Table of Contents
Reasons for Engine Misfire: Case Study of Mercedes-Benz E Class
Engine misfire is a common yet concerning issue for many Mercedes-Benz owners. A misfire happens when one or more cylinders in the engine fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture correctly. This can lead to rough idling, reduced performance, higher fuel consumption, and even long-term engine damage if ignored.
In this article, we’ll explore the reasons for engine misfire through a real-world case study of a Mercedes-Benz E Class W213 equipped with the M264 engine. By following the diagnostic steps, identifying the root cause, and applying the correct fix, this case shows how systematic troubleshooting can restore the engine to full health.
Case Study Overview
A customer brought their Mercedes-Benz E Class W213 into the workshop with the following complaints:
- – The engine light was illuminated.
- – The vehicle exhibited misfiring symptoms such as rough idle and hesitation.
After thorough testing, we were able to diagnose and fix the problem.

Step-by-Step Diagnostic and Repair Process
1. Performing a Quick Test and Analyzing Fault Codes
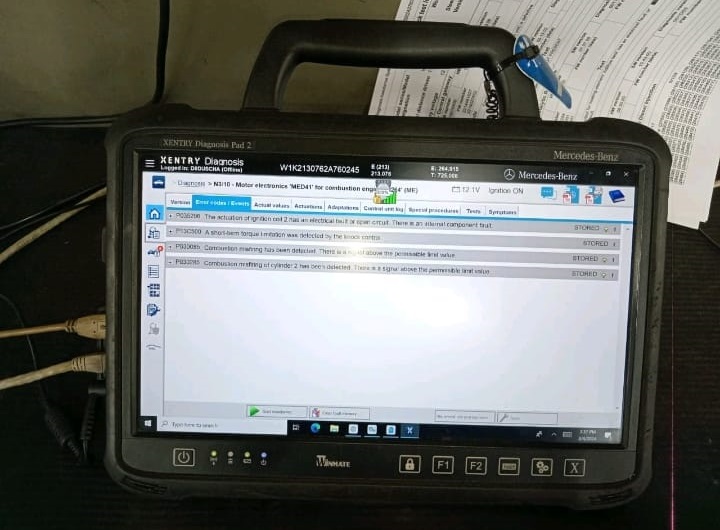
The first step was to connect the car to the Xentry diagnostic tool and run a quick test.
- – Findings: The ME (Motor Electronics) control unit logged fault codes pointing to a malfunction in the second ignition coil.
- – Conclusion: Ignition system issues are one of the most common reasons for engine misfire.
2. Visual Inspection of Wiring and Connections
Next, a visual inspection was performed on the wiring harness and connectors leading to the ignition coils.
- – Findings: No signs of fraying, corrosion, or loose connections were observed.
- – Conclusion: Wiring problems were ruled out as the cause.

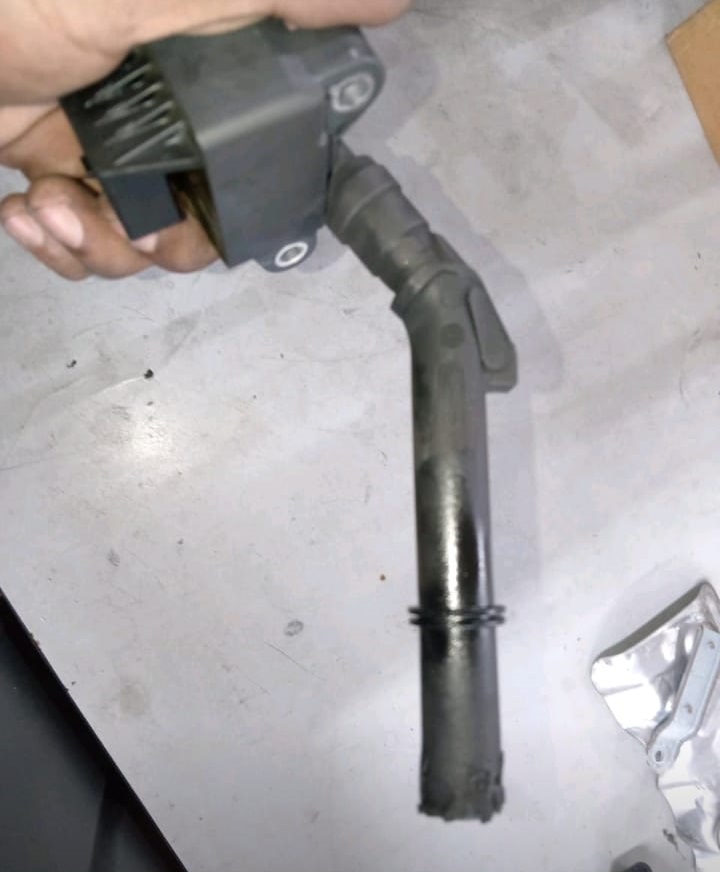
3. Removing and Examining the Ignition Coils
The ignition coils were removed for a closer inspection.
- – Findings: The second ignition coil showed physical damage.
- – Conclusion: This confirmed the root cause of the misfire an ignition coil failure.
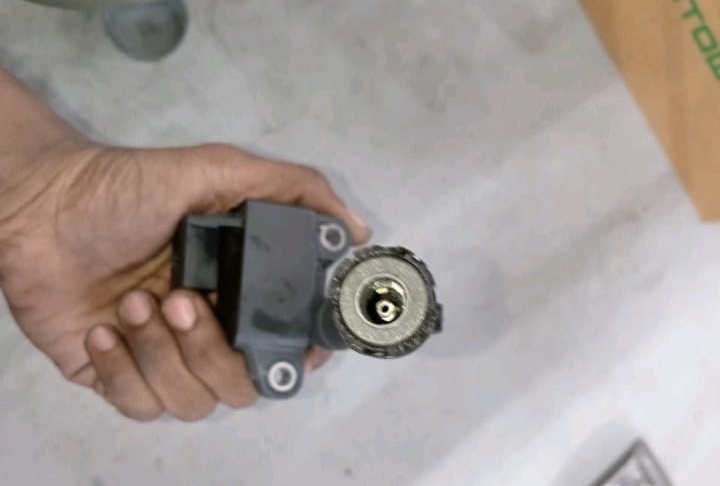


4. Replacing the Damaged Ignition Coil
The faulty coil was replaced with a new, genuine Mercedes-Benz ignition coil.
- – Action: Installed the new ignition coil, reassembled components, and cleared fault codes.
- – Result: The misfire disappeared, the engine ran smoothly, and the check engine light turned off.
Post-Repair Results
- – Engine started smoothly with no shaking.
- – No misfire fault codes were logged in the ME control unit.
- – Test drive confirmed smooth acceleration and idle.
The issue was successfully resolved by replacing the damaged ignition coil.
Explore More Mercedes Engine Misfire Issues
For a deeper dive into all misfire-related problems, visit our hub page: Mercedes Engine Misfire Issues – Causes and Fixes. You’ll find grouped case studies, step-by-step diagnostics, symptom–cause–fix tables, and prevention tips to help you resolve misfire problems quickly and effectively.
Key Takeaways
Common Reasons for Engine Misfire in Mercedes
- – Faulty Ignition Coil: Damaged coils fail to deliver voltage to spark plugs, causing misfires.
- – Spark Plug Issues: Worn, fouled, or incorrectly gapped spark plugs disrupt ignition.
- – Fuel System Problems: Blocked injectors or low fuel pressure prevent proper combustion.
- – Vacuum Leaks: Intake leaks lead to an incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- – Wiring or Connector Faults: Broken or loose connections disrupt the ignition system.
- – Mechanical Problems: Low compression due to valve, piston, or head gasket issues.
Symptom – Cause – Fix Table
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Recommended Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Rough idle and check engine light | Faulty ignition coil | Replace damaged ignition coil |
| Intermittent misfire on one cylinder | Spark plug wear or fouling | Replace spark plug, check gap |
| Misfire across multiple cylinders | Fuel injector clog or low pressure | Clean injectors, test fuel pump |
| Misfire at idle only | Vacuum leak | Inspect intake hoses and seals |
| Engine hesitation when accelerating | Weak ignition coil or injector imbalance | Replace coil, clean/replace injectors |
| Persistent misfire after replacing ignition components | Low compression | Perform compression/leak-down test and repair mechanical issues |
Preventative Tips
To avoid misfire issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- – Replace spark plugs at recommended intervals (usually 60,000–100,000 km).
- – Inspect ignition coils during every major service.
- – Use high-quality fuel to prevent carbon buildup in injectors.
- – Check wiring harnesses for signs of wear or corrosion.
- – Address warning lights immediately to prevent small faults from escalating.
- – Schedule regular diagnostic scans to catch early misfire patterns.
FAQs on Mercedes Engine Misfire
Q1: What does an engine misfire feel like in a Mercedes?
A misfire feels like shaking, hesitation, or vibration, especially noticeable at idle or during acceleration.
Q2: Can I drive my Mercedes with a misfire?
It’s not advisable. Driving with a misfire can cause catalytic converter damage and reduce overall engine life.
Q3: What is the most common cause of misfire in the Mercedes E Class W213?
The most frequent causes are ignition coil failures and spark plug wear.
Q4: How much does it cost to fix an ignition coil misfire?
Replacing one ignition coil typically costs between €200–€400, depending on labor and part quality.
Q5: Can misfires cause long-term engine damage?
Yes. Prolonged misfires can lead to catalytic converter failure, piston damage, and increased fuel consumption.
Author
Written by: Mercedes Expert
Automotive Technical Trainer & Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Specialist
With years of hands-on experience repairing and diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specializes in case-study-based troubleshooting guides that blend workshop accuracy with educational clarity.
Last Updated: September 2025
— Salim, Mercedes Expert
Independent specialist in Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, CAN Bus analysis, troubleshooting case studies, and EV systems.







Leave a Reply