Table of Contents
Blind Spot Assist Inoperative – Mercedes Fix & Troubleshooting Guide
When your Mercedes displays a “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” warning, one or more radar sensors in the rear bumper aren’t working turn signals may still flash, but the blind spot alert triangle won’t light. This affects other linked systems like Active Brake Assist. Let’s explore why it happens and how to fix it.
Common Causes & Diagnostics
| Cause | Symptoms | How to Diagnose |
|---|---|---|
| Misaligned radar sensor | Warning lights for Blind Spot & Active Brake Assist | Use Xentry to read codes (C3753xx, U150887); inspect and realign bracket |
| Dirty/obstructed sensors | Temporary inoperative message in bad weather | Clean rear bumper corner sensors; drive above ~15 km/h to self-reset |
| Damaged wiring or plugs | Persistent warning, no fault code read | Check harness, connectors for corrosion or bent contacts |
| Water ingress / corrosion | Warning appears in rain; may disable turn signal or wipers | Inspect sensors and connectors for moisture; may require module replacement and protective sealing |
| Failed sensor module | One-side aid missing or no detection | Faulty sensor triggers U150887; replace and calibrate with Xentry |
Diagnostic & Repair Steps
- Scan fault codes (C375xxx, U150887) using OBD-II or Xentry.
- Inspect sensor alignment: unbolt and reposition bracket if needed.
- Clean sensors: use mild water/microfiber; dry thoroughly and drive >15 km/h to reset.
- Check wiring/connectors under the bumper for corrosion or moisture.
- Apply moisture protection: dielectric grease and heat-shrink at connectors.
- Repair or replace sensor modules if they’re faulty, then recalibrate system via Xentry.
- Test systems: verify Blind Spot and Active Brake Assist work correctly after reset.
Case Study #1: Fixing Blind Spot Assist Inoperative in Mercedes W205
Customer Complaint
A customer driving a Mercedes C-Class reported persistent messages on the instrument cluster indicating Blind Spot Assist Inoperative and Active Brake Assist Inoperative. Concerned about the safety implications, the customer brought the vehicle to a certified Mercedes dealership for diagnosis and repair.
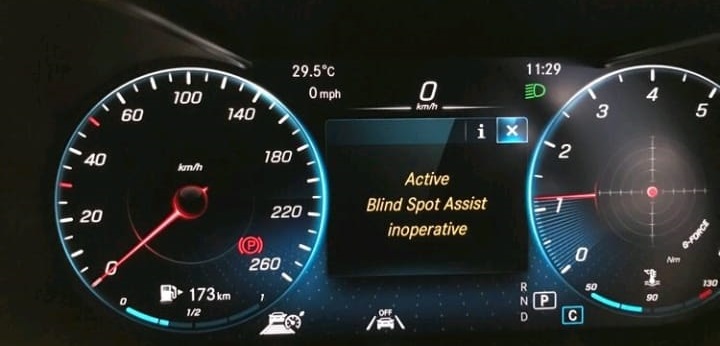
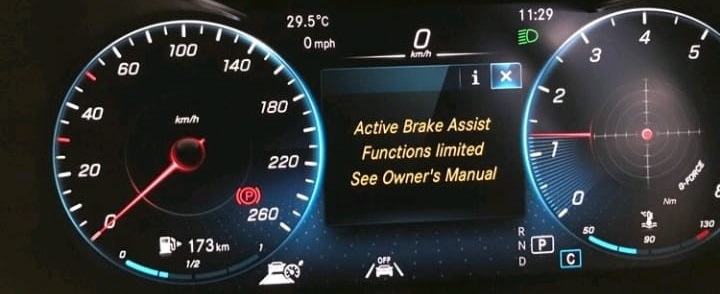
Initial Diagnostics
At the dealership, a qualified technician began by performing a comprehensive scan using the Xentry diagnostic pad, a tool specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
The scan revealed numerous fault codes related to the blind spot and brake assist systems. However, the technician narrowed down the potential causes to focus on the rear right short-range radar sensor.
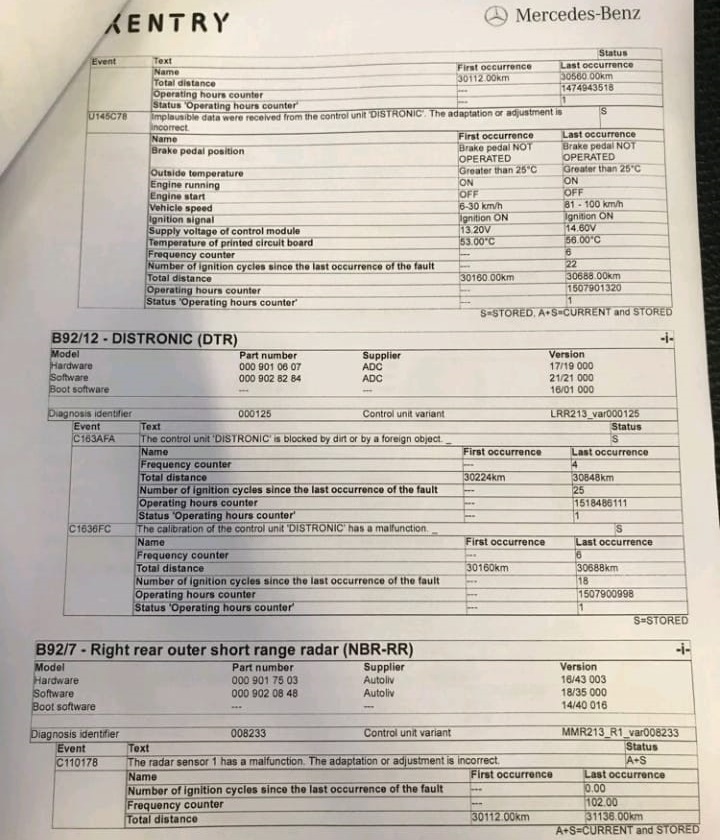
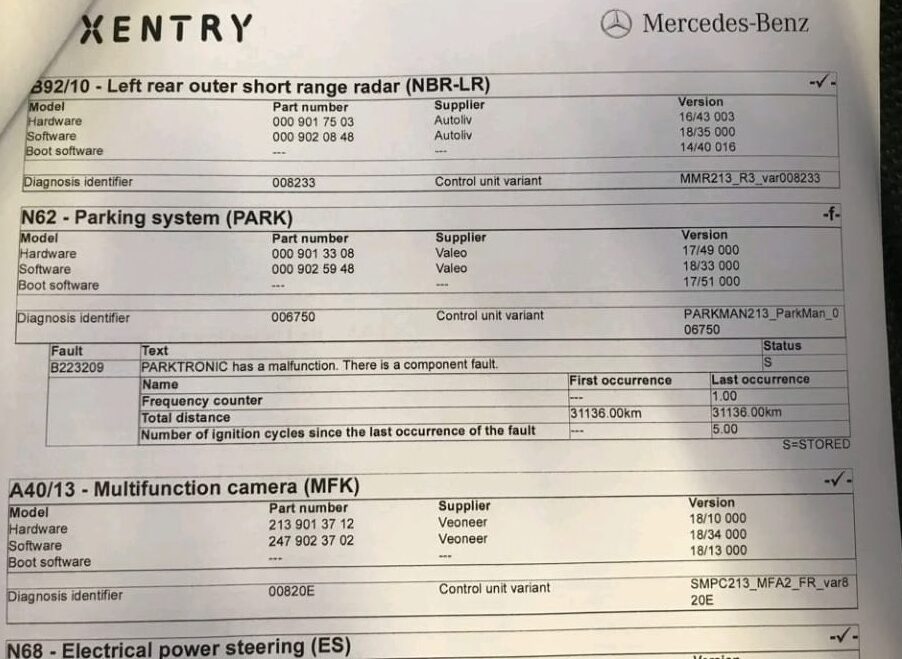
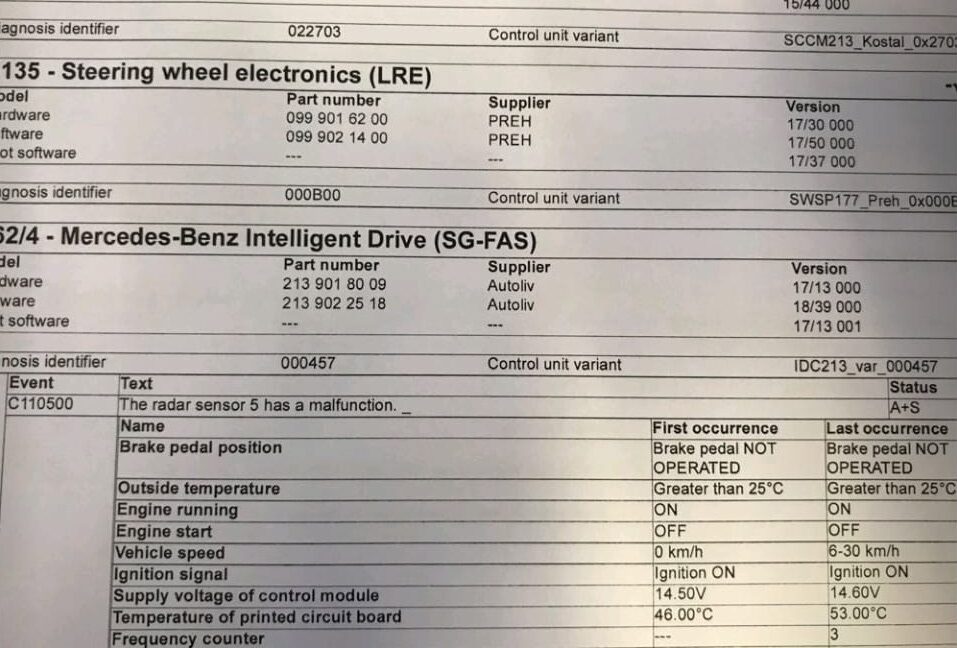
Diagnostic Procedure
To further investigate, the technician:
- Obtained the Wiring Diagram: The technician accessed the wiring diagram for the radar sensor to understand the electrical connections and system layout.
- Removed the Rear Bumper: This allowed for a visual inspection of the radar sensor brackets and connections.
- Inspected Wiring and Connections: The technician checked the power supply, CAN (Controller Area Network) lines, and three ground lines to ensure they were intact and functioning correctly.
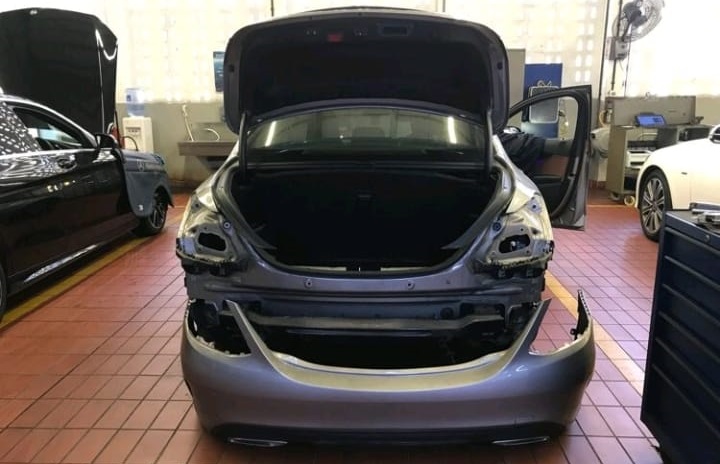

Actual Cause
After a thorough inspection, the technician discovered that the root cause of the issue was the misalignment of the rear right short-range radar sensor. This misalignment caused the sensor to malfunction, triggering the inoperative warnings for both the Blind Spot Assist and Active Brake Assist systems.
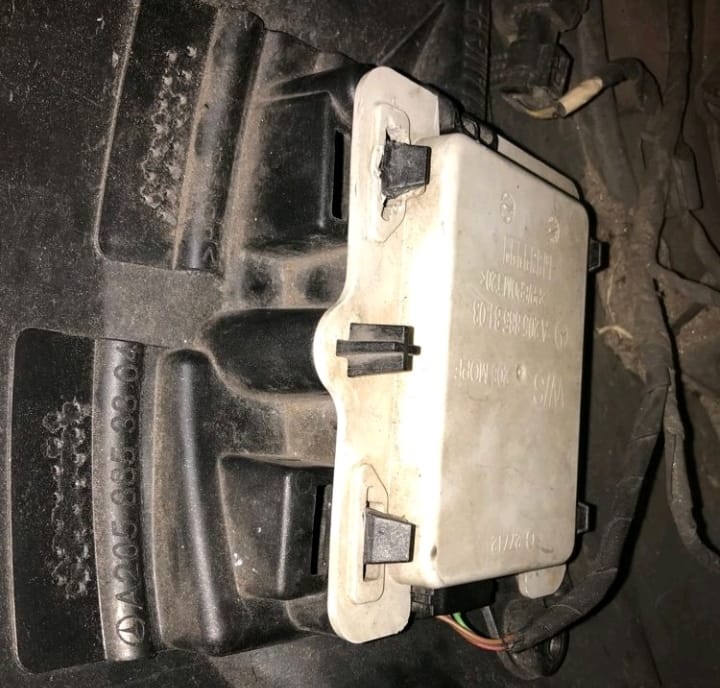
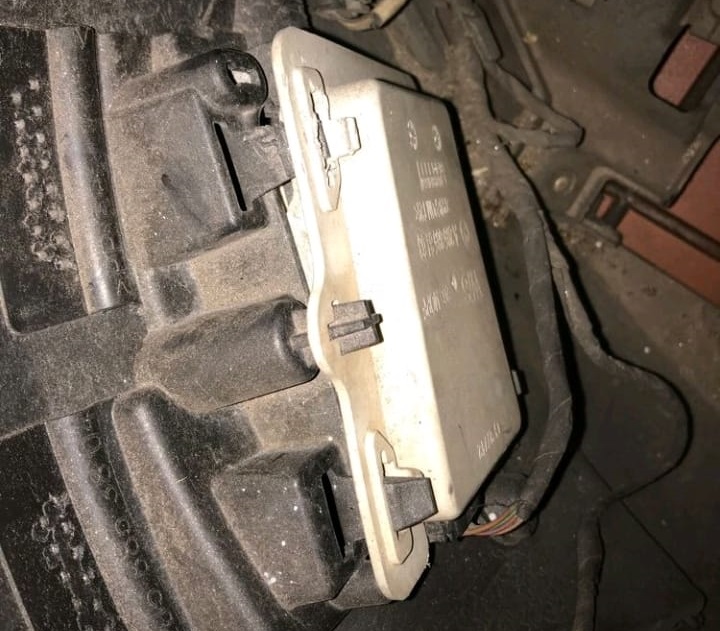


Correction
To correct the issue, the technician:
- 1. Referred to the Body Section: The vehicle was handed over to the body repair section to address the misaligned bracket.
- 2. Repaired the Bracket: The body repair team realigned and secured the radar sensor bracket to its proper position.
Outcome
Following the realignment and securing of the radar sensor, the vehicle was tested again. The fault codes were cleared, and the messages “Active Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” and “Active Brake Assist Inoperative” no longer appeared on the instrument cluster. The technician conducted a final verification to ensure the system was fully operational.

This case study highlights the importance of precise diagnostics and the role of specialized tools like the Xentry diagnostic pad in identifying complex issues. The misalignment of the radar sensor, though a seemingly minor issue, had significant implications for the vehicle’s safety systems.
By addressing the root cause, the technician successfully restored full functionality to both the Blind Spot Assist and Active Brake Assist systems, ensuring the vehicle’s safety features were reliable and effective once again.
Learn more about the same issue on Mercedes E Class W212 in the next link; Active Blind Spot Assist Inoperative : Case Study & Solution
Case Study #2: Blind Spot Assist Inoperative in a Mercedes-Benz C Class W206
Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz C Class W206
Customer Complaint: “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” warning displayed on the dashboard.


When the customer brought their vehicle into the workshop, the warning message “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” was persistently displayed in the instrument cluster. To investigate the issue, a diagnostic scan was performed using the official Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tool.
Fault Code Detected:
- – U150887 : Communication with the radar sensor 8 has a malfunction. The message is missing.
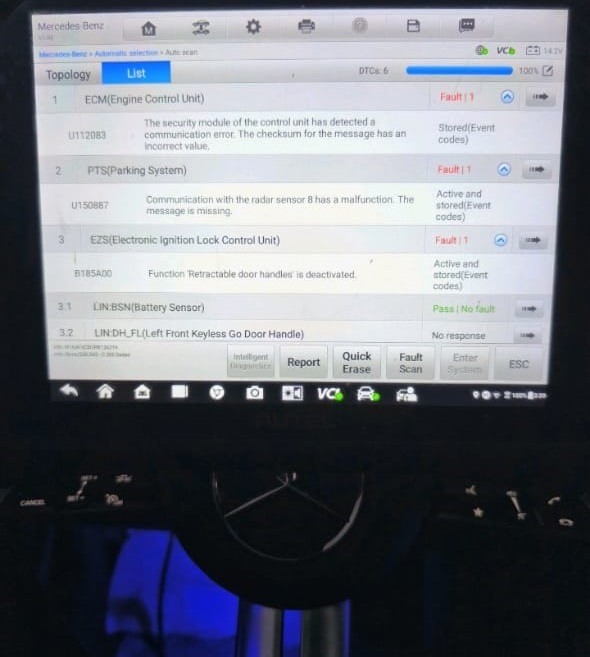
This fault code indicated a communication problem with Radar Sensor 8, which corresponds to the right-side blind spot radar unit. A qualified technician then proceeded to visually inspect the radar sensor and its associated wiring harness.
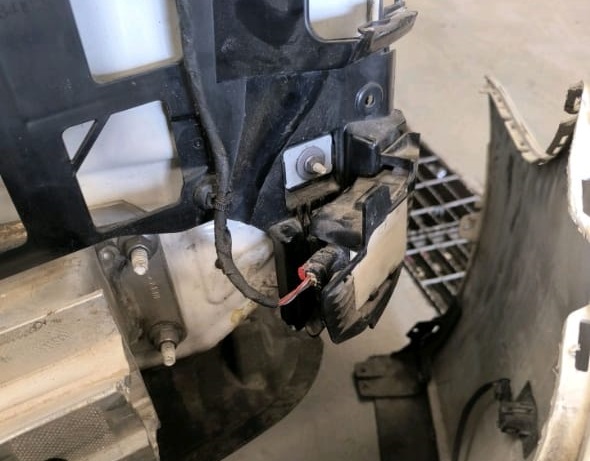
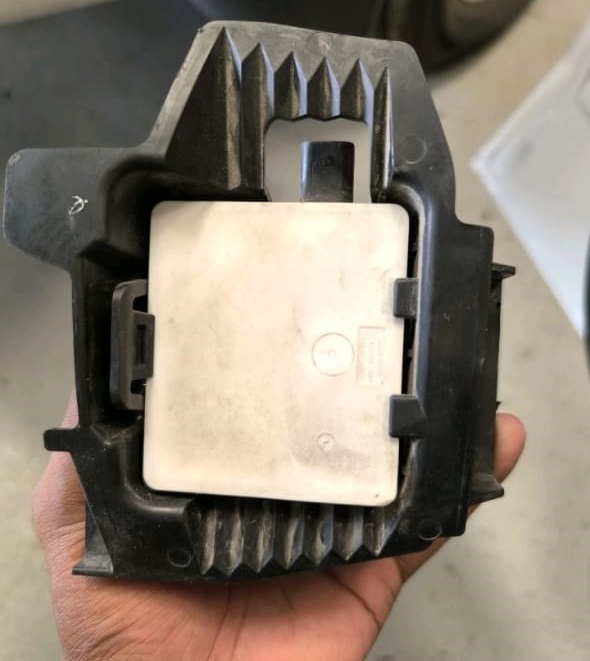


After a thorough check, it was confirmed that the issue originated from the radar sensor itself and not the wiring or connector. The faulty right blind spot radar was replaced, and the system was recalibrated.
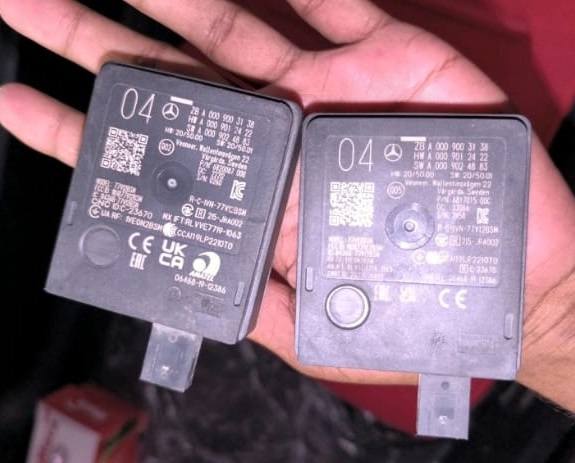

Following the repair, the Blind Spot Assist Inoperative warning was cleared, and the system returned to full functionality, ensuring the customer could once again rely on the vehicle’s blind spot monitoring for safe lane changes.
Blind spot assist inoperative reset
Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Reset is a process used to restore the functionality of the Blind Spot Assist system in Mercedes-Benz vehicles when the system becomes inactive or displays an “Inoperative” message.
This safety feature uses radar sensors, typically located in the rear bumper, to monitor adjacent lanes and alert the driver of vehicles in the blind spot during lane changes. When it stops working, it can be due to several reasons, and resetting it may resolve the issue depending on the root cause.
How to Perform a Blind Spot Assist Reset:
- 1. Clean the Radar Sensors: Ensure the rear bumper sensors are clean and free of obstructions.
- 2. Restart the Vehicle: Turn off the engine completely, wait a minute, and restart the car. Sometimes, this soft reset is enough.
- 3. Drive a Short Distance: In some cases, Blind Spot Assist reactivates after the vehicle exceeds a certain speed (usually above 10 mph or 15 km/h).
- 4. Use a Diagnostic Tool: If the warning persists, a reset using a diagnostic tool like Mercedes XENTRY or an advanced OBD-II scanner may be required. This will help identify specific fault codes and allow proper resetting or coding if necessary.
- 5. Check Battery Health: Ensure your vehicle’s battery is fully charged and in good condition, as low voltage can disable safety features.
DIY vs Professional Work
| Task | DIY | Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Scan & interpret fault codes | Basic OBD-II tools | Xentry diagnostics |
| Clean sensor lenses | Yes | — |
| Check sensor alignment | Moderate (requires bumper disassembly) | Expert re-mounting & calibration |
| Seal connectors from moisture | Yes (with dielectric grease) | Full waterproofing |
| Replace sensor & calibrate | Not recommended | Specialist module work |
Quick Maintenance Tips
- – Clean sensor surfaces whenever washing rear bumper area.
- – After impact repairs, ask your body shop to verify alignment and calibration.
- – In rainy climates, yearly connector inspections with waterproofing can prevent corrosion.
- – Include Blind Spot sensors in scheduled service check-ups.
Where is the Mercedes blind spot detection sensor located?
Mercedes blind spot sensors are typically located in the rear section of the vehicle. Here are the specific locations:
Rear Bumper
- – Rear Bumper Corners: The primary sensors for the Blind Spot Assist system are usually embedded in the rear bumper, near the corners. These radar sensors are strategically placed to monitor the blind spots along the sides and rear of the vehicle.
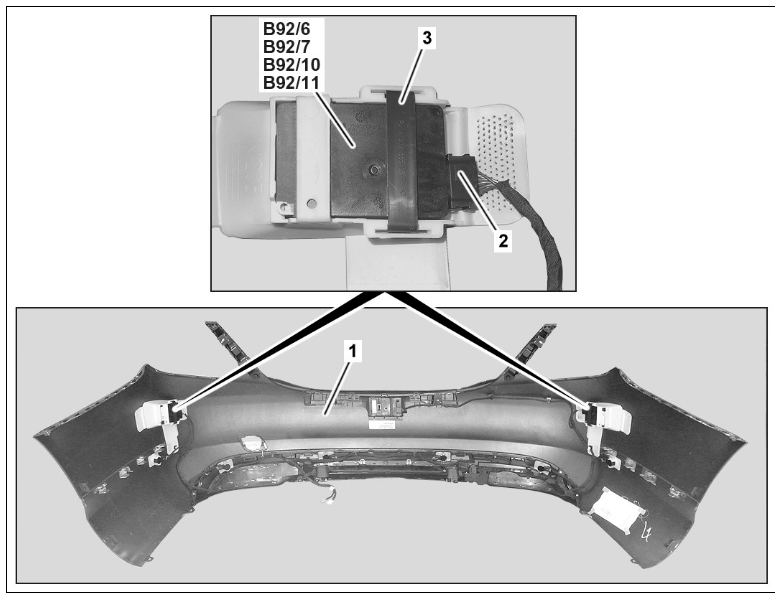
Side Mirrors
- – Integrated Indicators: While the sensors themselves are in the rear bumper, the visual indicators for the Blind Spot Assist system are integrated into the side mirrors. When a vehicle is detected in the blind spot, an icon (usually a triangle or a dot) lights up in the corresponding side mirror.
Generally: What is the meaning of blind spot assist inoperative?
Active Blind Spot Assist Inoperative means that the Blind Spot Assist system in your Mercedes is not functioning correctly. This safety feature uses radar sensors to monitor the blind spots on both sides of the vehicle and alerts the driver if another vehicle is detected, typically through visual or audible warnings.
When the system is inoperative, it means the feature is disabled or malfunctioning, and the vehicle will not provide these warnings. The issue could be caused by several factors, including:
Common Causes of Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Mercedes Message
Dirty or Blocked Sensors
- – Dirt, mud, or ice can obstruct the radar sensors, preventing them from working.
- – Solution: Clean the sensors, usually located in the rear bumper.
Sensor Malfunction or Damage
- – Physical damage to the radar sensors may cause the system to stop working.
- – Solution: Inspect the sensors and replace them if necessary.
Software Glitch
- – A software bug or communication error between the control modules could trigger the warning.
- – Solution: Try restarting the car or updating the software via a diagnostic tool.
Low Battery Voltage or Faulty Wiring
- – Low voltage or wiring problems can cause the system to malfunction.
- – Solution: Check the vehicle’s battery and inspect sensor connections for loose wiring.
Radar Calibration Needed
- – If the car has been in a minor collision or the bumper was removed, the radar might need recalibration.
- – Solution: Visit a Mercedes dealer or specialist for recalibration.
Driving Without Blind Spot Assist
When the Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Mercedes, the driver needs to rely on manual checks when changing lanes or merging. While the system is convenient, it is essential to develop safe driving habits to compensate when it is unavailable.
This message indicates a temporary or permanent issue that should be addressed promptly to maintain optimal safety.
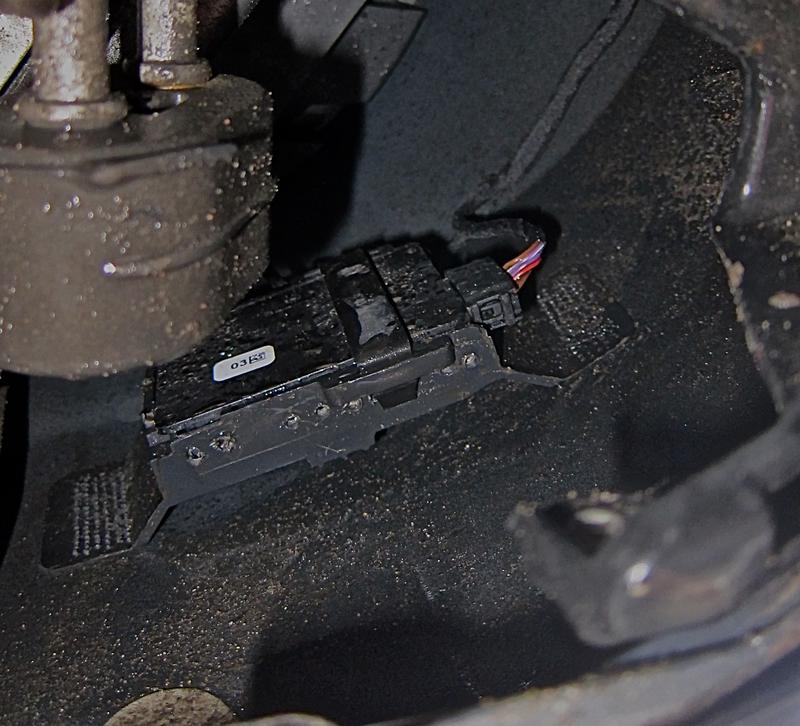

Diagnosing Active Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Issues
Diagnosing Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Mercedes issues involves a combination of self-checks and professional diagnostics:
- – Error Messages and Indicators: Modern vehicles are equipped with dashboard warnings and error codes that indicate Blind Spot Assist problems. Drivers should pay attention to these alerts and refer to the vehicle’s manual for initial troubleshooting steps.
- – Self-Diagnosis Steps: Drivers can perform simple checks, such as cleaning the sensors and ensuring they are free from obstructions. A visual inspection for any obvious physical damage is also helpful.
- – Professional Diagnostics: For more complex issues, a professional mechanic will use specialized diagnostic tools to check the system. This might include scanning for error codes, testing the electrical connections, and inspecting the software version.
Solutions for Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Mercedes
Depending on the cause, several solutions can resolve BSA inoperative issues:
- – Cleaning Sensors and Cameras: If sensor blockage is identified, cleaning them with appropriate products can restore functionality. It is essential to use gentle cleaners to avoid damaging the sensors.
- – Software Updates: Keeping the vehicle’s software up-to-date is crucial. Drivers should check for available updates through their vehicle’s infotainment system or by visiting the dealership.
- – Electrical Repairs: Identifying and fixing wiring issues often involves inspecting and securing connections or replacing faulty wires and connectors.
- – Replacing Damaged Components: When sensors or cameras are physically damaged, replacement is usually the only option. Professional mechanics can ensure the new components are correctly installed and calibrated.
Preventing Blind Spot Assist Inoperative Mercedes Issues
Prevention is key to maintaining the functionality of Blind Spot Assist:
- – Regular Maintenance: Regularly cleaning and inspecting sensors for damage or obstruction can prevent many BSA issues. Routine maintenance should be part of the vehicle’s overall care plan.
- – Software Maintenance: Keeping the vehicle’s software updated is critical. Regularly checking for updates and installing them can prevent many software-related problems.
- – Safe Driving Practices: Avoiding situations that may damage BSA components, such as parking in tight spaces where the rear bumper might get scratched or bumped, can help maintain the system’s integrity.
Conclusion
Blind Spot Assist is an essential safety feature that enhances driving safety by monitoring blind spots. Understanding the causes and solutions for Blind Spot Assist inoperative issues can help drivers maintain this system’s functionality.
Regular maintenance, timely software updates, and safe driving practices are crucial in preventing problems. By staying proactive, drivers can ensure their BSA system remains reliable and effective, contributing to a safer driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will cleaning the sensors fix the warning?
Often yes, especially if dirt or moisture triggered the warning. Drying and driving >15 km/h usually reactivates the system.
When should I worry about a misaligned sensor?
If cleaning doesn’t help and codes C375xxx or U150887 appear, the sensor’s bracket may be bent and needs recalibration.
Is water damage common? Can it wreck the sensor?
Yes, especially in regions with rain or road salt. Water in connectors can disable multiple systems. Waterproofing is recommended.
Do I need special tools to fix this?
Basic cleaning and realignment can be DIY. But module replacement and calibration require Mercedes-approved tools like Xentry.






Leave a Reply