Model | Engine | Customer Complaint |
|---|---|---|
| Mercedes-Benz C300 W204 | M271 | Engine does not start, prolonged cranking before ignition |
The vehicle was towed in after repeated no-start attempts. The owner reported long cranking before the engine finally stopped starting altogether.
1. Initial Diagnostics with XENTRY
The first step in diagnosing any Mercedes no-start condition is to run a complete system scan using XENTRY Diagnosis, Mercedes-Benz’s OEM diagnostic software.
Several fault codes were recorded in the engine control unit (ECU), all pointing to the crankshaft position sensor a key component in engine synchronization.
Fault Codes Identified:
- – P033631: Crankshaft position sensor 1 – no signal present.
- – P033664: Crankshaft position sensor 1 – implausible signal.
- – P037339: Incorrect number of teeth recorded – too few pulses.
- – P261062: Engine off time implausible – invalid signal comparison.
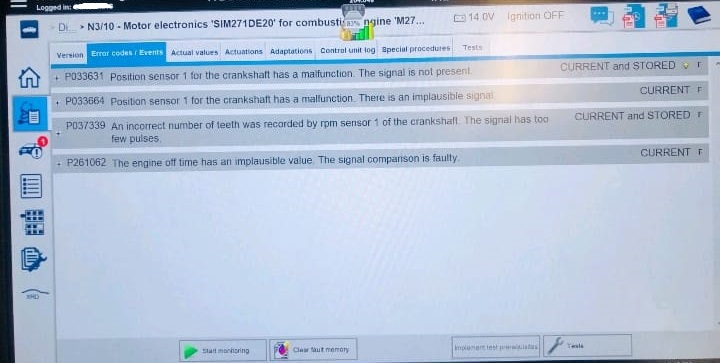
These codes suggested the ECU wasn’t receiving accurate crankshaft position data, preventing proper fuel injection and ignition timing.
2. Signal Verification with PicoScope
To confirm, we tested the crankshaft position sensor signal using a PicoScope oscilloscope.
- – Observation: No waveform signal was received from the sensor during cranking.
- – Conclusion: The sensor was not functioning correctly.
This test eliminated false positives from XENTRY and confirmed an actual sensor-related issue.
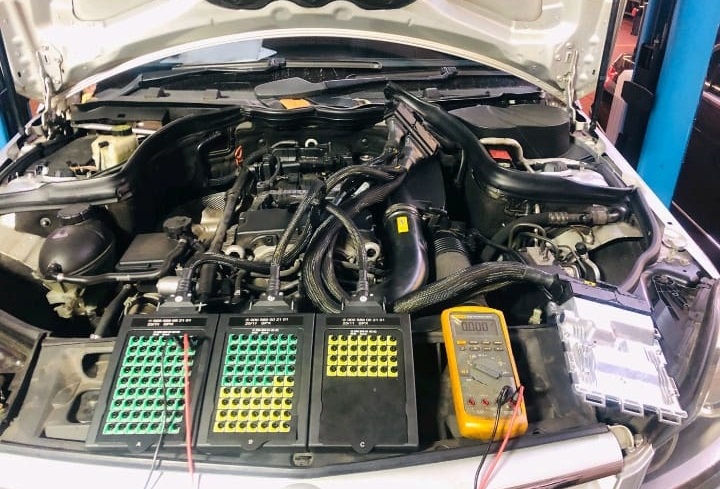

3. Electrical Supply & Continuity Checks
Before replacing the sensor, it’s vital to verify the supporting circuits.
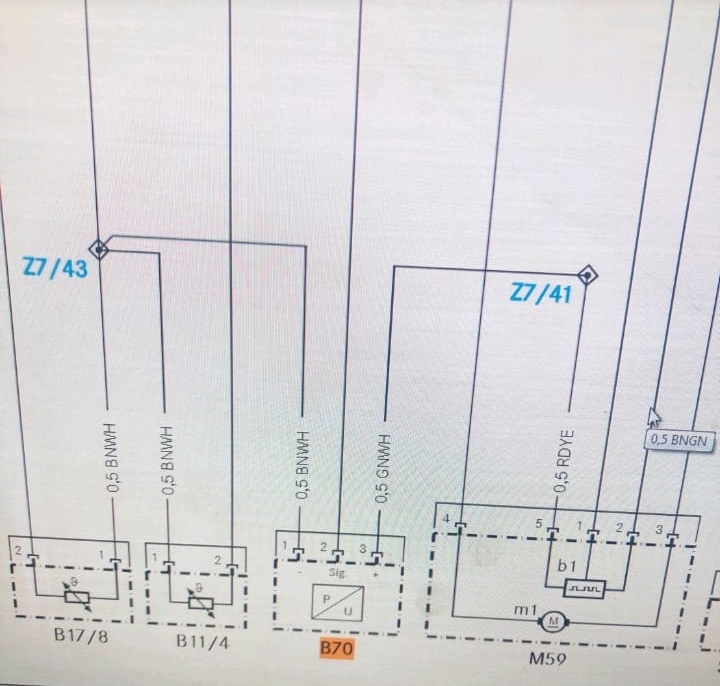
Power Supply Test:
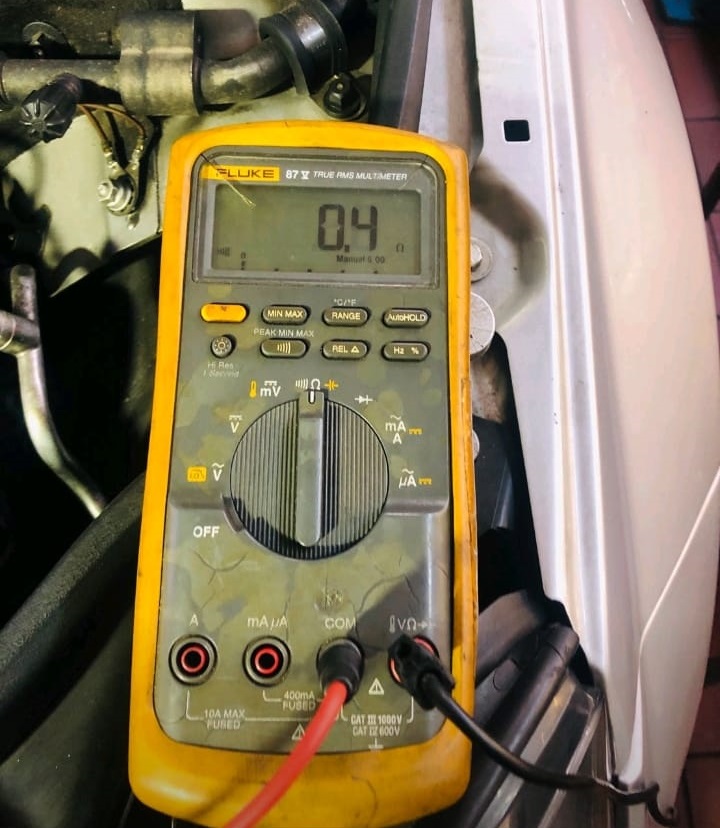
The crankshaft sensor’s supply voltage measured 5V within specification.
Signal Wire Continuity:
Checked with a multimeter; continuity was intact between the sensor and ECU pins.
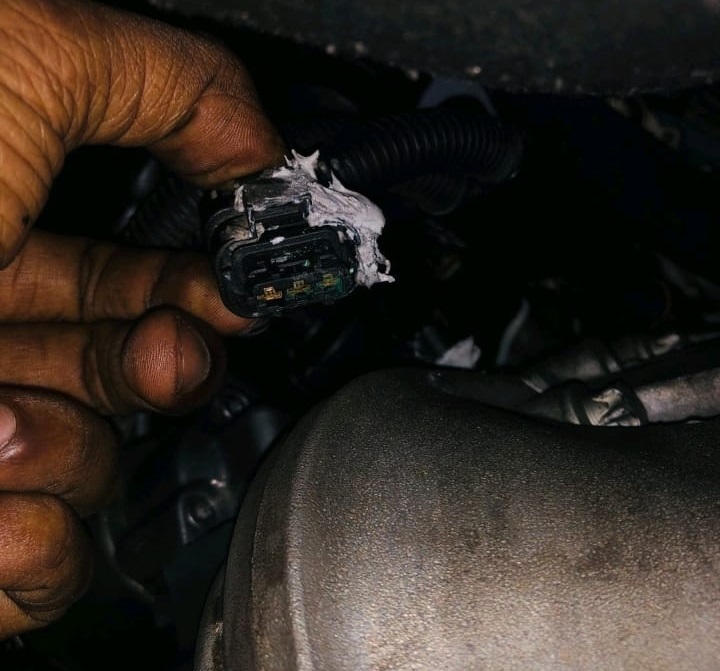
Wiring Socket Inspection:
Upon visual inspection, the sensor socket showed corrosion and poor pin locking. This minor but critical issue disrupted the electrical connection, leading to signal loss even though the sensor itself was fine.


4. Repair & Correction
The corroded sensor socket and pins were replaced with genuine Mercedes-Benz connectors, ensuring clean electrical contact and secure locking.
After reassembly:
- – The crankshaft sensor signal returned to normal.
- – The engine started immediately without hesitation or extended cranking.
- – All fault codes were cleared, and a final test drive confirmed proper operation.
This demonstrated how a small connector fault can cause a complete no-start condition, especially in vehicles where electronic systems are tightly integrated.

5. Root Cause Summary
| Symptom | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Long cranking, no start | Crankshaft sensor signal loss due to corroded connector | Replaced corroded socket and pins |
| ECU fault codes (P0336, P0373) | Signal irregularity from poor connection | Restored connection integrity |
| No RPM reading during crank | No signal to ECU | Confirmed after PicoScope test |
6. Position of the Crankshaft Sensor (M271 Engine)
The crankshaft position sensor on the Mercedes C300 W204 (M271) is located:
- – On the lower right side of the engine block, near the flywheel housing.
- – Typically accessible from underneath the vehicle near the transmission bell housing.
Proper lighting and a thin socket wrench are recommended for safe removal.
7. Common Symptoms of a Failing Crankshaft Sensor
| Symptom | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Engine won’t start | ECU receives no crank signal → ignition sequence blocked |
| Long or hard cranking | Weak or intermittent signal delays engine start |
| Rough idle or stalling | Loss of timing reference disrupts spark/fuel injection |
| Reduced power & poor throttle response | Incorrect timing data affects performance |
| Check engine light | ECU logs fault codes P0335–P0339 |
| Difficulty shifting (automatic) | TCU depends on RPM input from crank sensor |
If any of these occur, immediate inspection is recommended to prevent ECU synchronization loss or catalyst damage from misfiring.
8. Conclusion
This case study highlights that even simple faults like corrosion in a connector can mimic major engine failures.
Using a methodical diagnostic process with XENTRY and PicoScope, the issue was traced and resolved efficiently.
By understanding these steps, technicians and owners alike can avoid unnecessary part replacements and focus on accurate diagnosis.
Related Diagnostic Resource
If you’re facing similar starting problems, explore our full troubleshooting hub:
Mercedes No Start Issues: Causes, Fixes & Case Studies : a complete guide covering electrical, fuel, and ECU-related no-start scenarios across multiple Mercedes models.
9. Prevention Tips
- – Keep engine bay connectors clean and sealed.
- – Avoid washing near the transmission or sensor wiring area.
- – Use dielectric grease to protect sensor plugs.
- – Perform routine OBD scans to catch signal anomalies early.
FAQ
1. Can a faulty crankshaft sensor cause a no-start condition?
Yes. Without a valid signal, the ECU cannot synchronize spark and fuel injection, preventing ignition.
2. How can I tell if my Mercedes crankshaft sensor is bad?
Look for long cranking, no RPM reading, or diagnostic codes like P0336/P0339.
3. Is it safe to drive with a failing crankshaft sensor?
No. It can cause engine stalling and unpredictable loss of power.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: October 2025






Leave a Reply