Table of Contents
Case Study: Oil In Vacuum Pump in a Mercedes GLC X253 with OM654 Engine
This case study examines a Mercedes GLC X253 equipped with the OM654 engine, which was experiencing a noticeable lack of power. The owner brought the vehicle to a Mercedes dealership, where a qualified technician undertook a thorough diagnostic and repair process to resolve the issue.
Vehicle and Problem Overview
– Vehicle Model: Mercedes GLC X253
– Engine Type: OM654
– Issue: Lack of power, impacting overall driving performance
Initial Diagnostics
Upon receiving the vehicle, the technician initiated several such as checks to diagnose the root cause of the lack of power:
1. Boost Pressure Regulation Check: Ensuring the turbocharger system was functioning correctly. The technician used diagnostic tools to measure the boost pressure and confirmed that it was lower than the manufacturer’s specifications.
2. EGR Solenoid Valves Check: Inspecting for proper operation of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system. The technician noted irregularities in the EGR valve operation, which could affect engine performance.
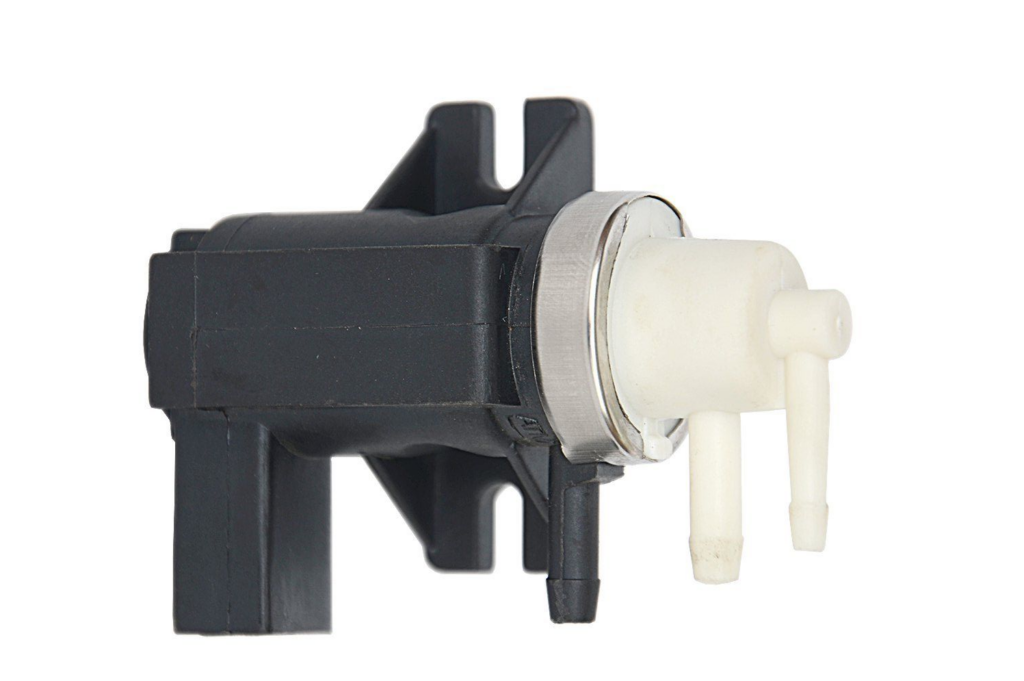

Key Findings
During these checks, the technician observed traces of oil around the solenoid valves, indicating a potential issue within the vacuum system. This finding was crucial as it pointed to a possible internal leak that could compromise engine performance.
Expert Analysis
With expertise, the technician hypothesized that the vacuum system was compromised due to oil contamination. The vacuum system pump and the engine oil pump are integrated within the OM654 engine, suggesting a possible leak or failure at this junction. The integration of these components meant that a failure in one could directly affect the other, leading to the observed lack of power.
Decision to Remove the Engine
To gain access to the compromised component, the technician decided to remove the engine:
1. Engine Removal: Detailed and careful removal of the engine to prevent further damage. This involved disconnecting various systems, including the fuel lines, electrical connectors, and exhaust components.
2. Component Inspection: Close examination of the vacuum system pump and surrounding areas. The technician looked for signs of wear, damage, and oil contamination that could explain the failure.
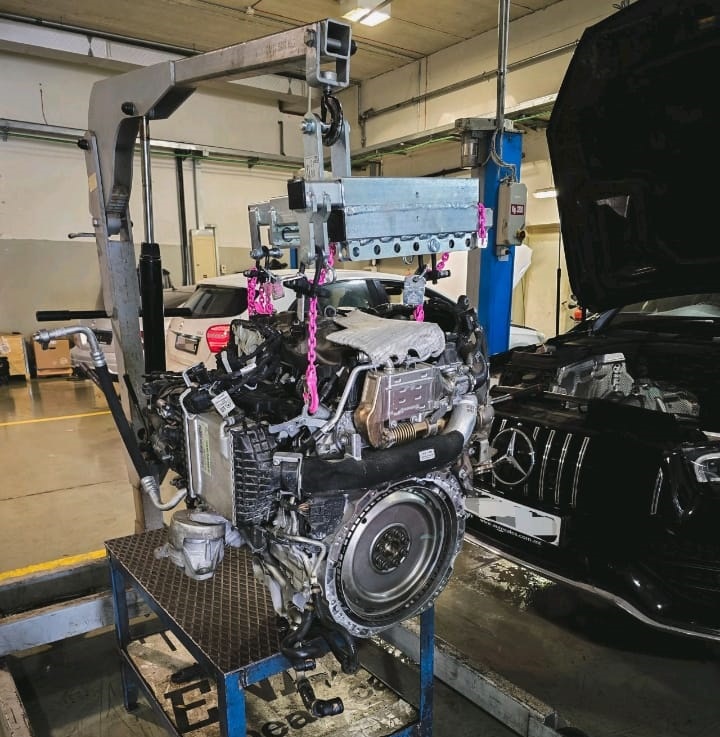
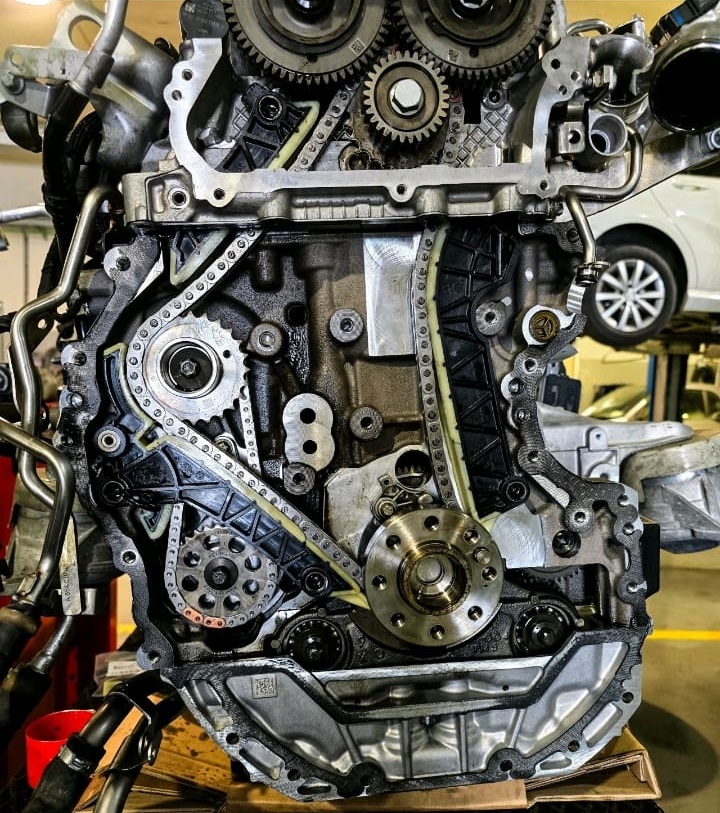


Repair Process
Upon inspection, it was confirmed that the vacuum system pump was indeed the source of the issue. The technician proceeded with:
Vacuum System Pump Replacement: Installation of a new pump to restore proper function. This involved selecting a genuine Mercedes replacement part to ensure compatibility and reliability.
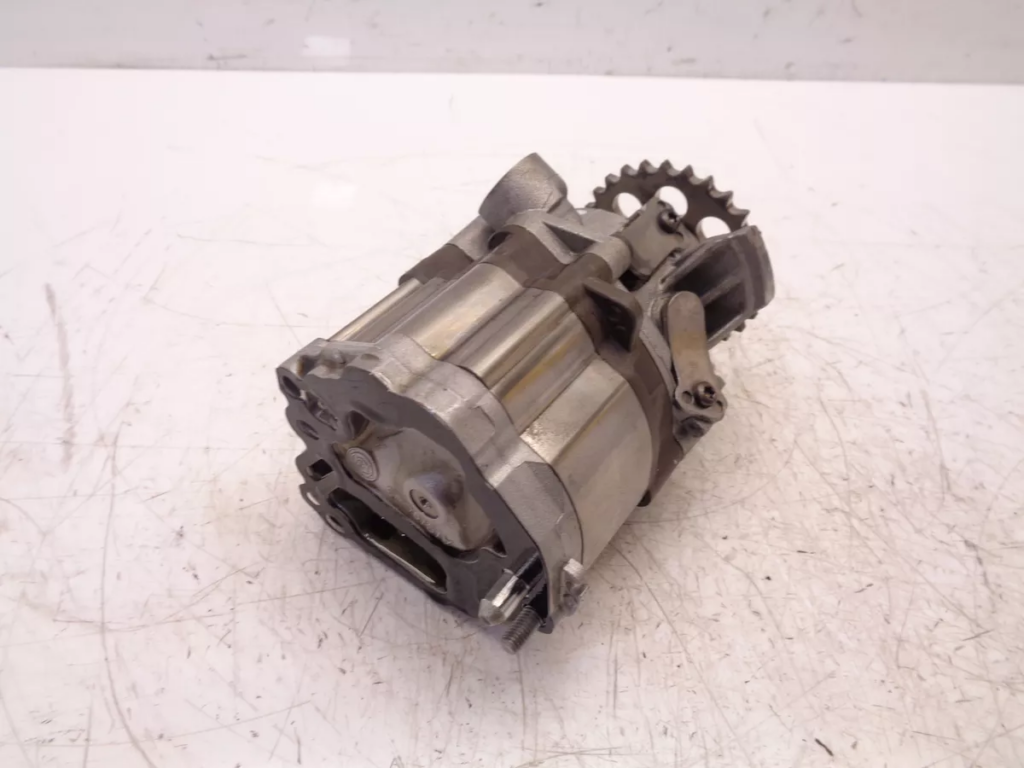
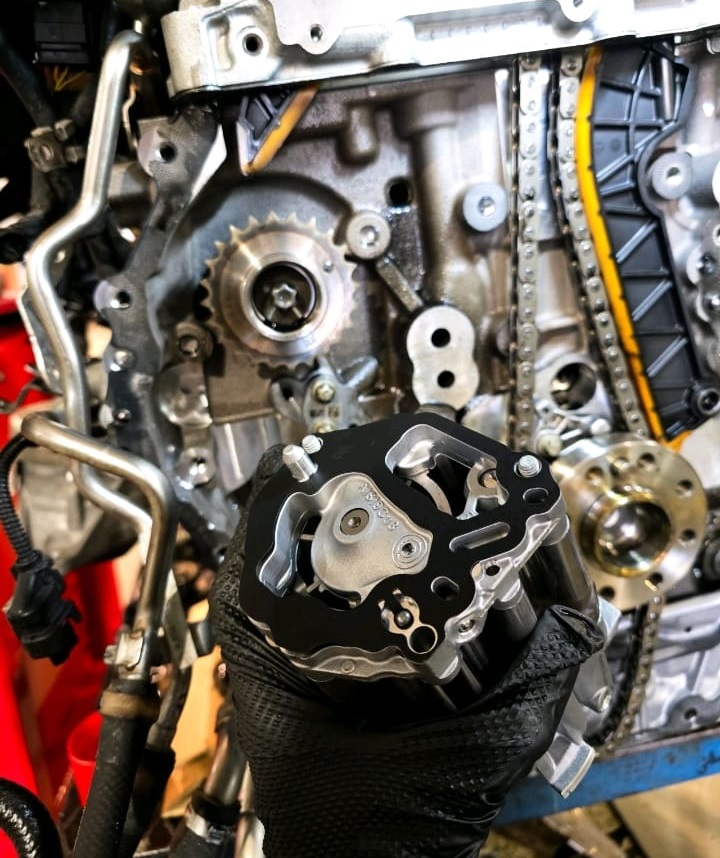


Reassembly: Reassembling the engine and reinstalling it into the vehicle. The technician meticulously followed the reverse order of the removal process, ensuring all connections were secure and components were properly aligned.
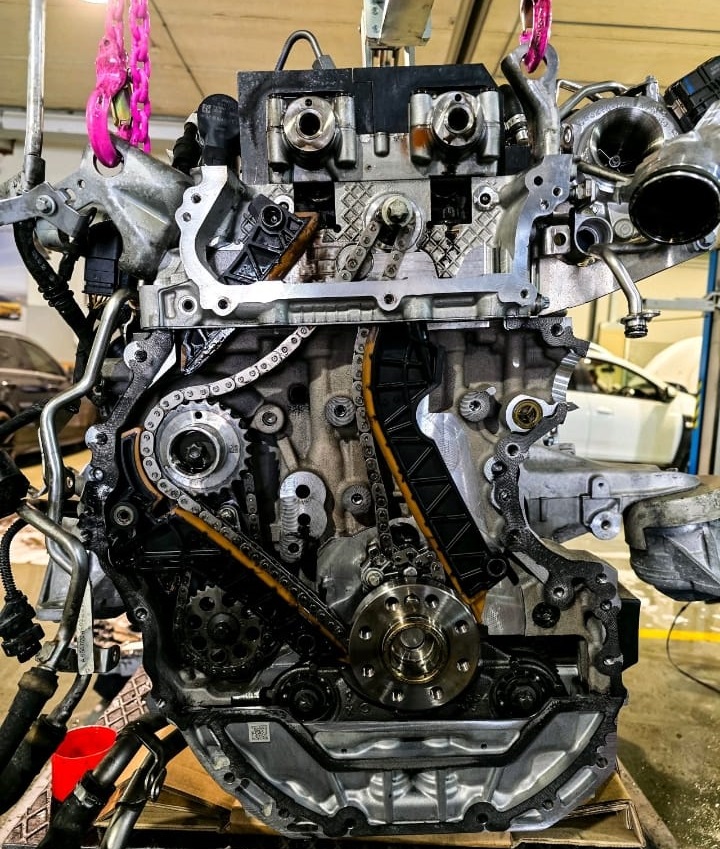

Post-Repair Testing
After the repair, the technician performed:
1. Road Test: Comprehensive road testing to ensure the issue was resolved. The technician monitored the engine’s performance under various driving conditions, including acceleration, cruising, and idling.
2. Vacuum System Check: Verification of the vacuum system’s functionality, confirming no further problems. This included checking for proper vacuum pressure and ensuring that there were no leaks or irregularities.
The meticulous approach of the technician resolved the lack of power in the Mercedes GLC X253. This case study highlights the importance of thorough diagnostics and expert analysis in addressing complex automotive issues.
The successful repair not only restored the vehicle’s performance but also provided insights into the integration of critical engine components and the potential for internal leaks.
What happens when vacuum pump fails?
When a vacuum pump fails, several issues can arise, impacting the performance and safety of a vehicle. Here are the key consequences:
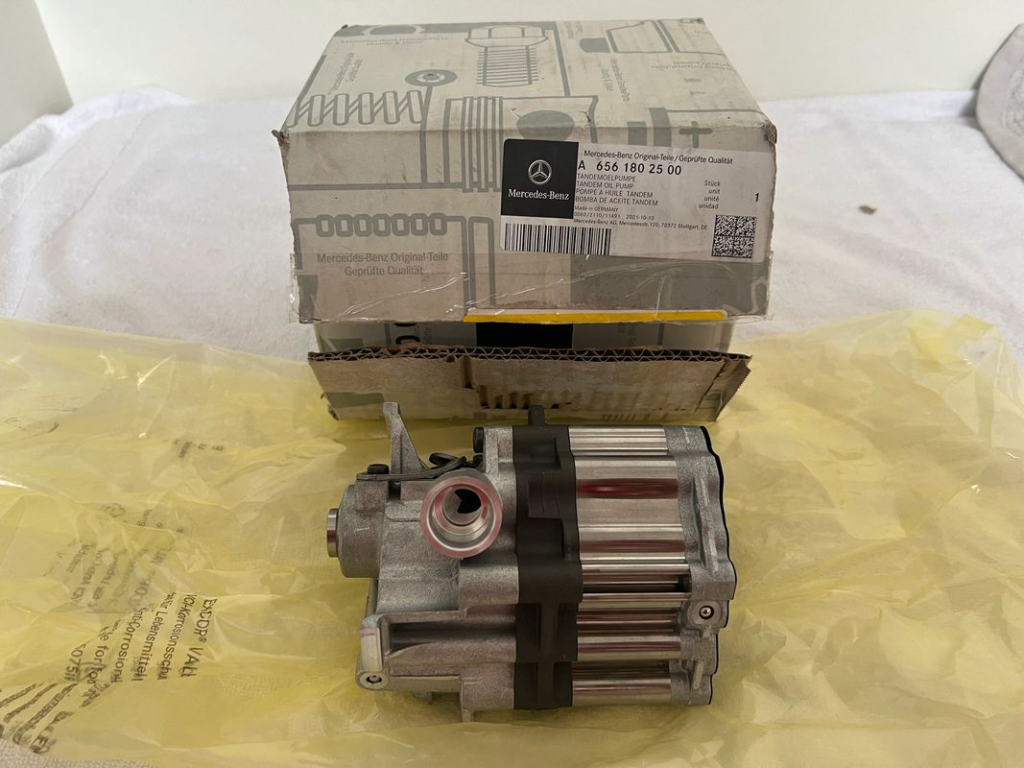

Loss of Brake Assistance
Modern vehicles often use a vacuum pump to provide the necessary vacuum for the brake booster. When the vacuum pump fails:
- Increased Brake Pedal Effort: Drivers will notice that the brake pedal becomes harder to press, requiring more effort to stop the vehicle.
- Reduced Braking Efficiency: The effectiveness of the braking system is compromised, leading to longer stopping distances and potentially unsafe driving conditions.
Poor Engine Performance
The vacuum pump also plays a role in maintaining proper engine operation by regulating various components:
- Misfiring or Stalling: A failing vacuum pump can lead to irregularities in the engine’s air-fuel mixture, causing misfires or engine stalling.
- Reduced Power Output: The engine may struggle to produce adequate power, resulting in sluggish acceleration and overall poor performance.
Impact on Turbocharged Engines
For turbocharged engines, the vacuum pump assists in managing turbocharger functions:
- Boost Pressure Issues: The turbocharger may not operate efficiently, leading to a loss of power and poor throttle response.
- Check Engine Light: Engine control systems may detect the vacuum pump failure and trigger the check engine light, indicating a problem that needs addressing.
Increased Emissions
A failing vacuum pump can affect emission control systems:
- Higher Emissions: Improper operation of the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve and other emission control components can lead to increased exhaust emissions, potentially failing emissions tests.
- Engine Warning Codes: The vehicle’s diagnostic system may log error codes related to emissions control, requiring diagnostic and repair work.
Potential Oil Contamination
In cases where the vacuum pump is integrated with the engine oil system, a failure can lead to:
- Oil Leaks: The vacuum pump may develop leaks, leading to oil loss and contamination of the vacuum system.
- Component Damage: Oil contamination can damage other engine components, leading to more extensive repairs.
Is it safe to drive with a bad vacuum pump?
No, it is not safe to drive with a bad vacuum pump because it can lead to reduced braking efficiency, poor engine performance, and increased emissions, compromising both safety and vehicle functionality.
Conclusion
The failure of a vacuum pump can have significant implications for vehicle safety, performance, and emissions. It is essential to diagnose and repair vacuum pump issues promptly to maintain the vehicle’s optimal functionality and ensure safe driving conditions.






Leave a Reply