Case Study: Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction in a Mercedes-Benz G Class W463
The Mercedes-Benz G Class 463 AMG is renowned for its off-road capabilities, and the differential lock system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance in challenging terrains. However, when the Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction warning message appears on the dashboard, it can be alarming.
This article delves into a real-life case study where this exact issue was diagnosed and resolved, providing valuable insights for G Class owners and automotive enthusiasts.
Vehicle Profile
- Model: Mercedes-Benz G Class 463 AMG
- Complaint: Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction warning message on the dashboard.
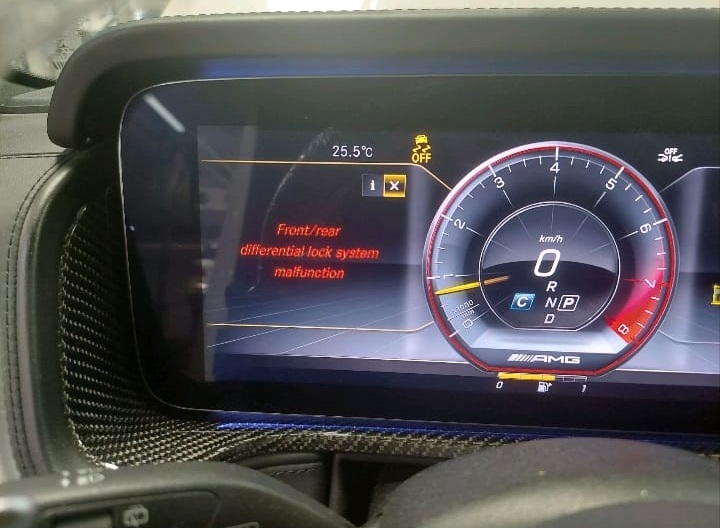
Initial Inspection
A Mercedes-Benz G Class W463 AMG was brought into the workshop with the Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction warning message prominently displayed on the dashboard. This message indicates a potential issue with the differential lock system, which could compromise the vehicle’s off-road performance.
Diagnostic Process
To accurately diagnose the problem, the first step involved connecting the Xentry diagnosis tool to the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. This advanced tool is essential for pinpointing the exact fault codes and understanding the underlying issue.
Fault Codes Identified:
- U11048F – Communication with output stage “Differential lock on rear axle” has a malfunction. The signal or message is erratic.
- U110A87 – Communication with output stage “Differential lock on front axle” has a malfunction. The message is missing.
- U110487 – Communication with output stage “Differential lock on rear axle” has a malfunction. The message is missing.
- U110A8F – Communication with output stage “Differential lock on front axle” has a malfunction. The signal or message is erratic.
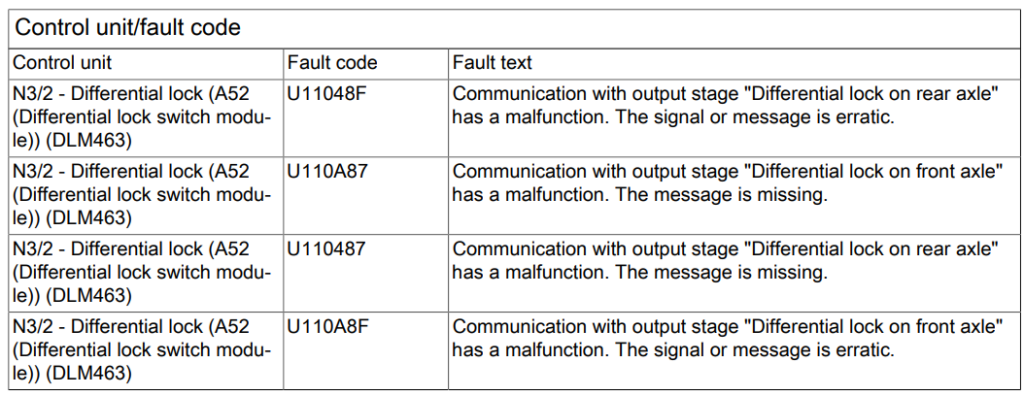
These codes indicated a malfunction in the communication with the differential lock’s output stages, both on the front and rear axles.
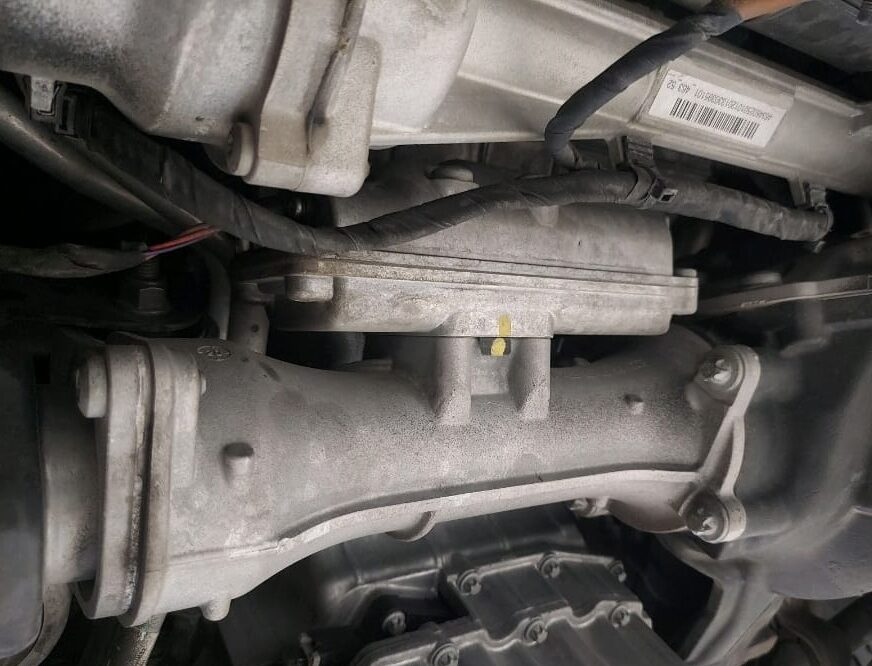

In-Depth Analysis
After identifying the fault codes, the next step was to check the actual values for the components related to the differential lock system. This included:
- Voltage Check: Ensuring that the voltage levels were within the normal range.
- Inspection of Electrical Lines and Connectors: Checking for any visible damage, wear, or corrosion that could affect the system’s performance.
The voltage readings were normal, and no physical damage was found in the electrical lines or connectors. This ruled out any obvious electrical issues and suggested that the problem might be with the differential actuators themselves.
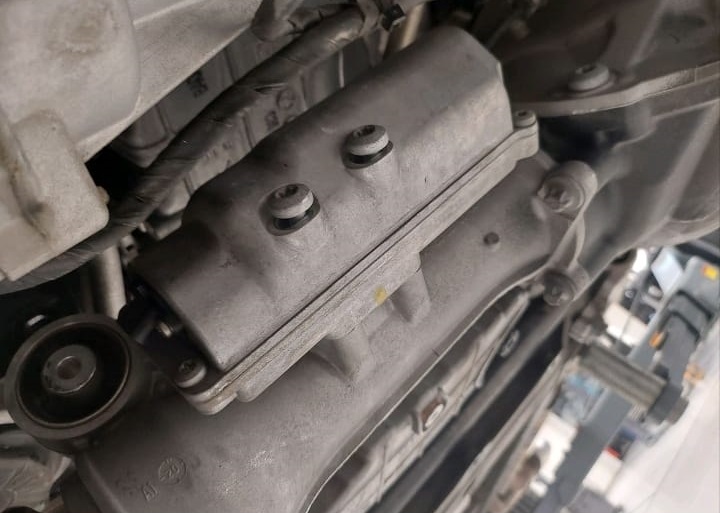

Resolution
Following the diagnosis, it was determined that the front differential actuator was malfunctioning. As per the diagnostic steps, the front differential actuator was replaced. After the replacement, the vehicle was tested to confirm that the Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction warning message had been resolved.
The replacement of the front differential actuator successfully rectified the issue, and the differential lock system was fully functional once again.
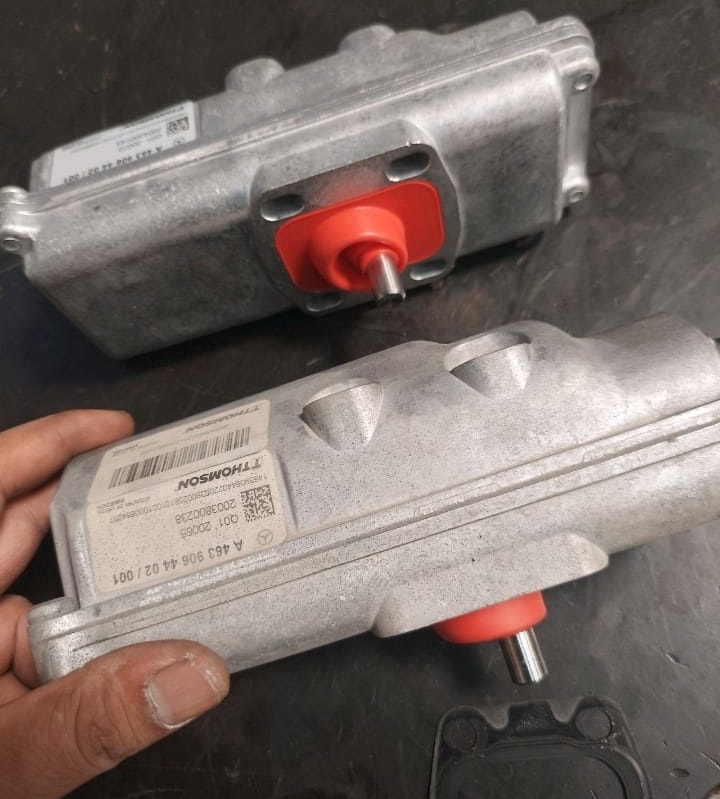
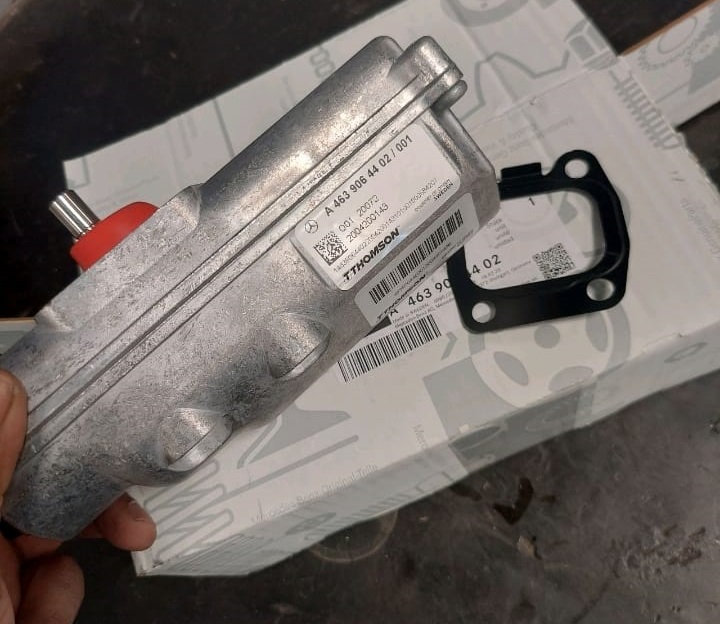


Conclusion
This case study highlights the importance of a thorough diagnostic process when dealing with complex systems like the differential lock in the Mercedes-Benz G Class 463 AMG. The Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction warning can stem from communication errors between the output stages and the differential lock actuators. By methodically diagnosing the issue and replacing the faulty component, the problem was effectively resolved.
For Mercedes-Benz G Class owners, understanding the potential causes and solutions for the Front Rear Differential Lock System Malfunction can help in maintaining the vehicle’s off-road prowess and ensure a swift resolution if this issue arises.
What is a differential lock
A differential lock is a feature in some vehicles, particularly in off-road and performance vehicles, that locks the differential to ensure both wheels on the same axle rotate at the same speed, regardless of the traction available to each wheel.
how does a differential lock work:
- Standard Differential: In normal driving conditions, a differential allows wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds. This is crucial when turning, as the wheel on the outside of the turn needs to travel a greater distance than the wheel on the inside. The differential facilitates this by allowing the outside wheel to rotate faster than the inside wheel.
Differential Lock Function:
- Engaging the Lock: When a differential lock is engaged, it overrides the differential’s ability to allow different wheel speeds. This means both wheels on the axle are forced to rotate at the same speed.
- Use Case: This is particularly useful in off-road situations or when driving on slippery surfaces, where one wheel might lose traction. If a wheel loses traction in a standard differential setup, it would spin freely while the other wheel remains stationary. Engaging the differential lock prevents this, ensuring power is distributed evenly to both wheels, helping the vehicle maintain momentum.
Types of Differential Locks:
- Manual Differential Lock: Typically found in off-road vehicles, this type allows the driver to engage the lock manually via a switch or lever.
- Automatic Differential Lock: Some systems automatically engage the differential lock when a loss of traction is detected.
- Limited-Slip Differential (LSD): While not a full lock, LSD limits the difference in speed between the two wheels, providing a compromise between a fully locked differential and a standard open differential.
Applications:
- Off-Road Driving: Ensures both wheels can continue to drive the vehicle forward, even if one wheel is in mud, sand, or other low-traction conditions.
- Performance Vehicles: Used to improve traction during high-speed driving, particularly in situations where maximum grip is required.
In essence, a differential lock is a vital feature for enhancing a vehicle’s capability in challenging driving conditions, ensuring that power is consistently delivered to the wheels, improving traction and control.
Rear differential locker
A rear differential locker is a specific type of differential lock that engages the differential on the rear axle of a vehicle. It ensures that both rear wheels turn at the same speed, providing enhanced traction in challenging driving conditions.
How a Rear Differential Locker Works:
- Standard Rear Differential: Normally, a vehicle’s rear differential allows the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds. This is necessary when turning, as the outside wheel needs to travel a longer distance than the inside wheel.
- Engaging the Rear Differential Locker: When the rear differential locker is engaged, it locks the differential, forcing both rear wheels to turn at the same speed, regardless of the traction each wheel has. This is crucial in situations where one wheel might lose traction, such as on slippery or uneven surfaces.
Use Cases:
- Off-Road Driving: Rear differential lockers are especially beneficial in off-road situations, such as when traversing rocky terrain, deep mud, or loose sand. If one of the rear wheels loses contact with the ground or encounters a slippery surface, the locker ensures that the wheel with better traction continues to receive power, allowing the vehicle to move forward.
- Towing and Hauling: For vehicles used in towing or carrying heavy loads, a rear differential locker can help maintain control and traction, particularly on steep or slippery inclines.
Types of Rear Differential Lockers:
- Manual Lockers: These require the driver to manually engage the locker, typically via a switch or lever inside the vehicle. This allows the driver to control when the locker is activated, usually in situations where extra traction is needed.
- Automatic Lockers: These engage automatically when the system detects a loss of traction. They provide convenience by not requiring driver intervention but may engage when not always desired.
- Selectable Lockers: These combine manual and automatic functions, allowing the driver to choose between automatic engagement or manual control.
Advantages of a Rear Differential Locker:
- Enhanced Traction: Ensures that power is evenly distributed to both rear wheels, preventing one wheel from spinning uselessly while the other remains stationary.
- Improved Off-Road Capability: Crucial for overcoming obstacles and maintaining momentum in tough off-road conditions.
- Increased Stability: Helps maintain vehicle stability by preventing one rear wheel from spinning faster than the other.
Disadvantages:
- Tight Turns: Engaging a rear differential locker can make tight turns more difficult, as both wheels are forced to rotate at the same speed, which can cause understeer.
- Increased Wear: Using a locker on high-traction surfaces can increase tire wear and place extra stress on the drivetrain.
Applications:
- Off-Road Vehicles: Commonly found in 4×4 vehicles and trucks designed for off-road use.
- Performance Cars: Some performance cars use rear differential lockers to improve traction during aggressive driving, particularly in racing or high-speed cornering scenarios.
- Towing and Heavy-Duty Vehicles: Often equipped with rear differential lockers to ensure stability and control when towing or carrying heavy loads.
In summary, a rear differential locker is a valuable feature for enhancing a vehicle’s traction and control, particularly in off-road or high-load scenarios, making it an essential tool for drivers who need reliable performance in challenging conditions.





Hello , first of all thank you for this informative post. I have similar malfunctions on my 2021 g350d amg line. I ordered 463900474 and 4639064402 (they dont have this one , they say we have 463964602 they are same) we are waiting this parts. I have 2 questions for you if you will help me ı pleasure. When i start my car firstly i see similar malfunction front rear differantial and also i see abs esp distronic and parktronic malfunctions did you have similar warnings ? If the remaining electronic system failures are not related to the differential, what could they be related to? All failures occurred at the same time. Is there anything you can suggest? Thank you.
Hi Sir, according to these warnings, the common point between them is the electronic stability program (ESP®) module, you need to check the error code in this module