Table of Contents
Car Is Not Starting: Mercedes-Benz G-Class W463 Case Study and Fix
When a Mercedes-Benz G-Class won’t start, it can be alarming especially in a vehicle celebrated for reliability and durability. Whether due to electrical faults, sensor failures, or throttle system issues, the cause can be complex.
In this article, we explore a real-world case study involving a Mercedes-Benz G 500 W463 that refused to start after sitting idle for weeks. You’ll see how a systematic diagnostic process uncovered the root cause and how the repair brought this iconic SUV back to life.
Vehicle Overview
| Model | Mercedes-Benz G-Class W463 |
|---|---|
| Engine | V8 Gasoline |
| Complaint | Car is not starting after extended parking |
| Symptoms | Engine starts briefly, then cuts off no throttle response |
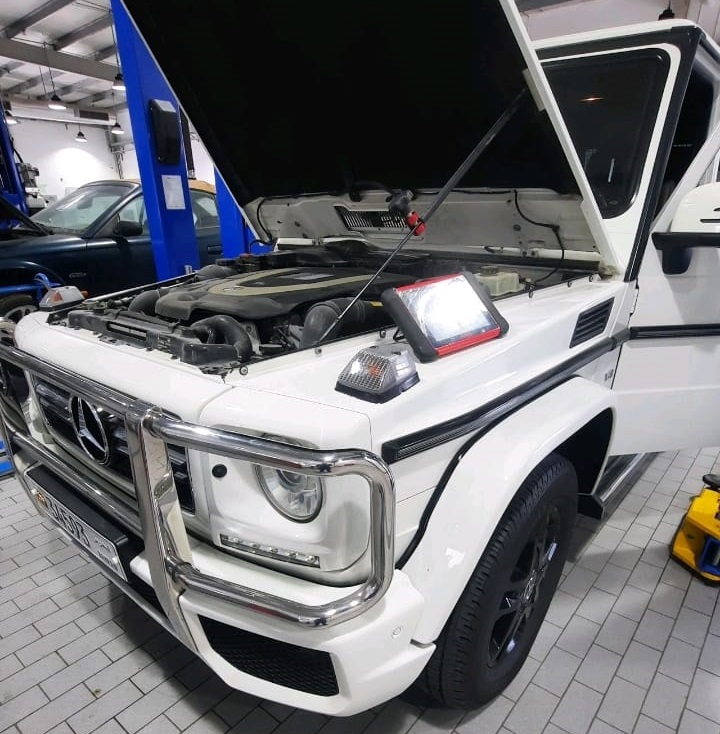

Customer Complaint: “Car Is Not Starting”
The customer reported that the G-Class had been parked for nearly two weeks. When attempting to start it afterward, the engine cranked and fired up but immediately shut off. Subsequent attempts failed entirely.
Given the combination of electrical inactivity and failed ignition response, the workshop began a comprehensive diagnostic process to isolate the fault.
Step 1: Initial Diagnostics
The first step was to connect the Mercedes-Benz STAR/XENTRY diagnostic system to retrieve fault codes from the ECU and related control units.
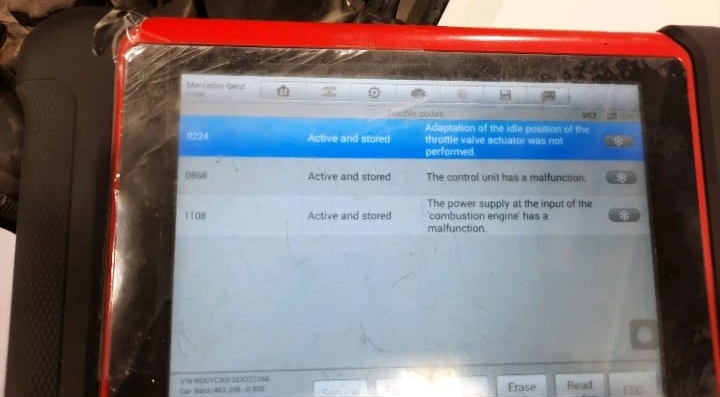
Several stored and current Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) were found:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0224 | Throttle valve adaptation not performed |
| 0868 | Control unit malfunction |
| 1108 | Power supply to engine control module malfunction |
These codes immediately pointed toward a combination of throttle system and power supply issues, possibly triggered by voltage instability after long inactivity.
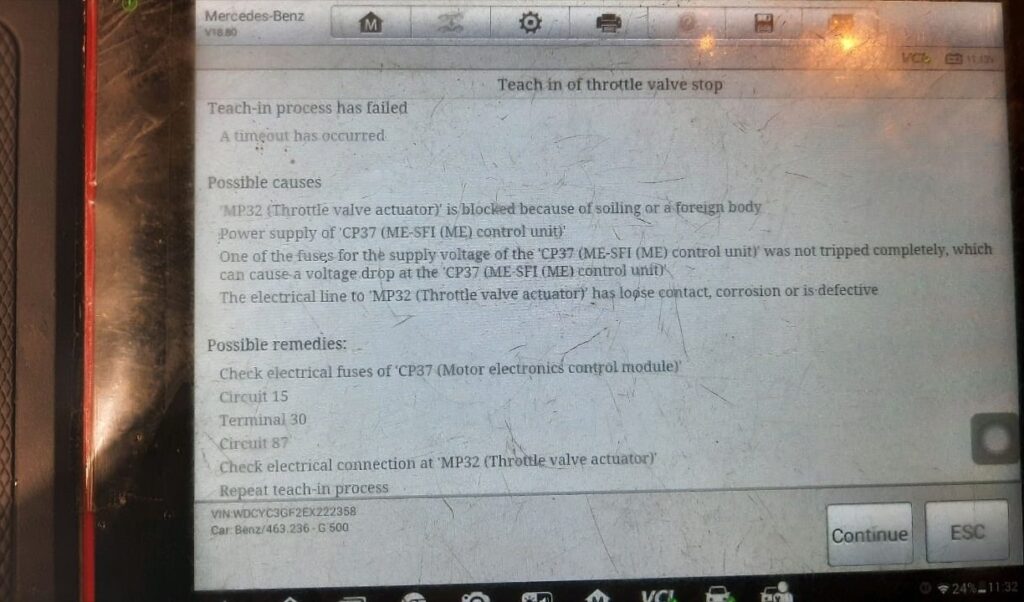
Step 2: Throttle Valve Adaptation Failure
The throttle valve adaptation is a calibration process that synchronizes throttle plate position with ECU reference values. When it fails, the engine may crank but won’t idle or stay running.
During the first adaptation attempt using SCAN guided functions, the system displayed:
“Requirement not met ; intake air temperature implausible.”
This meant the adaptation couldn’t proceed because the intake air temperature sensor was reading incorrectly likely due to contamination or carbon buildup.
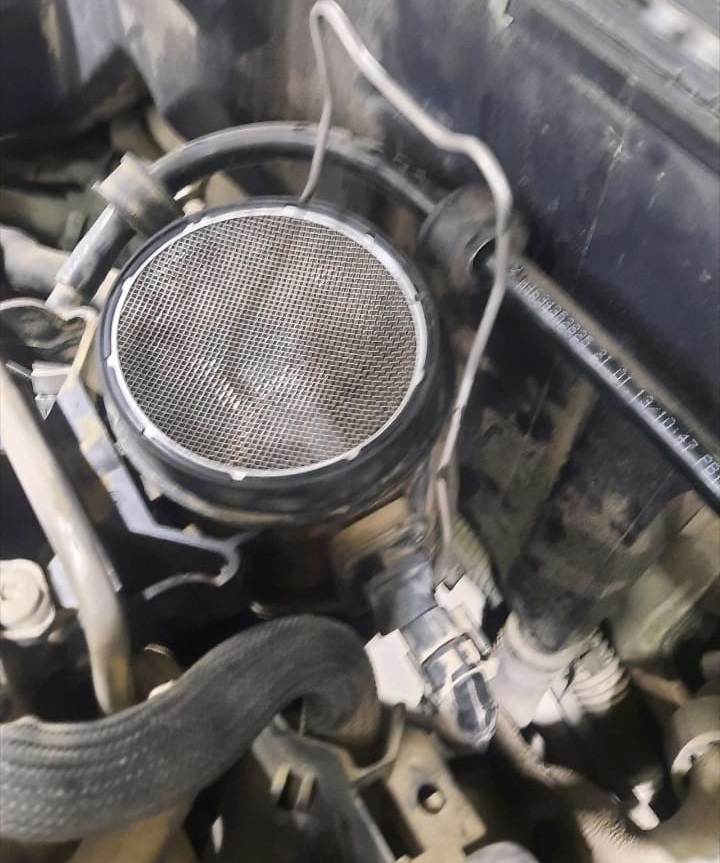
Sensor and Throttle Body Inspection
- 1. The intake air temperature sensor was removed and found dirty and carbon-coated.
- 2. The throttle flap housing was inspected and showed heavy carbon deposits around the butterfly valve, restricting airflow.
- 3. Both components were cleaned thoroughly using approved throttle body cleaner.
- 4. Electrical connections were checked for corrosion or looseness all were intact.
With airflow restored and sensor readings stable, the adaptation process was retried but another fault emerged.


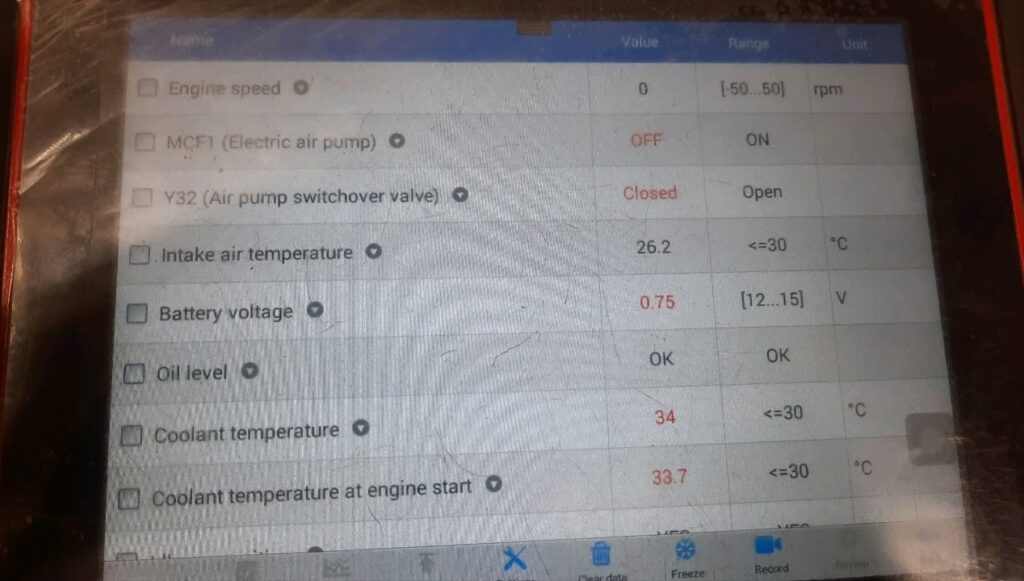
Step 3: Electrical Power Supply Fault
While performing throttle adaptation, the system failed again. Voltage readings dropped unexpectedly during the process.
Observation:
Despite using a battery booster to stabilize voltage, the XENTRY logs still showed power interruption. This suggested a fault in the fuse or wiring supplying the engine control unit (ME).
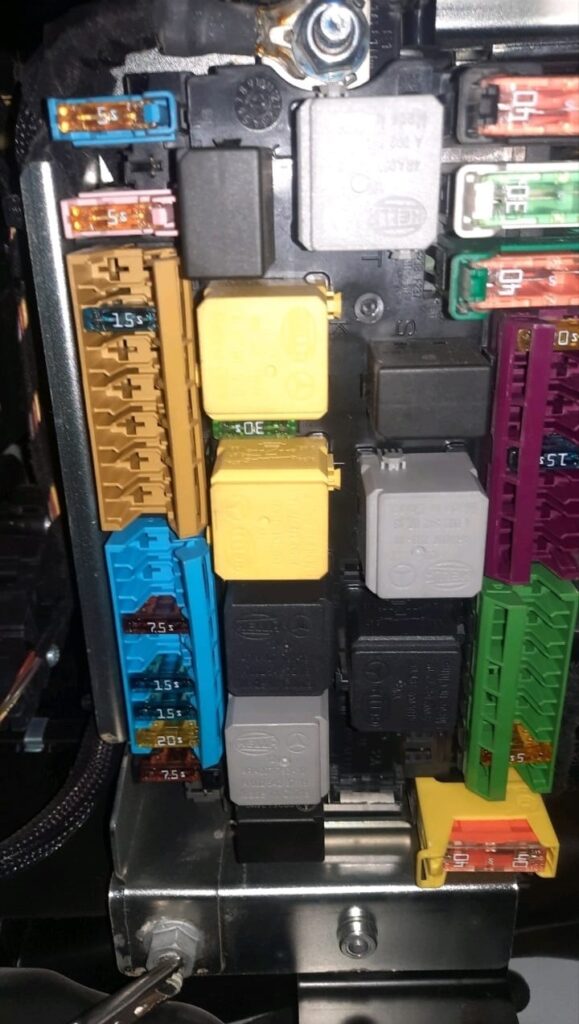
Fuse Inspection
- – Inspected the main engine bay fuse box and interior fuse panel.
- – Located a blown fuse responsible for the ECU’s power input line.
- – Checked continuity and found no short circuits, confirming that the failure was isolated to the fuse itself.
- – Replaced the damaged fuse with an OEM-rated one.
Once the fuse was replaced, the vehicle’s systems came online properly, and power supply stability was confirmed.

Step 4: Successful Throttle Valve Adaptation
With stable voltage and a clean intake sensor, the throttle valve adaptation was performed again.
This time, the process completed successfully:
“Adaptation values stored successfully.”
When the ignition was cycled and the engine started, the G-Class idled smoothly and responded to throttle input as expected.
Step 5: Final Verification & Test Drive
After confirming the successful adaptation, all DTCs were cleared from the control units.
A 15-minute test drive was conducted to monitor system performance:
| Test Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Throttle response | Smooth and linear |
| Voltage stability | 13.8–14.2 V at idle |
| Idle behavior | Stable at ~650 RPM |
| Fault codes after test | None |
After returning from the test drive, a post-scan confirmed that no new or stored codes reappeared verifying a full repair.

Root Cause Summary
The no-start condition resulted from a combination of issues triggered by prolonged inactivity:
- 1. Carbon buildup affected the intake air temperature sensor and throttle valve operation.
- 2. Voltage drop and blown fuse interrupted ECU power during calibration.
- 3. The throttle adaptation process failed, preventing proper throttle response and fuel delivery.
Once both mechanical (cleaning) and electrical (fuse replacement) issues were addressed, the system re-synchronized successfully.
Key Lessons Learned
| Lesson | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Inactivity can cause cascading faults | Long idle periods lead to carbon buildup, low battery voltage, and sensor contamination. |
| 2. Throttle adaptation is critical after power loss | Without recalibration, the ECU may misinterpret throttle plate position and block starting. |
| 3. Always stabilize voltage during diagnostics | Use a booster or charger to maintain >12.6 V during adaptation or programming. |
| 4. Blown fuses can mimic major failures | A single power-supply fuse can prevent the ECU from completing necessary start procedures. |
Preventive Maintenance Tips
To avoid similar “car not starting” issues after long parking periods:
| Action | Frequency / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Start the vehicle weekly | Keeps fuel and battery systems active |
| Clean throttle body every 20,000–30,000 km | Prevents carbon buildup |
| Check intake air sensors regularly | Maintains proper ECU data accuracy |
| Inspect fuses and voltage drops annually | Avoids unexpected electrical interruptions |
| Keep battery charged during storage | Prevents ECU memory resets and low-voltage errors |
Technical Notes for Technicians
- – Always use XENTRY or STAR Diagnosis for throttle adaptation on modern Mercedes engines.
- – If adaptation fails, check intake air temperature, battery voltage, and fuse integrity before suspecting hardware faults.
- – After fuse replacement, perform a full system scan and record freeze-frame data before clearing codes.
Related Diagnostic Resource
If you’re facing similar starting problems, explore our full troubleshooting hub:
Mercedes No Start Issues: Causes, Fixes & Case Studies : a complete guide covering electrical, fuel, and ECU-related no-start scenarios across multiple Mercedes models.
FAQ: Common “Car Is Not Starting” Questions
Q1: Why does my Mercedes fail to start after sitting parked?
Prolonged inactivity can cause battery drain, throttle adaptation loss, and sensor contamination, preventing proper engine startup.
Q2: What is throttle valve adaptation?
It’s a recalibration process where the ECU re-learns the throttle plate’s open/close positions for correct air-fuel mixture control.
Q3: Can a dirty throttle body cause a no-start?
Yes, carbon buildup can block airflow or cause incorrect sensor readings that prevent the ECU from allowing startup.
Q4: Why did the fuse blow after parking?
Voltage fluctuations or condensation during inactivity can stress circuits, leading to blown fuses or corroded connections.
Author Bio
Written by Mercedes Expert
With years of hands-on experience diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz systems, he brings technical depth and practical case studies to help car owners, technicians, and enthusiasts troubleshoot complex automotive issues. His work focuses on clear repair guides, OEM-level procedures, and knowledge-sharing to empower both professionals and drivers.
Last update: October 2025






Leave a Reply