Table of Contents
Problem with Power Steering in Mercedes; Full Diagnostic & Repair Case Study (C350e)
When your Mercedes displays “Problem with Power Steering”, it means the Electric Power Steering (EPS) system has either lost voltage supply or communication with the control unit. This can cause heavier steering effort, especially at low speeds, and may activate multiple warning lights such as ESP or Assist Inoperative.
This guide explains a real-life case study of a Mercedes-Benz C350e (W205) equipped with the M274 engine, where the customer experienced intermittent power steering failure.
We’ll walk through the diagnostic process, repair actions, and preventive tips to avoid future issues.
For a complete guide on diagnosing and repairing Mercedes electrical faults, including EPS, SAM, and CAN Bus communication errors; see our master resource:
Mercedes Electrical Problems: Fix SAM, ECU & CAN Bus Faults
Understanding the Mercedes Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Unlike older hydraulic systems, modern Mercedes models (like the C-Class W205, E-Class W213, and GLC X253) use Electric Power Steering (EPS).
It replaces the hydraulic pump with an electric motor integrated into the steering rack, controlled via the CAN Bus.
Core Components:
- – EPS Control Unit & Motor (N68/1): Provides steering assist based on driver torque and vehicle speed.
- – Power Supply (125 A pre-fuse): Feeds high current to the EPS module.
- – CAN Bus Network: Communicates between the steering rack, ESP, and front SAM.
- – Torque & Angle Sensors: Determine steering input and system response.
When voltage supply or CAN communication fails, EPS enters a protection mode disabling assist and displaying “Problem with Power Steering.”
Case Study: Mercedes C350e, Steering Stiffness & Warning Light
Customer Complaint
The owner reported:
- – Heavy steering, especially at low speeds.
- – Intermittent “Problem with Power Steering” warning on the instrument cluster.
- – Occasional electronic noise near the steering column.
The problem worsened progressively until steering assistance was lost entirely at idle speeds.
Initial Inspection
Visual inspection revealed:
- – Oil residue around the steering rack area.
- – Traces of engine oil contamination on the EPS wiring connector.
- – No mechanical binding or abnormal play in the suspension.
This indicated a possible electrical short caused by fluid ingress.
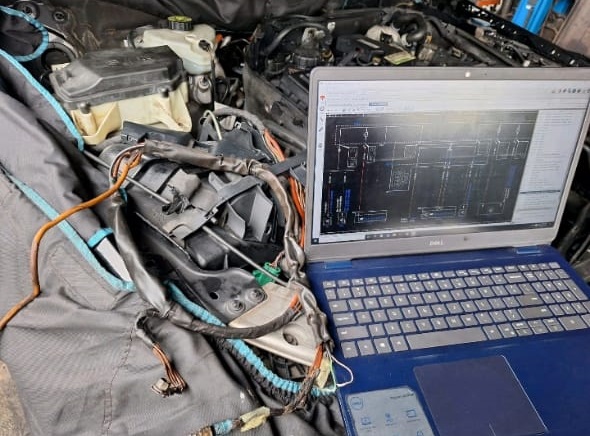
Diagnostic Procedure (XENTRY & Multimeter Tests)
Step 1: Fault Code Reading
Using Mercedes XENTRY, the following fault was logged:
C15AD29 – Electric Steering: Internal Electrical Fault (Short Circuit to Ground).
Step 2: Voltage & Ground Checks
| Test Point | Expected Value | Measured | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPS Power Feed | 12.6 V (engine off) | 12.6 V | OK |
| Ground Resistance | < 0.1 Ω | 0.05 Ω | OK |
| Signal Wire (CAN) | 2.5 V average | Fluctuating / noisy | Fault present |
Interpretation:
The EPS module was receiving voltage but communication lines were unstable indicating potential contamination or short at the connector level.

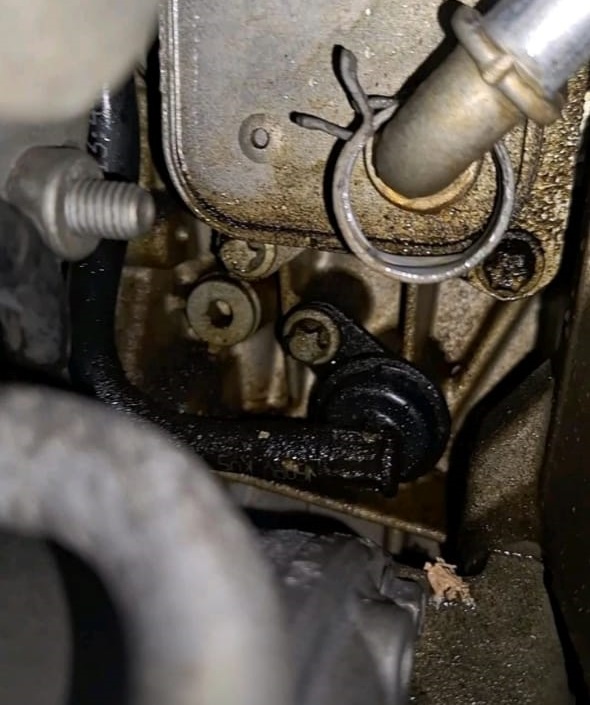
Root Cause: Oil Contamination from Breather Hose
Further inspection showed the engine crankcase breather hose had leaked oil onto the steering rack’s electrical connector.
Over time, the oil migrated into the wiring harness, creating a short circuit inside the EPS module.
This not only affected power steering assist but also caused intermittent CAN Bus interference, leading to random electrical warnings across other systems.
This case demonstrates how power steering faults often overlap with broader electrical issues. Many EPS errors originate from network disruptions rather than mechanical defects a common pattern explored in detail in Mercedes Electrical Problems: Fix SAM, ECU & CAN Bus Faults.

Secondary Issue; Coolant Leak at Thermostat Valve
While inspecting the steering rack, a coolant leak was observed near the thermostat housing.
This secondary fault posed a risk of coolant loss and possible temperature irregularities, so it was addressed during the same repair session.
Repair Procedure
Step 1: Replace the Faulty Steering Rack
- – Removed the EPS rack assembly.
- – Replaced it with a new OEM steering rack.
- – Cleaned all mounting areas and electrical connectors of residual oil.
- – Verified torque specs for mounting bolts and steering shaft alignment.

Step 2: Fix the Oil Leak (Breather Hose)
- – Replaced the crankcase breather hose with the updated version.
- – Cleaned surrounding areas to prevent oil migration.
- – Installed improved seals to minimize future leakage.
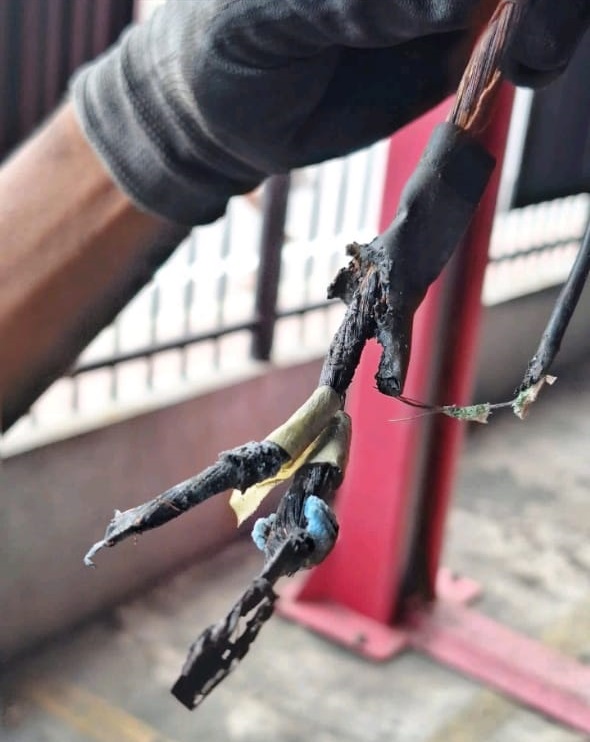
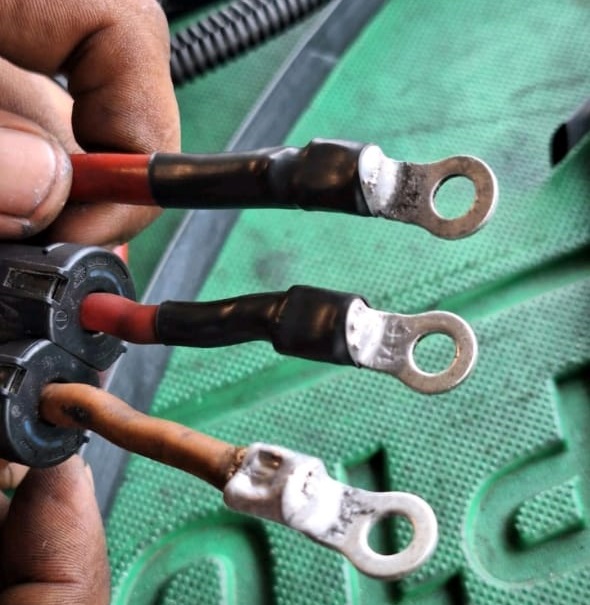
Step 3: Repair the Wiring Harness
- – Opened EPS connector and de-pinned corroded terminals.
- – Replaced damaged wires and applied heat-shrink insulation.
- – Tested for continuity and resistance stability.
- – Secured harness away from potential contamination sources.


Step 4: Replace the Thermostat Valve
- – Removed faulty thermostat assembly and cleaned mating surface.
- – Installed new gasket and valve unit.
- – Refilled and bled the cooling system using Mercedes-approved coolant (MB 325.0 spec).
Step 5: Final System Calibration & Test
- – Cleared all fault codes using XENTRY Diagnostics.
- – Recalibrated steering angle sensor and verified torque sensor response.
- – Conducted full function test:
- => EPS response at idle
- => Dynamic steering feedback
- => CAN Bus stability readings
Result:
All systems operational.
No residual fault codes.
Steering assistance fully restored with smooth, consistent feedback.
Validation Results
| Test Item | Before Repair | After Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Effort | Heavy, inconsistent | Smooth & responsive |
| EPS Fault Light | Active | Cleared |
| CAN Bus Voltage Stability | Fluctuating | 2.45–2.55 V steady |
| Oil Leaks | Present | None |
| Coolant Leaks | Present | None |
Root Cause Summary
| Fault Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Cause | Oil leak from crankcase breather hose contaminating EPS electrical connector |
| Secondary Fault | Coolant leak at thermostat valve |
| System Impact | Short circuit inside steering rack; CAN communication disturbance |
| Resolution | Replaced steering rack, breather hose, thermostat; repaired harness |
Technician Insights
- – EPS modules are extremely sensitive to oil and coolant contamination even small leaks can induce electrical shorts.
- – Always verify CAN communication stability before replacing the rack; EPS faults can sometimes originate from upstream SAM or ground points.
- – Cleanliness is key: apply dielectric grease after connector cleaning to prevent corrosion.
- – In hybrid models like the C350e, 12 V supply fluctuations can also trigger EPS faults confirm voltage integrity under load.
Preventive Maintenance
| Action | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect breather hoses | Every 20,000 km | Prevent oil seepage onto electricals |
| Check coolant system | Every 2 years | Detect thermostat leaks early |
| Scan EPS module | At service intervals | Identify intermittent voltage drops |
| Clean connectors | As needed | Ensure corrosion-free contacts |
Related Diagnostic Resource
For deeper analysis of electrical communication faults, SAM power loss, and CAN Bus voltage errors, explore:
Mercedes Electrical Problems: Fix SAM, ECU & CAN Bus Faults
A comprehensive troubleshooting hub covering module failures, short circuits, and communication dropouts in modern Mercedes electrical systems.
Conclusion
This Mercedes-Benz C350e Power Steering Problem case highlights how electrical contamination can disable EPS systems and even affect other vehicle functions.
Through step-by-step diagnostics visual inspection, voltage testing, connector repair, and steering rack replacement the workshop successfully restored safe, reliable steering performance.
The lesson is clear: many “power steering” issues in modern Mercedes vehicles are electrical in nature, and a structured approach using XENTRY diagnostics and careful inspection can prevent unnecessary parts replacement.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: November 2025





Leave a Reply