Table of Contents
Car Overheated: Case Study in a Mercedes-Benz S Class W222 with M278 Engine
When a customer arrives with a complaint about their Mercedes-Benz S Class W222 experiencing engine overheating, inoperative air conditioning, and an inability to crank in the morning, it requires a structured and meticulous diagnostic process. This article dives into the troubleshooting and resolution steps, guiding you on how to fix this issue effectively.
Understanding the Symptoms
- – Engine Overheat: The engine temperature rises beyond normal operating levels, which could lead to severe mechanical damage if not addressed promptly.
- – A/C Inoperative: A failing cooling system often impacts auxiliary systems like the air conditioning.
- – No Crank on Morning Start: This indicates potential electrical or mechanical issues related to the engine or battery.
Symptoms Overview Table
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Related Component |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Overheat | Cooling fan inoperative | Electric fan, wiring, LIN communication |
| A/C Inoperative | Cooling system safety shutdown | Cooling fan relay/wiring |
| No Crank in Morning | Electrical fault or battery weakness | Wiring harness, battery, starter |
Step-by-Step Diagnosis and Repair
1. Initial Diagnostics: Performed a Short Test
The first step in troubleshooting an overheated engine and inoperative A/C is a short test using a diagnostic tool. This reveals fault codes stored in the drivetrain or other control units. In this case, no initial fault codes were helpful for pinpointing the issue, necessitating further investigation.
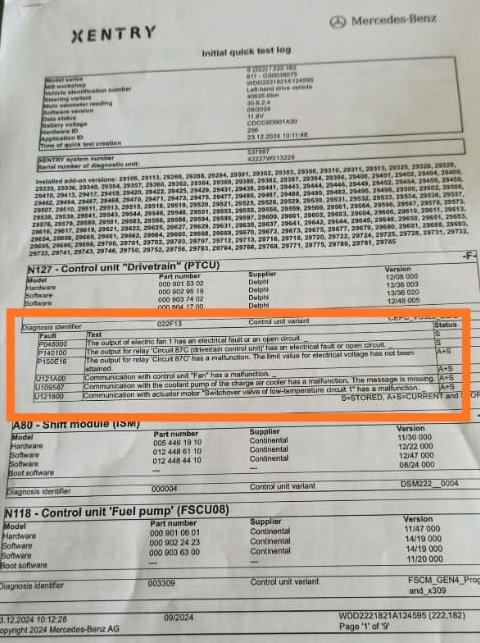
2. Electric Fan Function Check
The cooling fan plays a critical role in managing engine temperature:
- – Observation: The electric fan was non-functional.
- – Actuation Test: Testing the fan actuation revealed it was unresponsive.
| Observation | Result |
|---|---|
| Electric fan operation | Not working |
| Fan actuation test | Unresponsive |
3. Power Supply and LIN Communication Analysis
The cooling fan communicates with the drivetrain control unit using LIN (Local Interconnect Network) communication. A thorough inspection was necessary to identify any disruptions:
- – Power Supply Check: Voltage to the fan was measured and found adequate.
- – LIN Communication Check: There was no LIN signal between the drivetrain control unit and the fan.
| Check | Finding |
|---|---|
| Power supply voltage | Correct |
| LIN signal | Absent |
4. Inspect Wiring Harness
Electrical faults often trace back to damaged wiring. Referring to the wiring diagram, the following steps were taken:
- – Wiring Harness Inspection: Visual checks revealed cuts and damage to wires in the engine compartment fuse and relay area.
- – Cause of Damage: Rat activity had damaged the wiring harness, severing key connections required for fan operation and LIN communication.
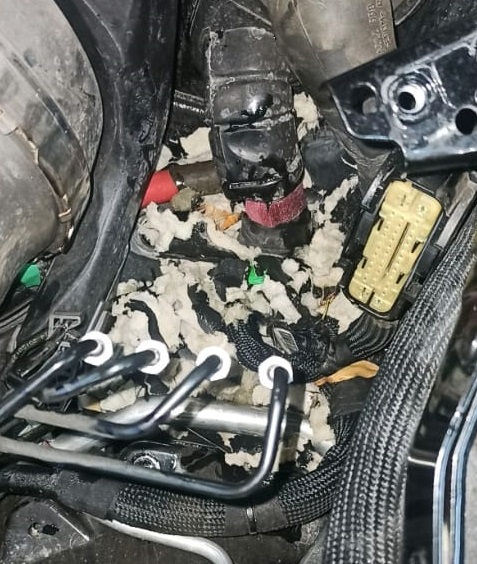
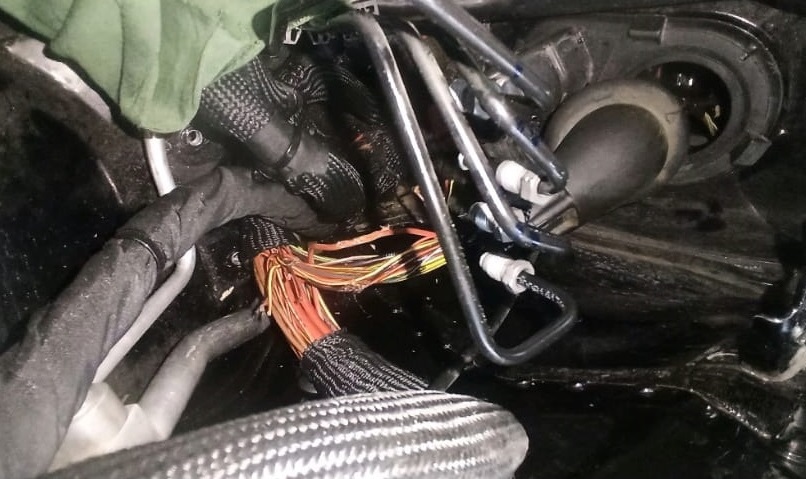


5. Repair and Reassembly
- – Wiring Repair: The damaged sections of the fuse and relay wiring harness were repaired and securely insulated.
- – Proper Fitting: The repaired harness was fitted back into the vehicle with added protection to prevent future damage.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Wiring repair | Replaced damaged sections, insulated with protective sheathing |
| Refitment | Secured harness with extra protection |
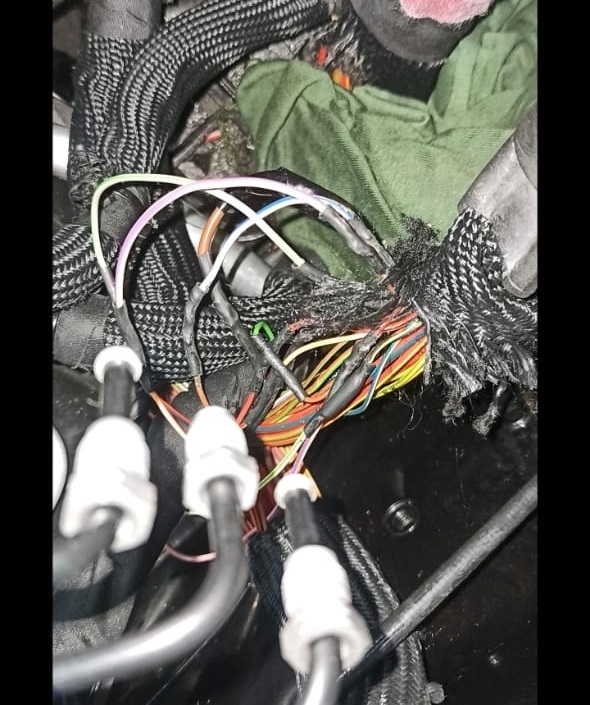

6. Post-Repair Validation
After completing the repairs, thorough checks were conducted:
- – Actuation Test: The fan functioned correctly during the test.
- – Test Drive: The vehicle was driven under various conditions to confirm:
- – No overheating.
- – A/C operating as expected.
- – Smooth engine start in subsequent morning tests.
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| Fan actuation test | Passed – fan worked correctly |
| Road test | No overheating, A/C restored, smooth morning start |
7. Final Diagnostic Checks
- – Fault Code Recheck: After repairs, the drivetrain control unit was scanned again. No fault codes were present.
- – Customer Assurance: The vehicle was returned to the customer in a safe, operational condition.
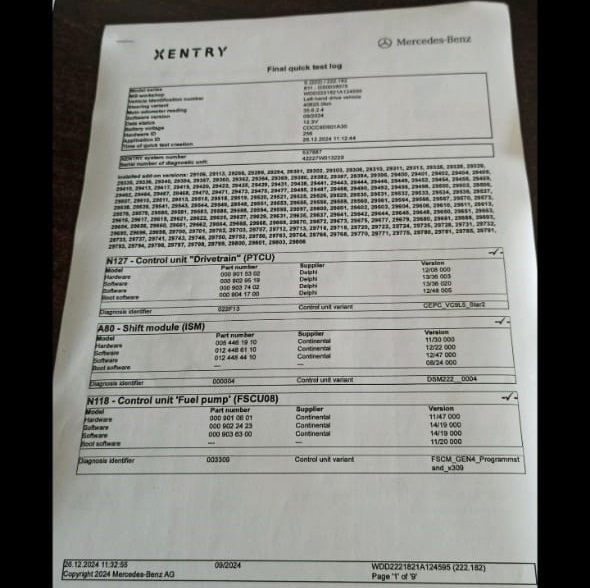
Key Takeaways
- 1. Proactive Diagnostics: Always start with a short test and systematically investigate potential fault areas.
- 2. Understand LIN Communication: Disruptions in the LIN system can cause cascading failures in fan and cooling functions.
- 3. Inspect for External Damage: Rodents often cause electrical issues, making wiring inspections crucial.
- 4. Reinforce Repairs: Ensure repaired sections are insulated and secure to prevent future problems.
Conclusion
Resolving a Car Overheated issue in a Mercedes-Benz S Class W222 requires a combination of diagnostic precision and methodical repairs. By addressing electrical failures caused by external factors like rats,
this case study highlights the importance of inspecting and securing critical wiring components. Following these steps ensures the vehicle can operate safely and smoothly, keeping your customer satisfied.
Why does my car not want to start in the morning?
Morning start issues can result from various factors, often aggravated by temperature changes or prolonged inactivity overnight. Below are the common causes, explanations, and potential solutions:
| Cause | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Weak battery | Dim lights, slow crank | Test voltage, replace if weak |
| Faulty starter motor | Clicking, no crank | Inspect motor, replace if faulty |
| Fuel system issues | Long cranking, sputtering | Check pump, filter, injectors |
| Ignition problems | Cranks but no start | Replace spark plugs/coils |
| Thick engine oil | Slow crank in cold | Use correct viscosity oil |
| Parasitic drain | Battery dead by morning | Test for current draw |
| Faulty ECT sensor | Hard cold starts | Replace ECT sensor |
| Moisture/condensation | Cold damp starting issues | Use fuel additive, dry wiring |
| Defective module/sensor | No ignition | Scan, replace faulty sensor/module |
FAQ – Car Overheated in Mercedes S Class W222
Q1: Why did my Mercedes S Class W222 overheat and A/C stop working?
A: Overheating in this model is often linked to a faulty cooling fan, wiring damage, or communication failure between the fan and control unit.
Q2: Can rodent damage cause my Mercedes not to start?
A: Yes. Rodents can chew wiring harnesses, interrupting power to critical components like the cooling fan, starter, or sensors.
Q3: Is LIN communication failure common in Mercedes cooling systems?
A: It’s not very common, but when it happens, it can cause complete fan shutdown and A/C disablement.
More Mercedes Cooling System Resources
Want to explore more causes, symptoms, and repair tips for coolant leaks, overheating, and contamination?
Learn more about Mercedes cooling system faults in our full Cooling System Guide.
Author
Mercedes Expert : Mercedes-Benz Specialist with over 12 years of hands-on experience in diagnostics and repair.
Last Updated: August 2025






Leave a Reply