Table of Contents
Gear Shifting Problem: Mercedes-Benz E300 W212 (722.9 7G-Tronic)
A Mercedes Benz E300 W212 equipped with the 722.9 (7G-Tronic) arrived with harsh/hesitant shifting under acceleration. An OE-level scan (XENTRY) showed multiple pressure-regulating valve electrical faults and two key DTCs: P2759 (TCC pressure valve electrical fault) and P2716 (Y3/8y4 K3 clutch control solenoid internal test failed).
Below is the full workflow we used to diagnose and fix the issue, written to be practical for owners and useful for technicians.
Quick snapshot
| Item | Detail |
|---|---|
| Vehicle | Mercedes Benz E300 W212 |
| Transmission | 722.9 7G-Tronic (VGS mechatronics Y3/8) |
| Complaint | Gear shifting problem during acceleration (harsh/late shifts) |
| Scan findings | PRV 1/2/3/5/6/7 electrical faults; P2759, P2716 |
| Root cause | Degraded/contaminated valve body & solenoids; VGS driver fault |
| Fix | Valve body removed, solenoids cleaned/checked, then VGS replaced & coded, ATF/filter renewed, adaptations performed |
| Result | Smooth shifts restored, no returning DTCs |
What the codes mean
| Code | Module | Description | Practical meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2716 | TCU/EGS | Internal electrical test failed for Y3/8y4 (K3 clutch control solenoid) | K3 solenoid or VGS driver fault; wiring/connectors to be ruled out |
| P2759 | TCU/EGS | Torque converter clutch (TCC) pressure-regulating valve – electrical fault | TCC pressure control can’t be modulated correctly |
| PRV 1/2/3/5/6/7 | TCU/EGS | Electrical faults across multiple pressure valves | Points to valve-body contamination or VGS internal driver problems (not just one bad solenoid) |
On many 722.9 units, speed/pressure control and drivers are integrated in the VGS mechatronics. When several PRVs flag “electrical,” suspect the controller/driver after verifying power/ground/wiring.
Diagnostic workflow (repeatable)
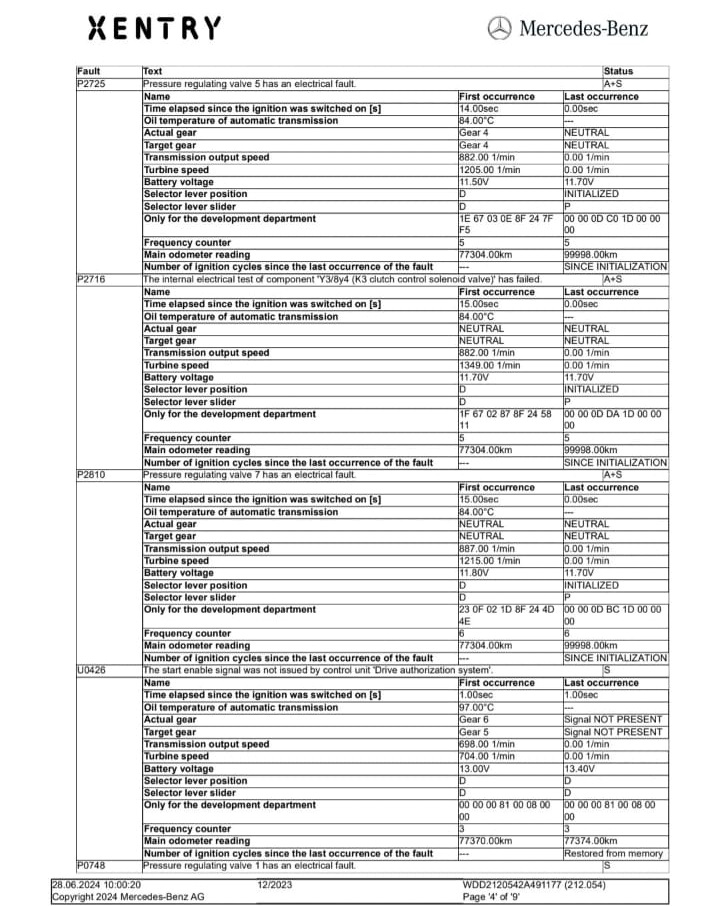
1. Global short test & freeze frames (XENTRY).
Confirmed P2716, P2759, and multiple PRV electrical DTCs as current (not just stored).
2. Prerequisites.
Stable system voltage (12.5–14.5 V); ATF temperature in spec for level checks.
3. Connector & wiring sanity.
Inspect the 13-pin connector for fluid wicking, bent pins, and corrosion; verify grounds and power feeds to the VGS.
4. ATF/pan inspection.
Drop the pan and filter; check the magnet and fluid for debris/varnish indicating overheating or contamination.
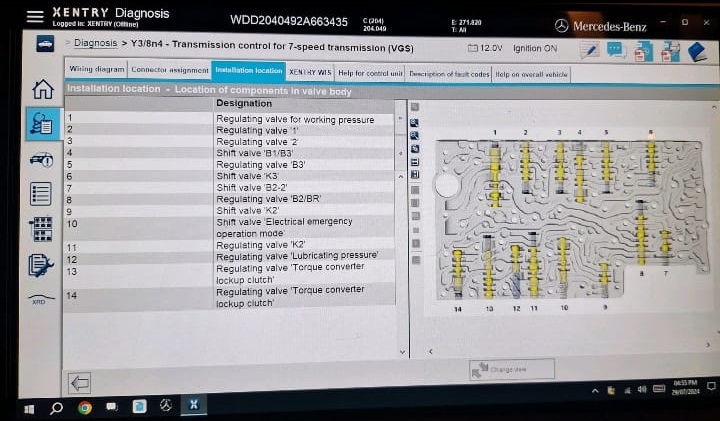
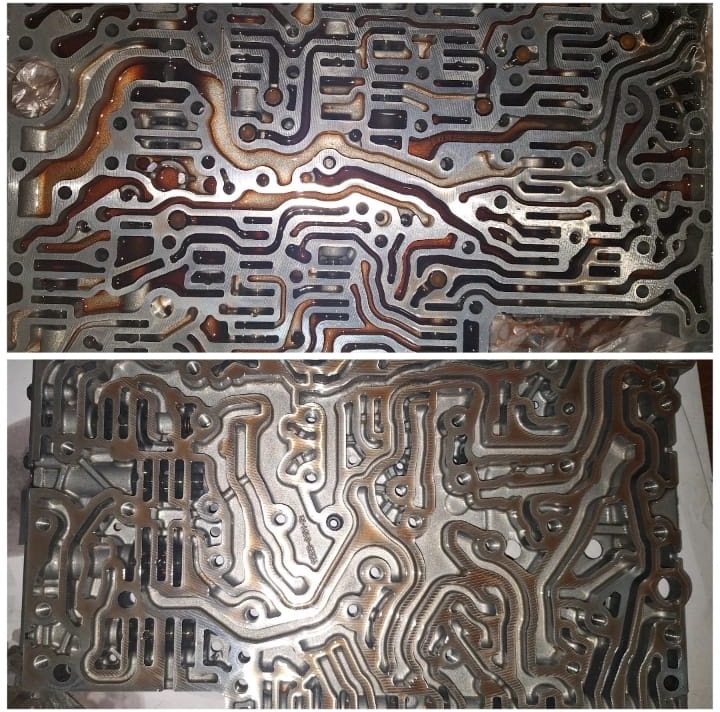
5. Valve-body assessment.
With multiple electrical PRV faults, remove valve body to:
- – Clean hydraulic passages with fresh ATF (per WIS).
- – Bench-check solenoids (actuation, response) and measure coil resistance (confirm spec in WIS for your variant).
6. Decision point.
Because DTCs persisted after cleaning and checks, diagnosis pointed to VGS internal driver failure → replace VGS/mechatronics.
7. Programming & adaptations.
Install new VGS, perform SCN coding/data restore, then complete standstill & running adaptations with all preconditions met.
8. Validation drive.
City + highway loop while logging turbine/internal/output speeds, clutch pressures, and TCC slip. Confirm no DTCs return.
Repair process (step-by-step)
1. Prepare & secure
- – Connect a battery maintainer.
- – Raise vehicle safely; protect under-trays.
2. Drain & remove pan
- – Drain ATF, remove pan and filter; inspect debris on magnet.
- – Note fluid condition (burnt smell = heat stress).
3. Remove valve body (mechatronics)
- – Follow WIS torque/sequence; avoid pin damage at the 13-pin connector.
- – Keep a clean work surface.
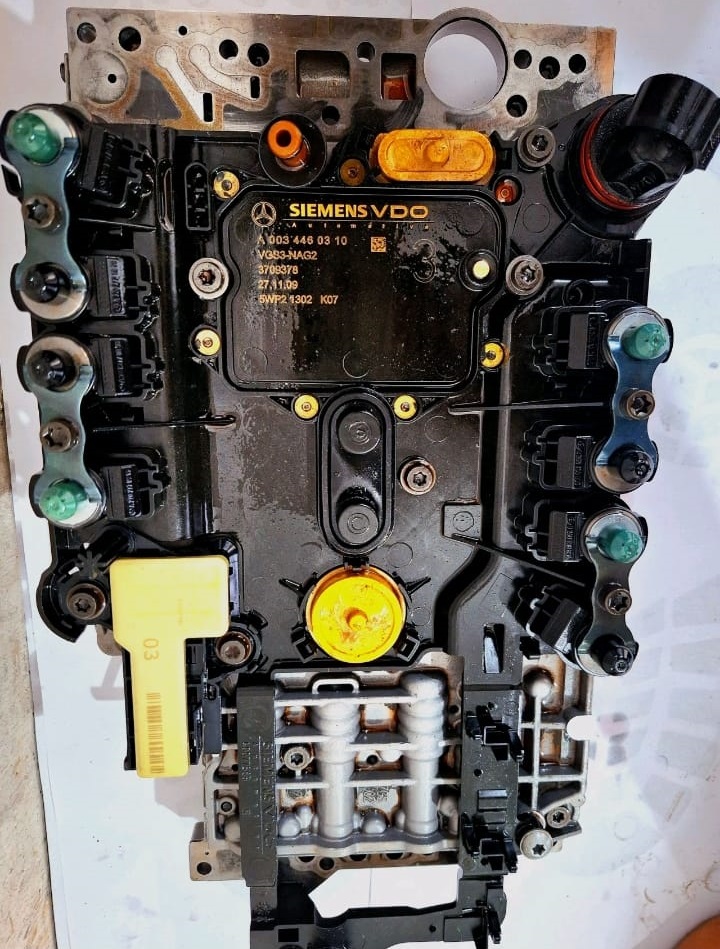
4. Clean & test solenoids
- – Flush passages with fresh, correct-spec ATF.
- – Check solenoid response/actuation; measure resistance (compare to WIS spec).
- – Refit if within spec.

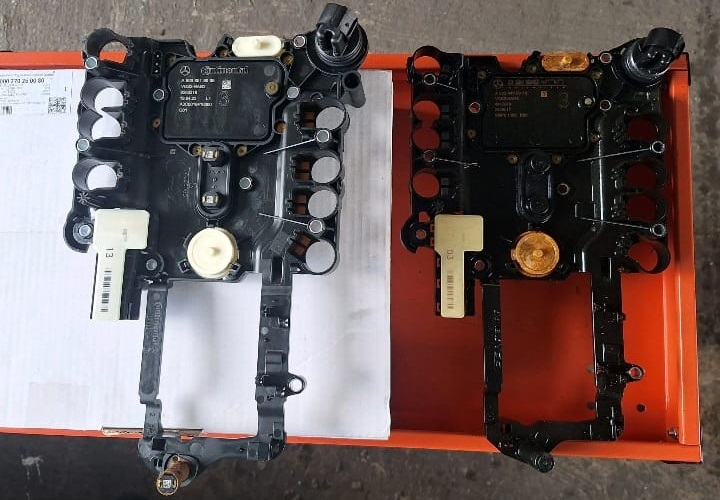
5. VGS replacement
- – Fit new VGS/mechatronics if electrical faults persist after cleaning.
- – Renew sealing sleeves/O-rings/bolts as specified.

6. Reassembly & fill
- – Install new filter and pan gasket.
- – Refill with MB-approved ATF; set level at temperature via WIS procedure.
7. SCN coding & adaptations
- – Code the VGS, then run standstill and running adaptations in XENTRY.
- – Ensure ATF temp is in range, tires at spec pressure, and no blocking DTCs.
8. Road test & QA
- – Multiple launch/shift events, gentle to moderate throttle.
- – Final scan: no current or stored DTCs; recheck for leaks after heat soak.
Outcome: Shift quality returned to normal; no further codes.
Symptom → cause → fix
| Symptom | Likely cause | Recommended fix |
|---|---|---|
| Harsh/late shifts under acceleration | Contaminated valve body; PRV modulation off | Clean valve body, verify solenoids; renew ATF/filter |
| Multiple PRV “electrical” codes | VGS driver fault or power/ground issue | Verify wiring/grounds → replace VGS if persistent |
| TCC shudder with P2759 | TCC pressure valve control fault; ATF breakdown | Valve-body service; ATF/filter; if needed VGS |
| P2716 (Y3/8y4) returns after cleaning | K3 solenoid or driver faulty | Replace VGS/mechatronics; re-adapt |
| Harshness after repair | Adaptations not completed; ATF level off | Re-run adaptations; confirm level/temp |
Explore More Mercedes Transmission Issues
For a deeper dive into gearbox problems slipping into Neutral, delayed/harsh shifts, “Not in P” warnings, and hybrid faults visit our hub: Mercedes Transmission Issues – Causes and Fixes. You’ll find grouped case studies, step-by-step diagnostics, symptom–cause–fix tables, and prevention tips to resolve shifting issues quickly and confidently.
Live-data checkpoints
| Parameter | Healthy behavior | Red flags |
|---|---|---|
| Turbine vs engine speed | Track proportionally at stall; smooth rise | Zero/erratic turbine speed under load |
| TCC slip | Near zero when locked; smooth ramps | High/unstable slip during steady cruise |
| Gear target vs actual | Small delay only | Frequent mismatch; forced downshifts |
| PRV currents | Stable, repeatable profiles | Dropouts/spikes (after wiring ruled out) |
Tools & prerequisites
| Category | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | XENTRY (or OE-level) for coding/adaptations & guided tests |
| Fluids | MB-approved ATF for 722.9; new filter, pan gasket, connector sleeve |
| Power | Battery maintainer; avoid low-voltage interruptions |
| Info | WIS/ASRA for procedures, torque, temperatures, and specs |
| Safety | Eye/hand protection; hot ATF handling; proper supports |
Time & cost (indicative)
| Operation | Typical time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis + logs | 1.0–1.5 h | Replicate complaint; capture freeze frames |
| Valve-body R&R + clean/test | 3.0–5.0 h | Varies by access/corrosion |
| VGS/mechatronics replace + SCN | 1.0–2.0 h | Coding/data restore required |
| ATF/filter service & level set | 0.8–1.2 h | Temp-based level procedure |
| Adaptations + validation drive | 0.5–1.0 h | Must meet all preconditions |
Total parts/labor varies by region and parts source.
Prevention & maintenance
- – ATF & filter at sensible intervals (many specialists target 60–80k km / 4–5 years), even if “lifetime.”
- – Keep battery/charging healthy; low voltage can corrupt adaptations and trigger false electrical DTCs.
- – Fix minor harshness/shudder early don’t wait for widespread PRV faults.
- – After battery replacement or module work, perform adaptations promptly.
- – Inspect the 13-pin connector sleeve for leaks at service visits.
About the Transmission Control Unit (VGS/TCU)
The VGS (Y3/8) is the 7G-Tronic’s electro-hydraulic brain. It:
- – Reads sensors (speeds, temperatures, pressures).
- – Commands solenoids/PRVs for clutch fill and overlap timing.
- – Stores adaptations to tailor shift feel to wear and driving style.
- – Communicates with engine, ABS/ESP, and cluster for coordinated torque management.
When the VGS driver circuitry degrades, multiple “electrical” PRV faults appear even if individual solenoids ohm-test fine exactly what we saw here.
FAQs: Gear Shifting Problem
1) Can a fluid change alone fix these faults?
If the issue is mild contamination, a service can help shift feel but electrical PRV codes that persist after cleaning typically require VGS replacement and coding.
2) Do I need adaptations after replacing VGS or servicing the valve body?
Yes. Run standstill and running adaptations with ATF at spec temperature and no blocking DTCs. Skipping this step leaves harshness.
3) What’s a normal solenoid resistance?
It varies by revision always check WIS for your VIN. Large deviations indicate coil issues; normal readings with electrical DTCs often point to the VGS driver.
4) Is it safe to keep driving with these codes?
Not recommended. Hard shifts and improper TCC control accelerate clutch wear and can raise repair costs.
5) Could engine/trans mounts cause the harshness?
Worn mounts amplify perceived jerk but won’t cause electrical PRV faults. Address hydraulics/VGS first, then assess mounts.
6) Why do many valves flag “electrical” at once?
Shared driver and power/ground paths in the VGS. Once wiring and power are verified, multiple PRV electrical codes usually indicate internal VGS failure.
Conclusion
In this E300 W212, the combination of P2716, P2759, and multi-PRV electrical faults traced to a contaminated valve body and a failing VGS driver. Cleaning the valve body, verifying solenoids, then replacing and coding the VGS, followed by ATF service and adaptations, restored factory-smooth shifts no more codes, no more harshness.
Author
Written by: Mercedes Expert
Automotive Technical Trainer & Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Specialist
With years of hands-on experience repairing and diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specializes in case-study-based troubleshooting guides that blend workshop accuracy with educational clarity.
Last Updated: September 2025






Leave a Reply