Table of Contents
Mercedes Parking Sensors Not Working – Troubleshooting & Fix Guide
When your Mercedes fails to beep or displays no visual indicator while parking, here’s how to systematically restore your park‑assist functionality. This guide follows Google’s core update best practices with clear headings, concise answers, bullet points, and rich schema.
Common Causes & Symptoms
| Cause | Symptoms | Quick Diagnostic & Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Dirt / debris on sensors | No beep or delayed beep | Clean sensors thoroughly on bumpers ultrasonic sensors lose function when obstructed |
| Loose or unplugged sensor | One zone dead, uneven detection | Remove bumper, inspect connectors, reseat or replace faulty harness |
| Blown Parktronic fuse or poor ground | System not active at all | Locate fuse (often in trunk fuse box), test voltage, fix grounds if voltage off |
| Damaged sensor or wiring | Constant red bars, false positives | Check wiring for corrosion or damage; repair harness |
| Control module failure | No progression past initial alerts | Scan with XENTRY/OBD, recalibrate or replace module if defective |
| Weak battery / aux battery | Parking sensors intermittent or silent | Test main and aux battery; reinstall both resolved many cases |
Diagnostic & Repair Flow
- – Clean bumpers and sensors thoroughly remove mud, snow, ice
- – Check fuse(s) for Parktronic in trunk or dashboard fuse boxes—test for ~12 V
- – Inspect and reseat connectors especially for sensors showing no activity
- – Scan for fault codes (B1023, B1248, etc.) to identify module or sensor faults
- – Repair wiring or replace sensors as needed, sealing connectors
- – Test-drive system with diagnostics tool to display audible and visual feedback zones
Case Study Overview : Mercedes Parking Sensors Not Working
Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz G Class 2017
Issue: Parking sensors not working
Customer Complaint: Mercedes parking assist not working
Diagnostic Tool: Xentry Diagnosis
Diagnostic Process
1. Initial Assessment:
- – After receiving the vehicle, the technician performed an initial assessment using the Xentry diagnostic tool.
- – Fault Code: PTS A12500 – Power supply of the sensors is outside the valid range. Self-test failed.
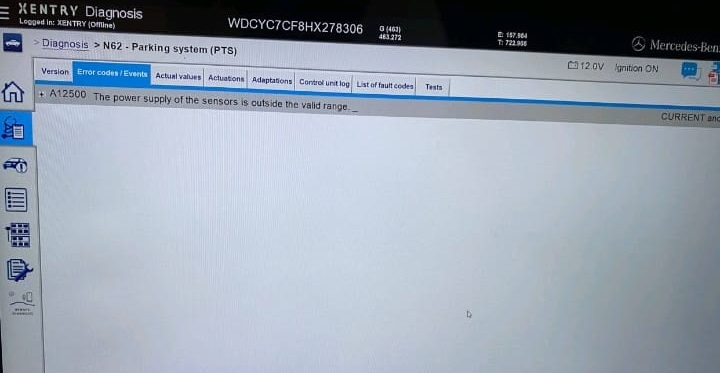
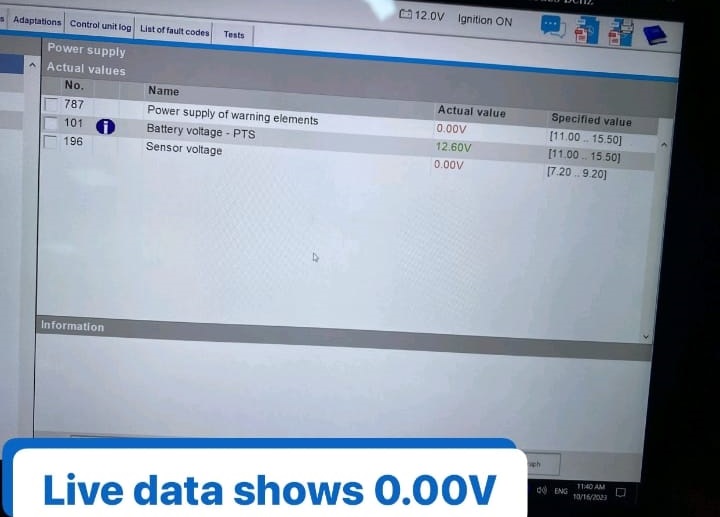
- – Live Data: Sensor voltages read 0.00V (should be between 6.0V and 10V).
2. Power Supply Check:
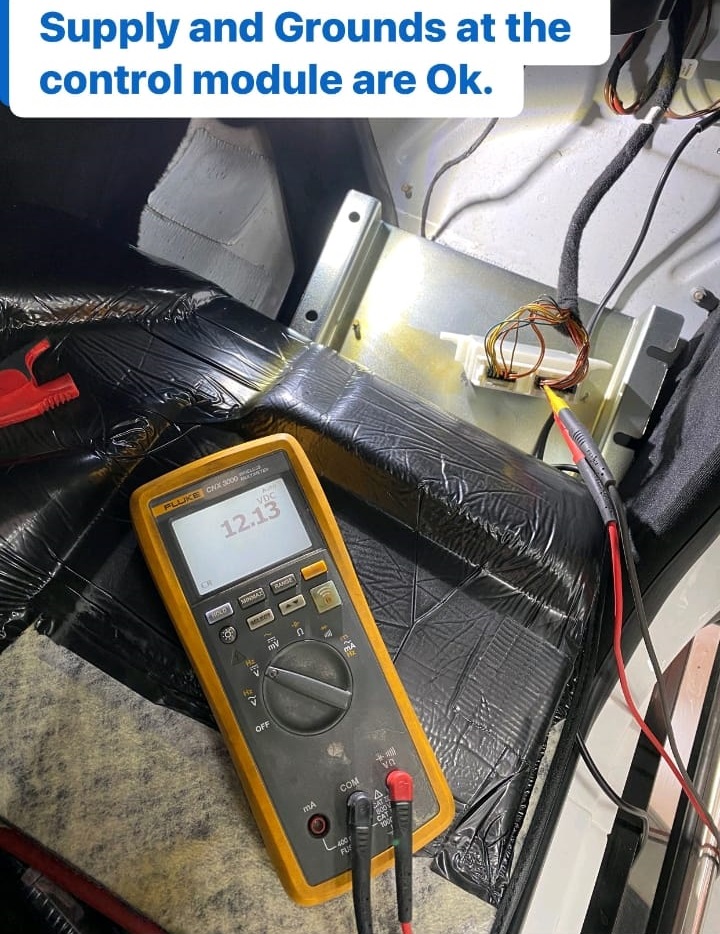
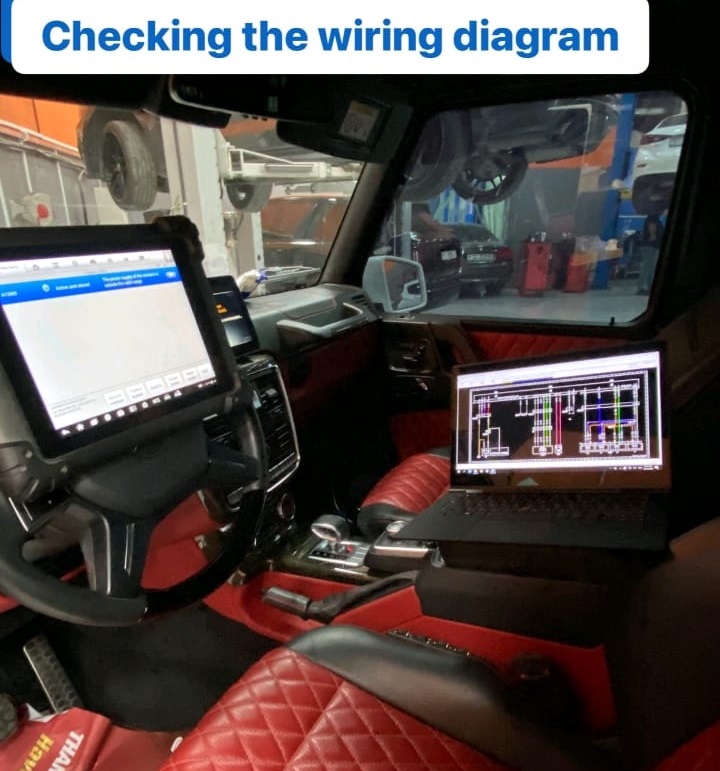
- – Using a wiring diagram, the technician verified that the supply to the parking control unit was functioning correctly.

3. Voltage Drop Investigation:
- – When connecting the front sensors’ connector, the power supply to the sensors and warning elements dropped significantly.

Detailed Examination
1. Front Bumper and Sensor Harness Inspection:
- – The technician decided to remove the front bumper to inspect the sensors and harness more closely.
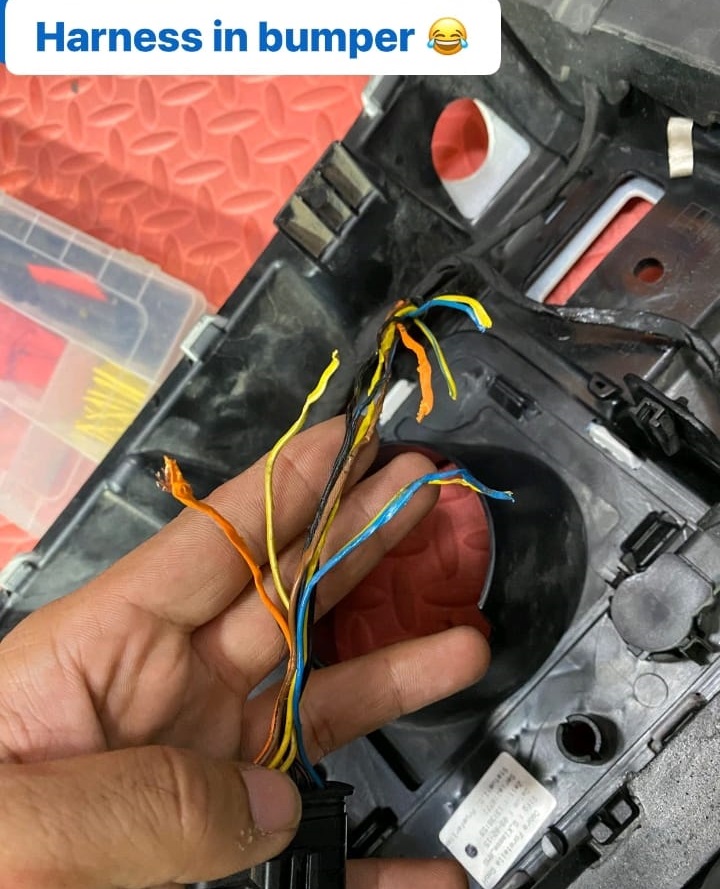
- – Upon removal, it was evident that the body shop had improperly fitted the bumper and sensor harness, causing electrical issues.
2. Harness and Connector Examination:
- – The sensor harness was checked for any visible damage, improper connections, or signs of wear that might be causing the power supply drop.
Findings
- – The improper fitting of the bumper and harness by the body shop was causing the power supply to the sensors to drop, leading to the sensors not receiving the required voltage to function correctly.

Solution and Repair
1. Reinstallation and Repair:
- – The technician reinstalled the bumper and sensor harness correctly, ensuring all connections were secure and free from damage.
- – After properly fitting the components, the power supply to the sensors was rechecked, showing a stable voltage within the required range (6.0V to 10V).
2. Final Testing:
- – A final diagnostic test was conducted using Xentry, confirming that the fault code was cleared, and the sensors were operating correctly.
- – The technician performed a practical test by parking the vehicle to ensure the sensors detected obstacles accurately.
In this case study, we explored how a seemingly complex issue with the parking sensors on a Mercedes-Benz G Class was resolved through systematic diagnosis and inspection. The improper fitting of the bumper and sensor harness by the body shop was the root cause of the problem.
By carefully examining and correcting the installation, the technician restored the functionality of the parking sensors.
DIY vs Professional
| Task | DIY-Friendly | Professional Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Clean sensors | Yes | — |
| Check fuses & battery voltage | Yes | If modules involved |
| Reseat sensor harnesses | Yes | — |
| Scan fault codes & recalibrate | Needs tool | Dealer/Xentry |
| Module replacement | No | Specialist |
| Wiring repair | Intermediate | Professional advisable |
How to activate parking sensors on mercedes a class
How to Activate Parking Sensors on Mercedes A-Class is a common question for drivers who want to make full use of the car’s advanced safety features. In most Mercedes A-Class models, including the Mercedes- Benz A Class W177
How to Activate Parking Sensors on Mercedes A-Class – Step-by-Step
Start the Engine or Turn On the Ignition
Ensure your Mercedes A-Class is on by starting the engine or switching the ignition to position II.
Engage Reverse Gear
The parking sensors activate automatically when you shift into reverse. You’ll hear a beep and see visual indicators on the infotainment screen.
Use the Park Assist Button (If Needed)
If you want to activate the sensors manually (without reversing), press the Park Assist button on the dashboard or center console marked with a “P” and soundwave icon.
Drive at Low Speed
The sensors also engage automatically when driving at low speeds (usually under 10–15 km/h), especially near obstacles.
Check for Visual & Audio Alerts
Once active, the system will display distance bars on the screen and emit beeps as you approach objects. The closer you get, the faster the beeping.
Keep Sensors Clean
Ensure the front and rear bumpers, where the sensors are located, are clean and free from dirt or snow to ensure proper function.
Mercedes parking assist not working?
Parking assist can fail for a variety of reasons, including:
1. Physical Damage:
- – Impact or Collision: Parking sensors are often located on the bumper, making them vulnerable to damage from minor collisions, parking bumps, or road debris.
- – Weather Exposure: Harsh weather conditions, such as extreme heat, cold, or moisture, can damage sensors over time.
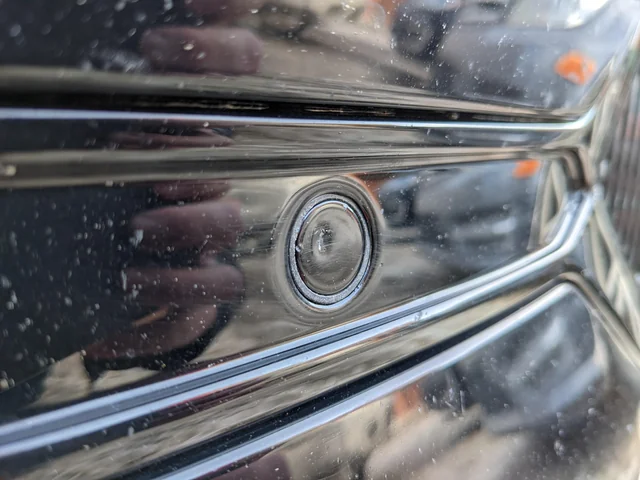

2. Electrical Issues:
- – Wiring Problems: Faulty or corroded wiring can disrupt the electrical connection between the sensors and the control unit.
- – Connector Issues: Loose or damaged connectors can cause intermittent or complete failure of the sensors.
3. Dirt and Debris:
- – Obstructions: Dirt, mud, snow, or other debris can cover the sensors, preventing them from accurately detecting objects.
- – Cleaning Products: Some cleaning agents can leave residues on the sensors, affecting their performance.
4. Sensor Malfunction:
- – Manufacturing Defects: Occasionally, sensors may fail due to defects in manufacturing.
- – Wear and Tear: Over time, sensors may degrade and become less effective or stop working altogether.
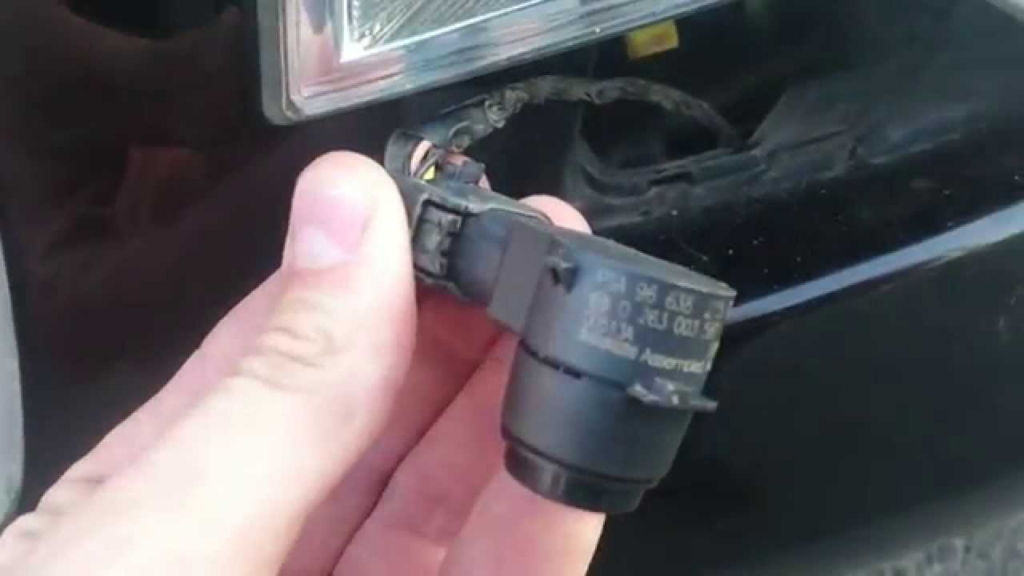

5. Software Issues:
- – Software Glitches: The vehicle’s onboard computer system may experience software glitches that affect the sensor system.
- – Updates Needed: Outdated software might not properly communicate with the sensors, requiring an update or reprogramming.
6. Improper Installation:
- – Incorrect Alignment: If sensors are not correctly aligned or positioned, they may not function properly.
- – Poor Wiring Installation: Improperly routed or secured wiring can lead to electrical issues.
7. Control Unit Failure:
- – Defective Control Unit: The control unit that processes signals from the sensors can fail, causing the entire system to malfunction.
- – Power Supply Issues: Inconsistent or insufficient power supply to the control unit can affect sensor performance.
Understanding the common causes of parking sensor failure can help in diagnosing issues promptly and taking appropriate actions to maintain their functionality.
Can parking sensors be replaced?
Yes, parking sensors can be replaced. If a parking sensor is found to be faulty or damaged, it can be replaced with a new one. The replacement process typically involves the following steps:
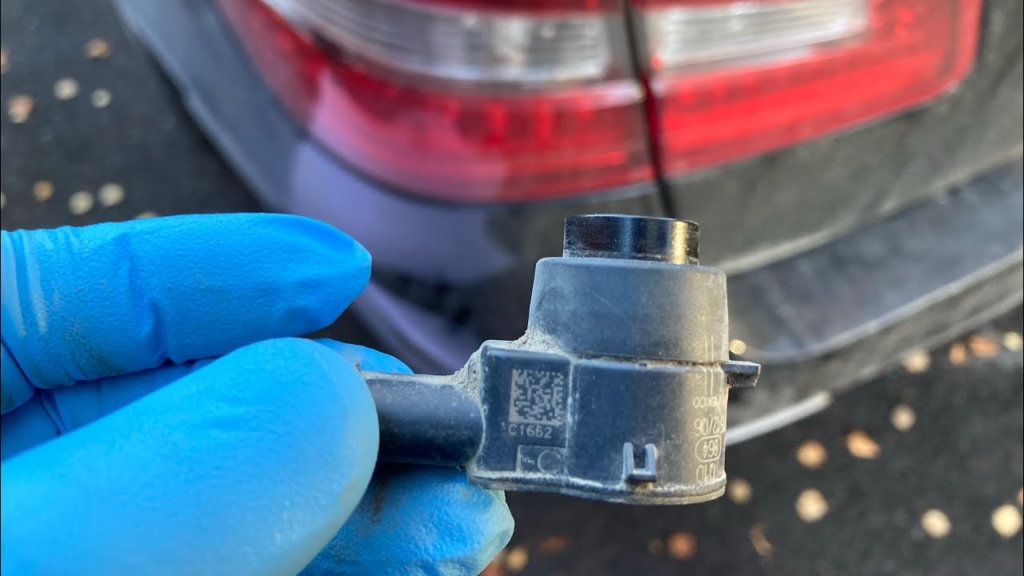

- 1. Diagnosis: Use a diagnostic tool to identify which sensor is malfunctioning.
- 2. Access the Sensor: Remove any necessary components, such as the bumper, to access the faulty sensor.
- 3. Disconnect the Sensor: Unplug the electrical connector from the faulty sensor.
- 4. Remove the Sensor: Detach the sensor from its mounting.
- 5. Install the New Sensor: Fit the new sensor into the mounting and secure it.
- 6. Reconnect the Sensor: Plug the electrical connector into the new sensor.
- 7. Test the Sensor: Reassemble any removed components and test the new sensor to ensure it works correctly.
It’s important to use the correct type and model of sensor that is compatible with the vehicle. If you’re not comfortable performing the replacement yourself, it’s advisable to have a professional technician handle the task to ensure it’s done correctly.
Can you install your own parking sensors?
Yes, you can install your own parking sensors if you have the necessary tools and basic knowledge of automotive electrical systems. Here’s a general guide on how to do it:
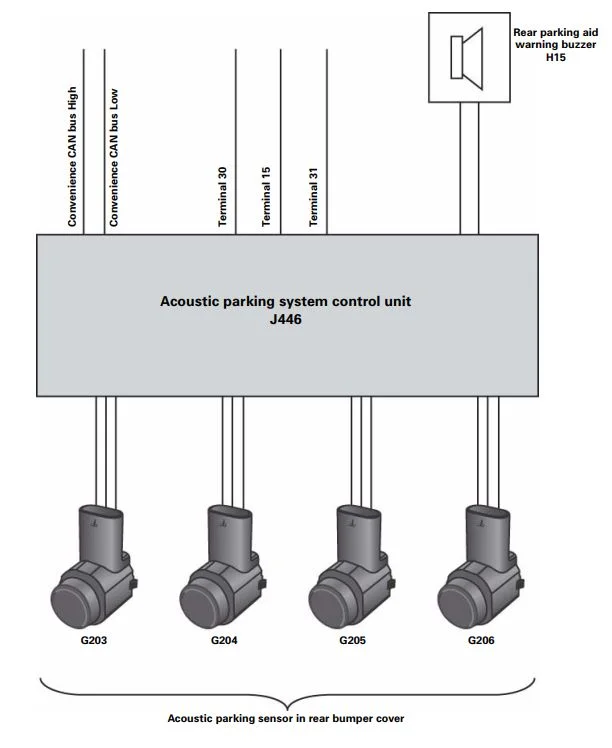
Tools and Materials Needed:
- – Parking sensor kit
- – Drill and appropriate drill bits
- – Screwdrivers
- – Wire cutters/strippers
- – Electrical tape
- – Multimeter (optional, for testing connections)
- – Vehicle-specific wiring diagram (recommended)
Installation Steps:
1. Choose the Sensor Locations:
- – Decide where you want to install the sensors on your bumper. Most kits come with recommendations for optimal placement.
2. Mark the Positions:
- – Use the template provided in the kit or measure and mark the positions on the bumper where the sensors will be installed.
3. Drill Holes:
- – Carefully drill holes in the marked positions. Make sure the drill bit matches the size required for the sensors.
4. Install the Sensors:
- – Insert the sensors into the drilled holes and secure them according to the kit instructions.
5. Run the Wiring:
- – Route the sensor wiring through the bumper and into the vehicle’s interior. Be careful to avoid any sharp edges or moving parts that could damage the wires.
6. Connect to the Control Unit:
- – Mount the control unit in a suitable location inside the vehicle, such as the trunk or under a seat. Connect the sensor wires to the control unit as per the kit’s instructions.
7. Power the System:
- – Connect the control unit to the vehicle’s power supply. This often involves tapping into the reverse light circuit so the sensors activate when the vehicle is in reverse.
8. Install the Display/Buzzer:
- – If your kit includes a display or buzzer, mount it in a visible or audible location for the driver. Connect it to the control unit.
9. Test the System:
- – Turn on your vehicle and shift into reverse to test the sensors. Ensure they are detecting obstacles correctly and the display/buzzer is functioning properly.
10. Secure and Finish:
- – Once everything is working correctly, secure all wiring with zip ties and electrical tape to prevent any loose connections. Reassemble any parts of the vehicle you had to remove.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why did parking sensors stop working after rain?
Water or debris can cover ultrasonic sensors cleaning bumper surfaces often restores function.
One sensor not working can I fix it?
Yes remove bumper, unplug faulty sensor, clean connectors, reseat; replace if needed.
Could a fuse or battery issue cause this?
Yes check Parktronic fuse and battery voltage. Low or uneven power due to aux/main battery issues may disable sensors.
Why does my car beep with no obstacle?
Misaligned sensor or wiring issue can cause false positives. Inspect connectors and replace damaged sensors.






Leave a Reply