Table of Contents
Engine Vibrate at Idle: Case Study on Mercedes C-Class (M264 Engine)
If your Mercedes engine vibrates at idle, it can indicate anything from mild misfires to serious internal mechanical damage. This case study explains a real Mercedes-Benz C-Class on M264 Engine, how the issue was diagnosed step-by-step, and how technicians resolved the vibration problem completely.
For more Mercedes noise and vibration troubleshooting, visit:
Mercedes Engine Noise and Vibration Problems: Full Diagnosis
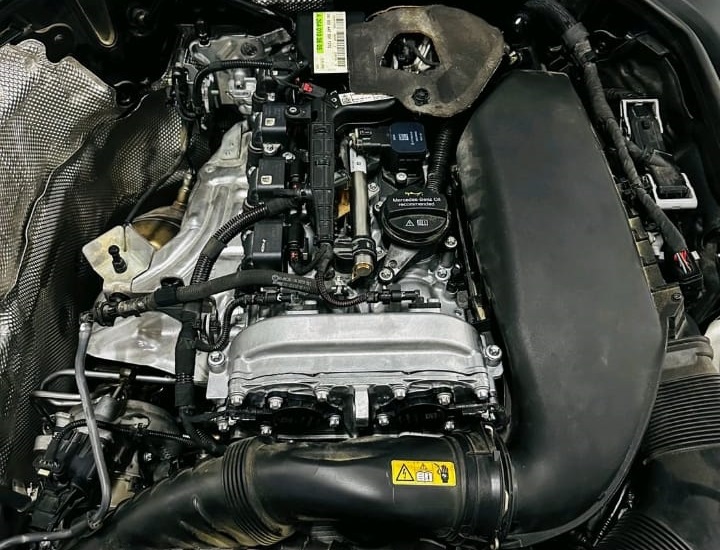

Why Engine Vibration at Idle Matters
Engine vibration at idle is more than an annoyance it’s a red flag for issues such as:
- – Misfires
- – Compression loss
- – Injector imbalance
- – Faulty engine mounts
- – Burnt valves
- – Timing or combustion problems
Ignoring early symptoms can lead to severe engine damage, reduced fuel economy, and costly repairs.
This case study demonstrates how a systematic diagnostic process solved a severe vibration issue in a Mercedes-Benz C-Class with the M264 engine.
Case Study Overview
Vehicle Details
- – Model: Mercedes-Benz C-Class
- – Engine: M264 4-cylinder
- – Complaint: Strong engine vibration at idle
The customer reported noticeable shaking whenever the car was stopped in traffic or at a red light.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
The technician followed a structured workflow, combining Xentry diagnostics, mechanical testing, and physical inspection.
Complaint Verification
The technician confirmed significant vibration during idle consistent and clearly abnormal.
Quick Test & Fault Code Check
A full quick test was performed.
Result: No relevant fault codes.
This indicated the issue was not caused by standard sensor or ECU-detectable faults.
Visual Inspection
The engine bay and underbody were inspected.
Findings:
- – No leaks
- – No loose components
- – No visible damage
This eliminated simple external causes.
Misfire Counter Check (Xentry)
Using Xentry fault counters:
Cylinder 3 showed 4 misfire events
This is an early indication of combustion imbalance.
Injector Performance Analysis
Live injector performance data showed:
- – Cylinder 3 & Cylinder 2 injectors showing abnormal values
This suggested the ECU was compensating for poor combustion.
Smooth Running Test
Xentry’s smooth running test showed:
- – Clear deviation in cylinders 3 and 2
- – Uneven combustion curves
- – Poor cylinder balance
This confirmed non-uniform combustion.
Technical Documents (TIPS) Search
No factory bulletins or known issues matched the customer complaint.
Software Update & SCN Coding
The ECU software was checked no update available.
SCN coding was performed.
Result: No improvement.
Vibration remained exactly the same.
This suggested the issue was mechanical, not electronic.
Manual Compression Test
Compression test results:
| Cylinder | Compression Pressure |
|---|---|
| #1 | Normal |
| #2 | 9.5 bars (low) |
| #3 | 9.5 bars (low) |
| #4 | Normal |
M264 minimum specification was not met in cylinders 2 and 3.

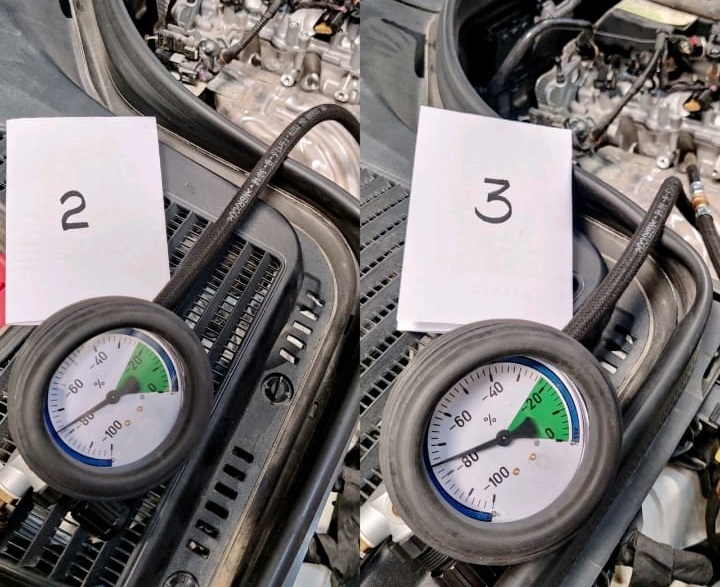
Cylinder Leakage Test
Leak-down test results:
- – Cylinders 2 and 3 → 75% leakage
- – Allowable leakage: 20%
This indicated severe internal leakage.

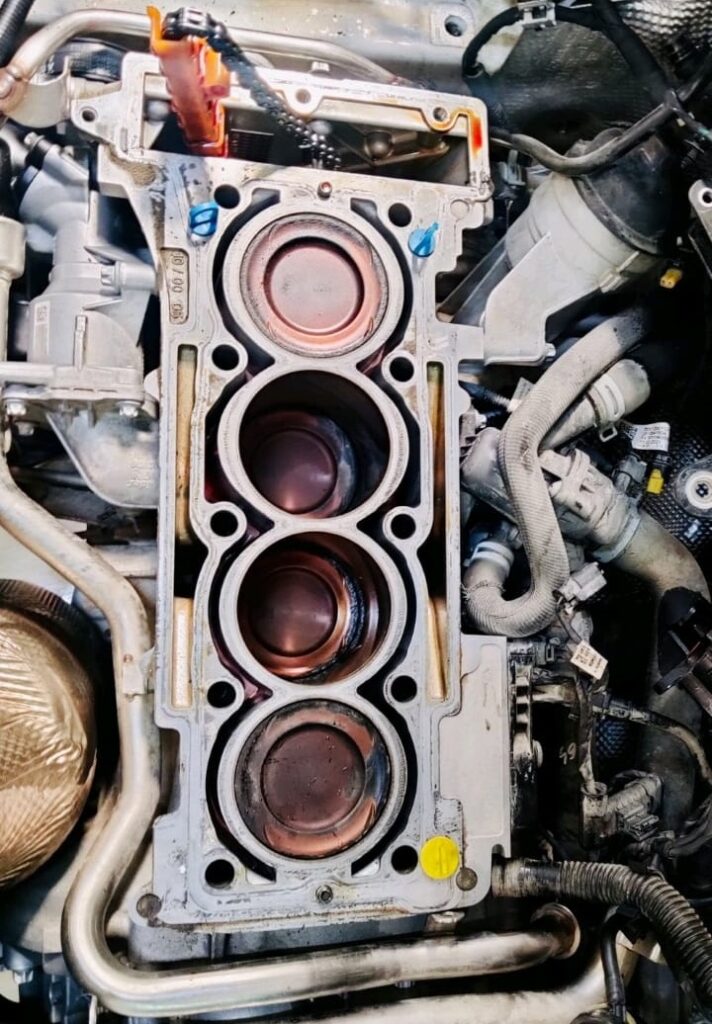
Endoscopic (Borescope) Inspection
Endoscopy revealed:
- – Burnt valves
- – Heavy carbon buildup
- – Valve seat damage
Cylinders 2 and 3 showed significantly more carbon deposits than others.
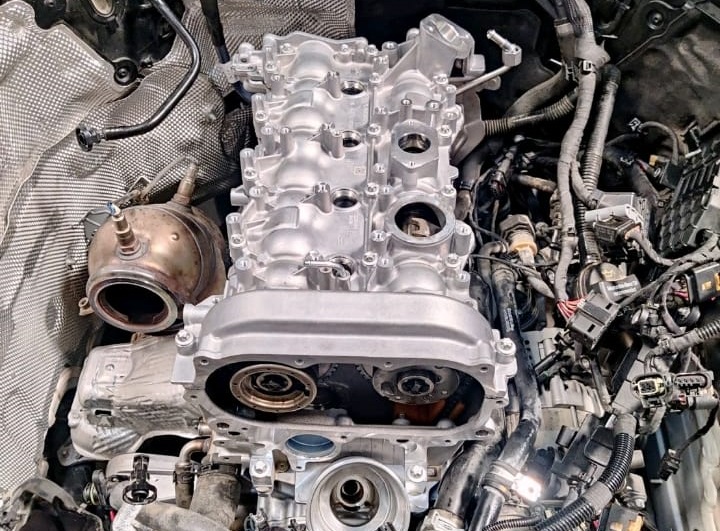
Cylinder Head Removal & Final Diagnosis
Removing the cylinder head confirmed:
=> Burnt exhaust valves
=> Cracked or worn valve seats
=> Compression loss due to valve sealing failure
These faults directly cause:
- – Strong vibration at idle
- – Poor combustion
- – Misfires
- – ECU injector compensation
This matched all earlier symptoms.

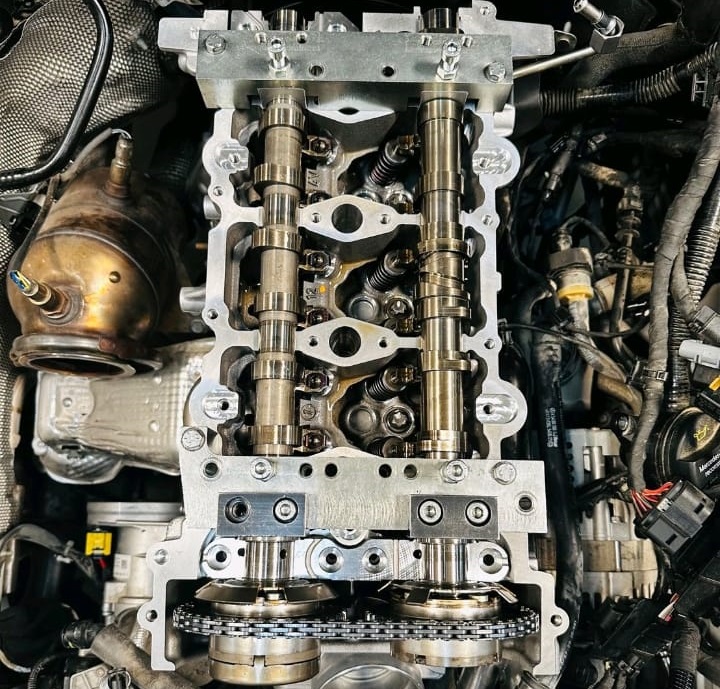

Repair Process & Outcome
Cylinder Head Replacement
The technician replaced:
- – Cylinder head
- – All affected valves
- – Valve seats
- – Associated seals and gaskets
A full reassembly was performed following Mercedes specifications.
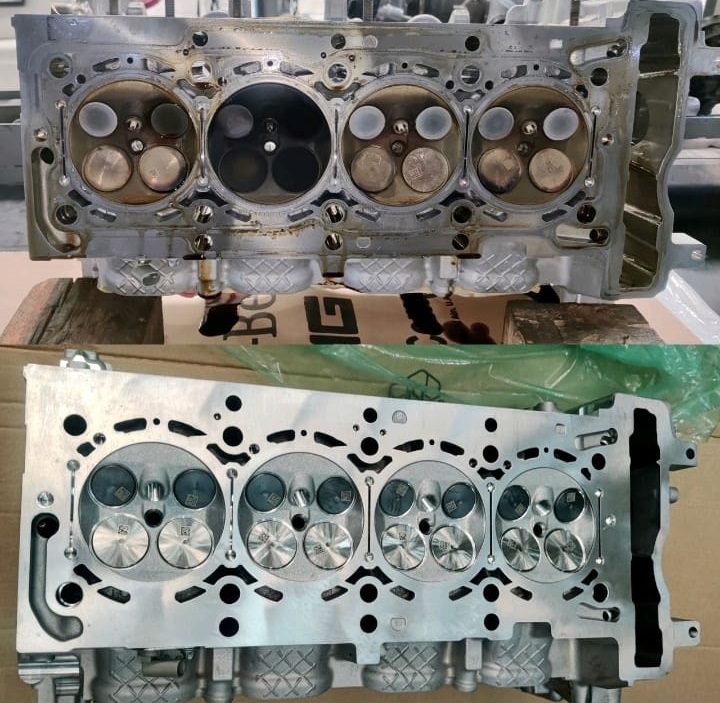
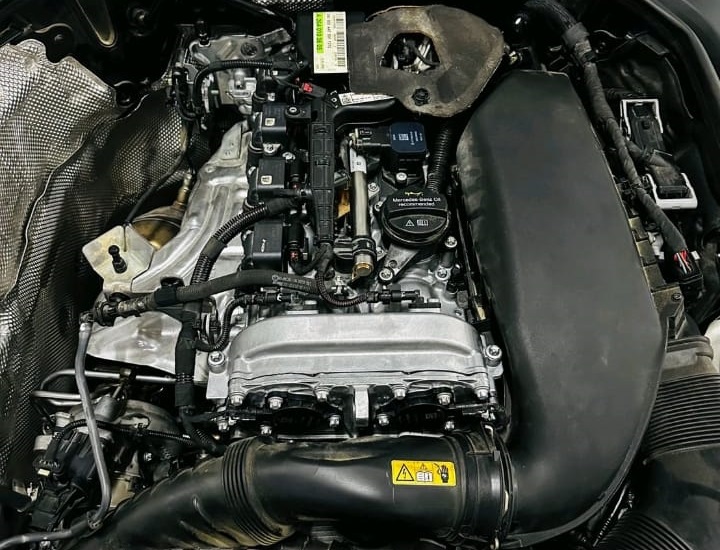
Final Testing After Repair
– Idle vibration completely eliminated
– Injectors performing normally
– Compression restored
– No misfire counters
– Smooth idle and stable engine operation
The vehicle was returned to the customer in perfect running condition.

What This Case Study Teaches Us
1. Injector performance data is crucial
It reflects not only injector status but also combustion, valves, and cylinder health.
2. Misfires are symptoms not root causes
The ECU often compensates by adjusting ignition & injection values.
3. Compression testing is mandatory for vibration diagnostics
Low compression almost always causes idle vibration.
4. Burnt valves are a common cause of idle vibration in modern engines
Especially in turbocharged engines like M274/M264.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Engine Vibration at Idle
Regular Maintenance
Follow Mercedes service intervals strictly.
Use OEM Parts
Genuine plugs, injectors, filters, and oils ensure proper combustion.
Clean Driving Habits
Avoid short trips that prevent the engine from reaching operating temperature.
Fuel Quality
Use high-quality fuels to reduce carbon buildup and protect valves.
FAQs
Can I drive with engine vibration at idle?
Driving with engine vibration at idle is not recommended.
It may indicate misfires, compression loss, burnt valves, or injector faults.
Continuing to drive may worsen the damage.
Are engine vibrations a sign of serious problems?
Yes.
Engine vibrations often indicate:
- – Misfires
- – Worn valves
- – Bad engine mounts
- – Fuel injector issues
- – Internal mechanical damage
These problems become more expensive if ignored.
The step-by-step diagnosis including misfire counters, injector analysis, compression testing, and borescope inspection allowed the technician to pinpoint the exact cause and apply the correct repair.
Conclusion
This real-world case study demonstrates how a Mercedes C-Class M264 engine developed severe vibration at idle due to burnt valves and failing valve seats.
For more Mercedes noise & vibration diagnostics, visit:
Mercedes Engine Noise and Vibration Problems: Full Diagnosis
— Salim, Mercedes Expert
Independent specialist in Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, CAN Bus analysis, troubleshooting case studies, and EV systems.







Same problem happened with my car 2 time cylender head removed valve replaced with old head still had fault count on same cylender
I hope this article helped you Sir